Submitted:
12 February 2025
Posted:
13 February 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
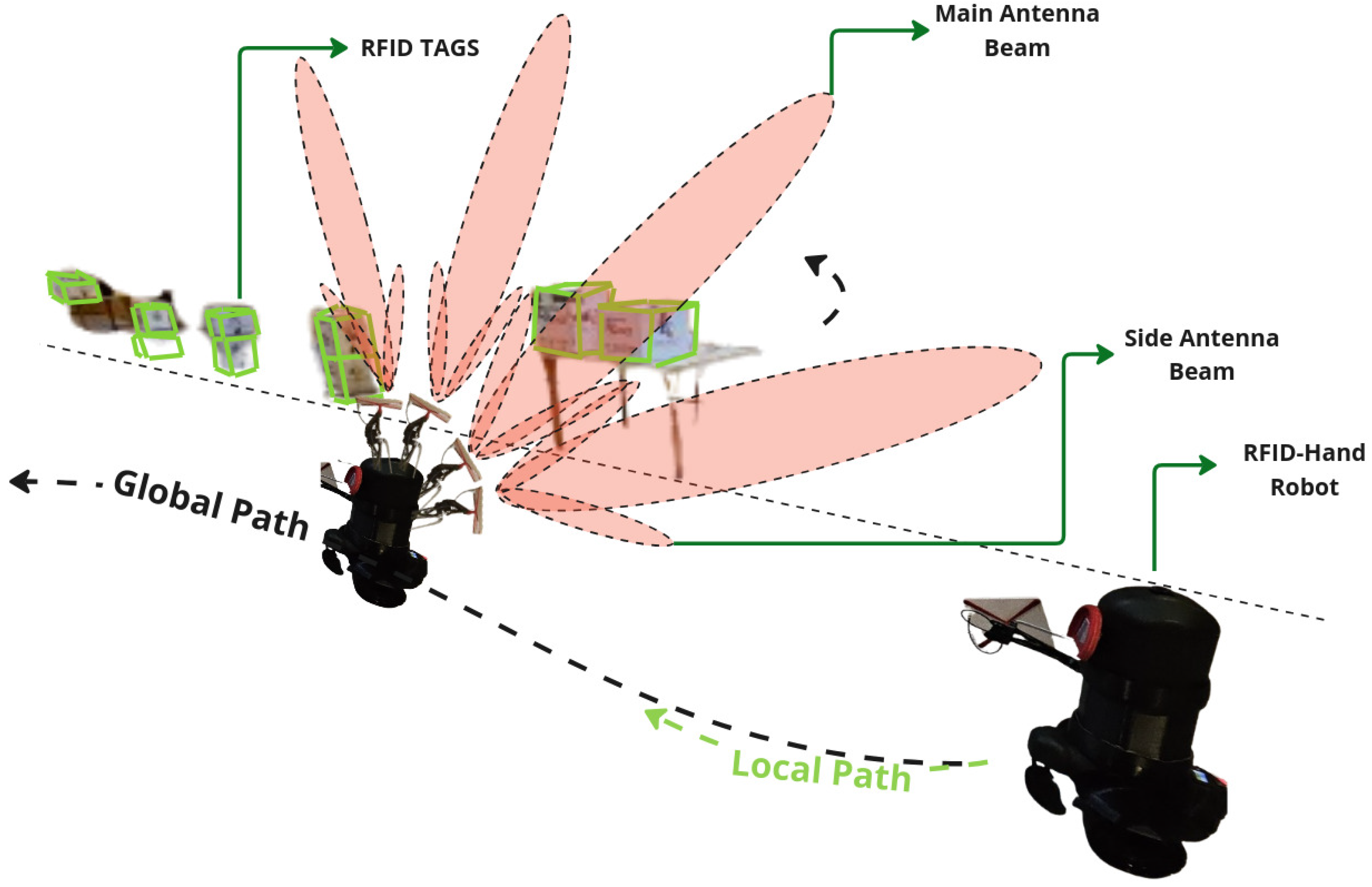
1. Introduction
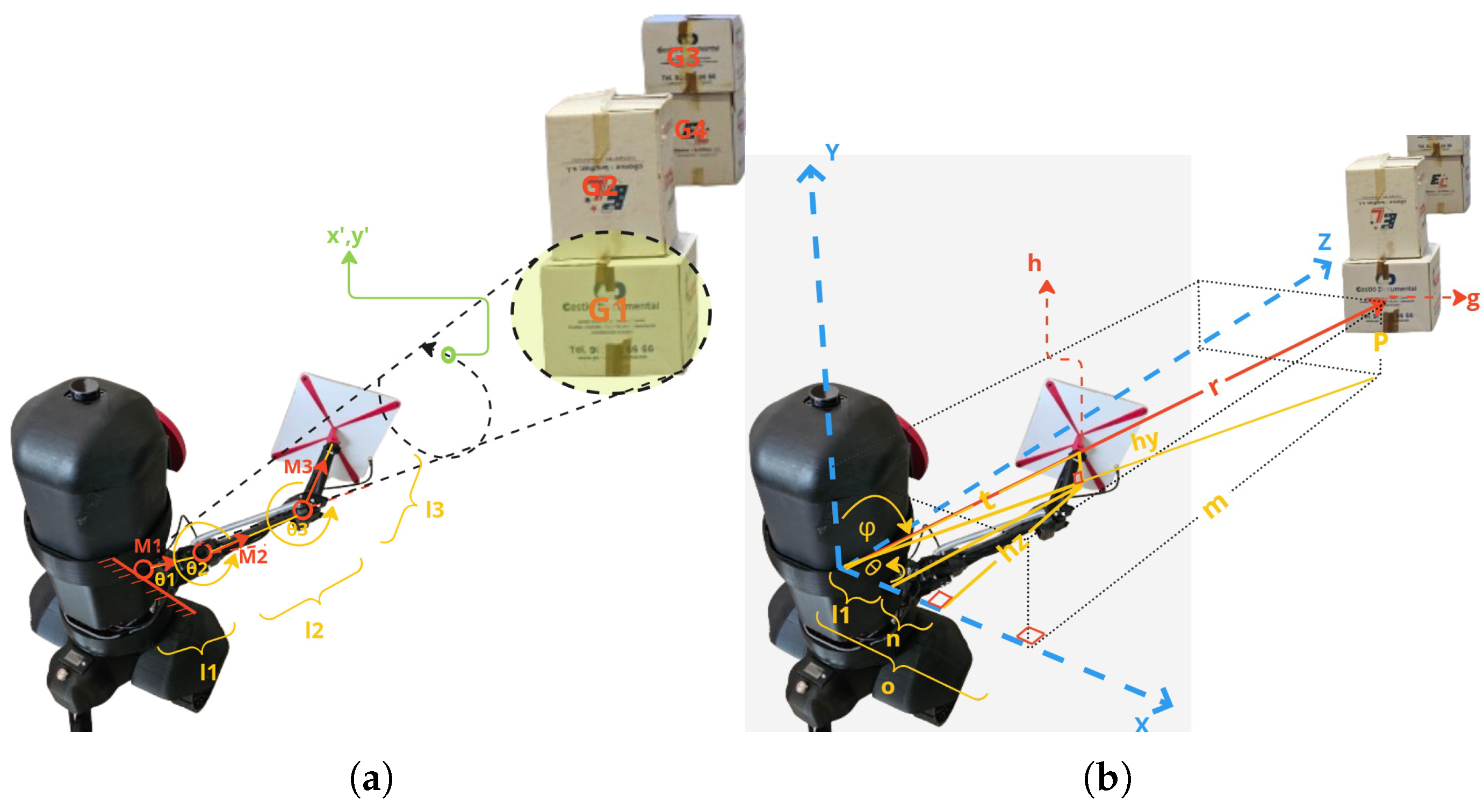
2. Robot Design
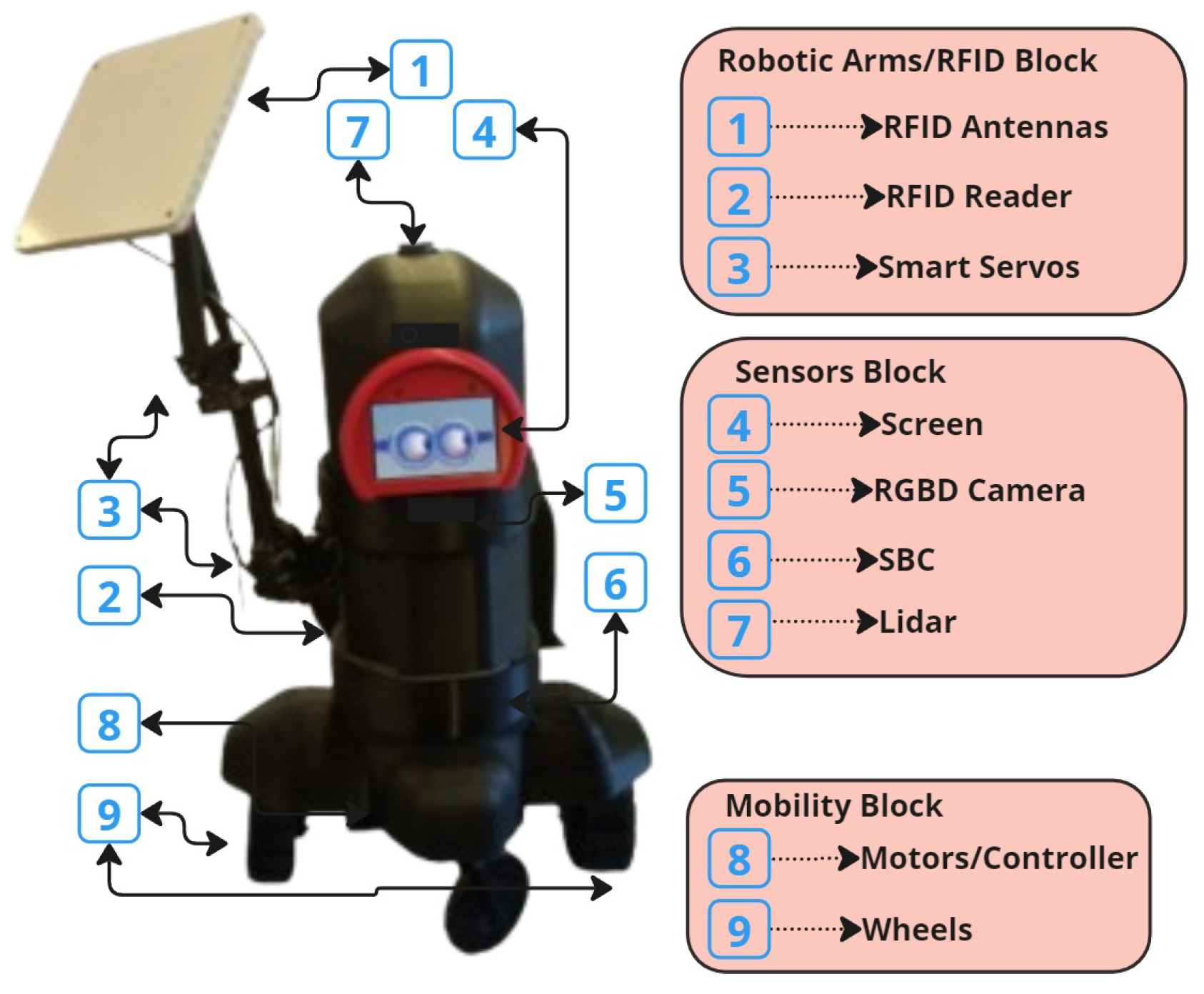
2.1. RFID-HAND Robot Hardware Description
- Robot arms block: The robot is designed with a robotic hand offering 3 DOF, powered by three cost-effective servo motors equipped with feedback capabilities for precise and accurate movement. An RFID antenna is mounted on the end effector, allowing for efficient spatial manipulation. The joints of the robotic hand are interconnected with an elastic rubber band, capable of supporting weights up to 30 kg, which not only reduces pressure on the servos but also enhances the stall torque limit, thus optimizing the performance of each joint.
- Sensors block: The sensor array of the robot is meticulously arranged, featuring a Lidar sensor mounted atop the chassis for critical proximity detection and 3D environmental mapping. Additionally, an RGBD camera is integrated to capture both color images and depth information, enabling the robot to accurately perceive the shape, size, and distance of objects in its vicinity. The computational backbone of the robot is a cost-effective and energy-efficient single-board computer (SBC), specifically the n100, which processes sensor data, executes control algorithms, and supports advanced functionalities such as neural network-based object recognition, navigation, and localization.
- Mobility block: For mobility, the robot is equipped with two 24V high-torque motors, each fitted with hall sensors and a motion controller, ensuring precise control over the robot’s movement, velocity, and acceleration. The power system is designed for sustained operation, either via a rechargeable battery pack or an external power source, ensuring the robot’s continuous functionality.
2.2. RFID-HAND Robot Software Description
3. Technical Overview
4. Experiments
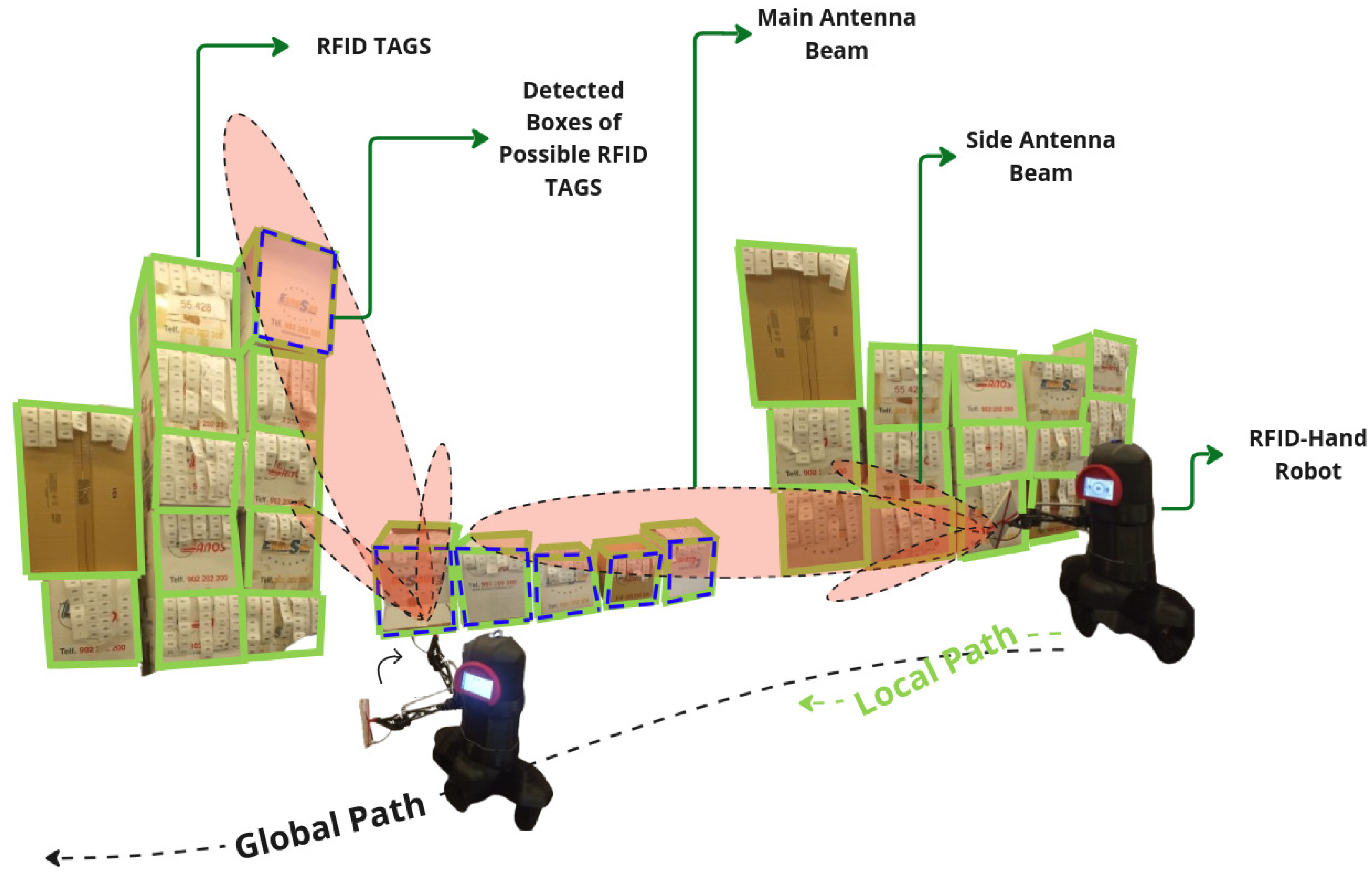
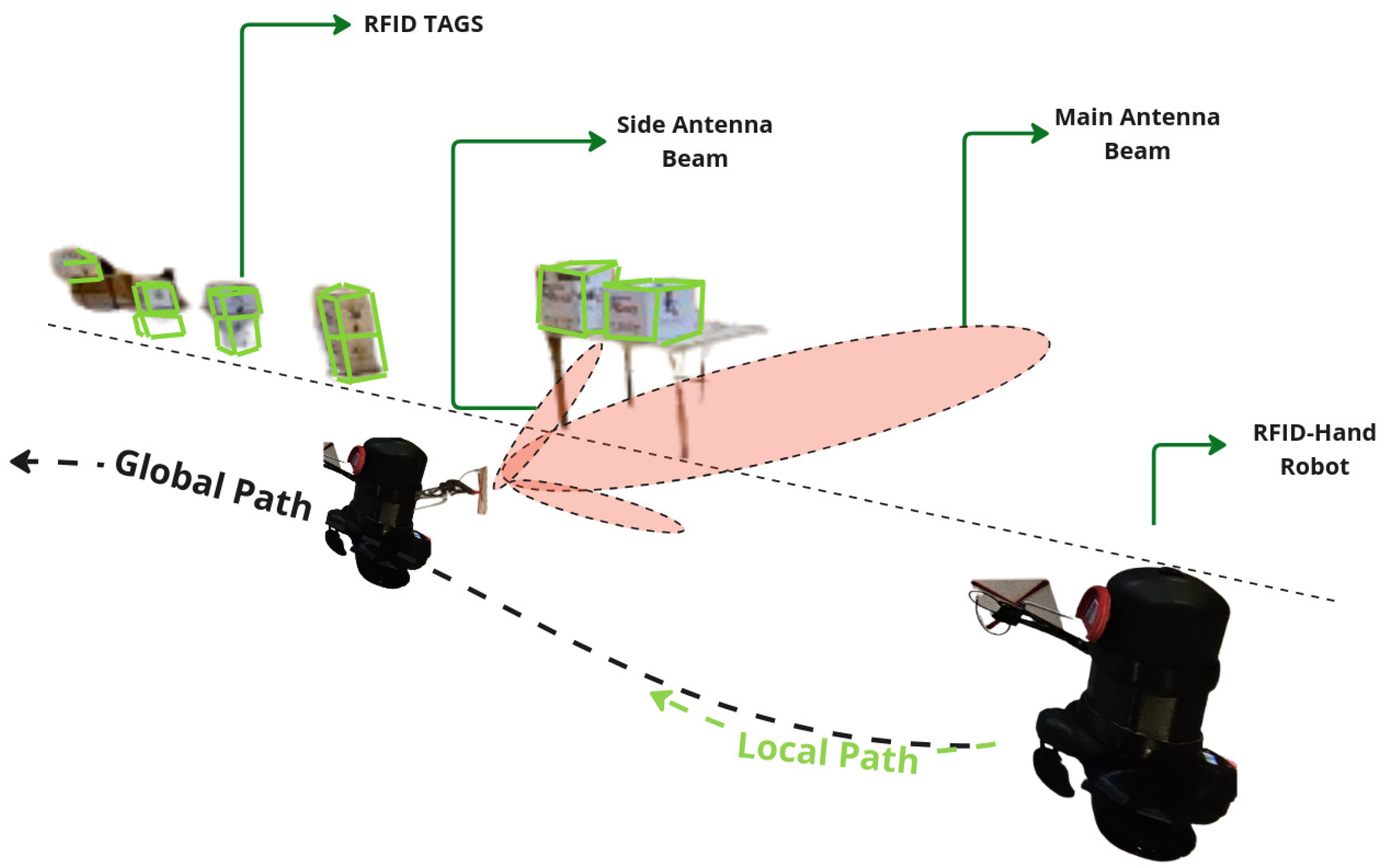
4.1. Short Aile Low Shelves Scanning
4.1.1. Fixed Antenna
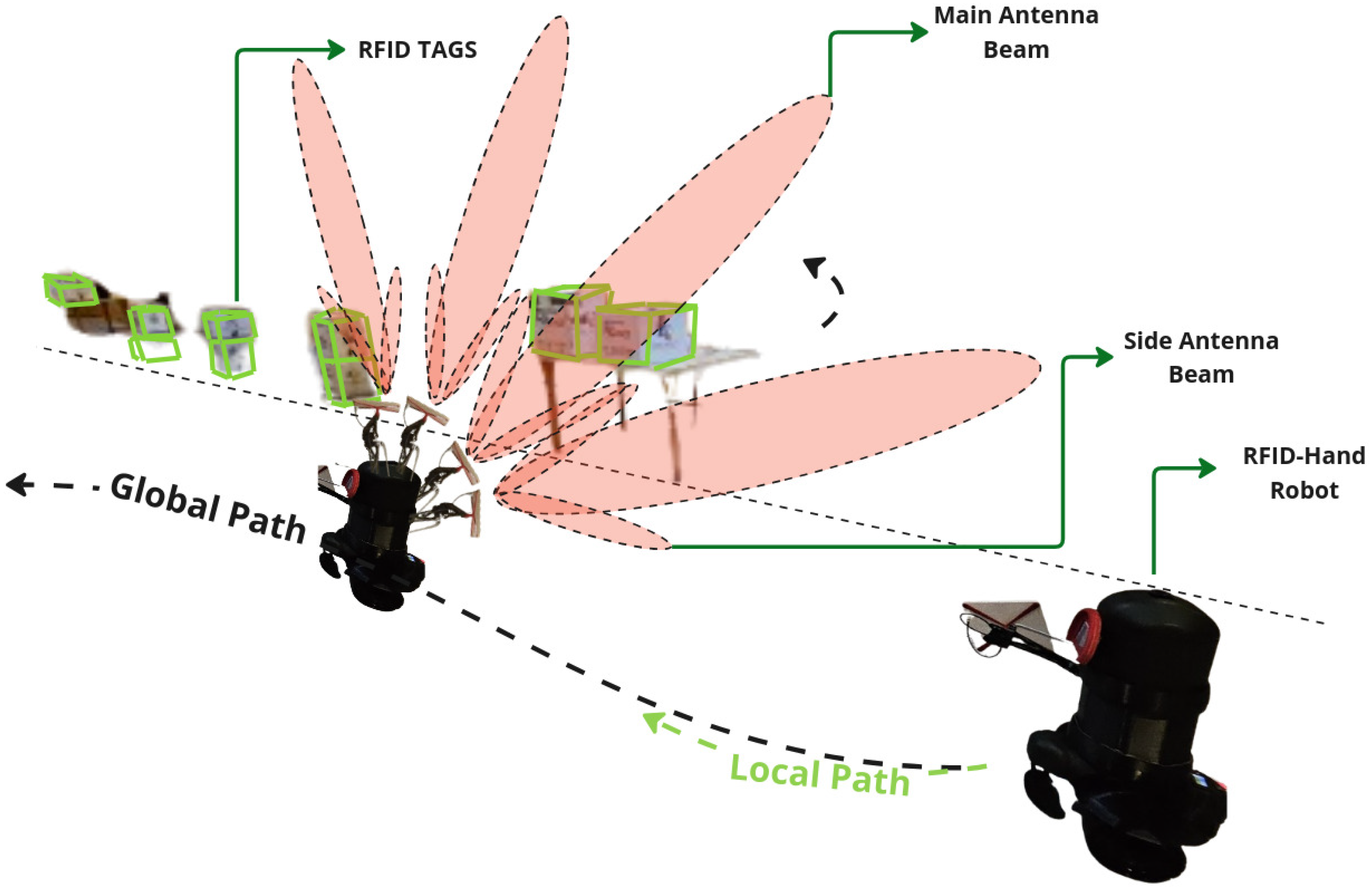
4.1.2. Articulated Antenna
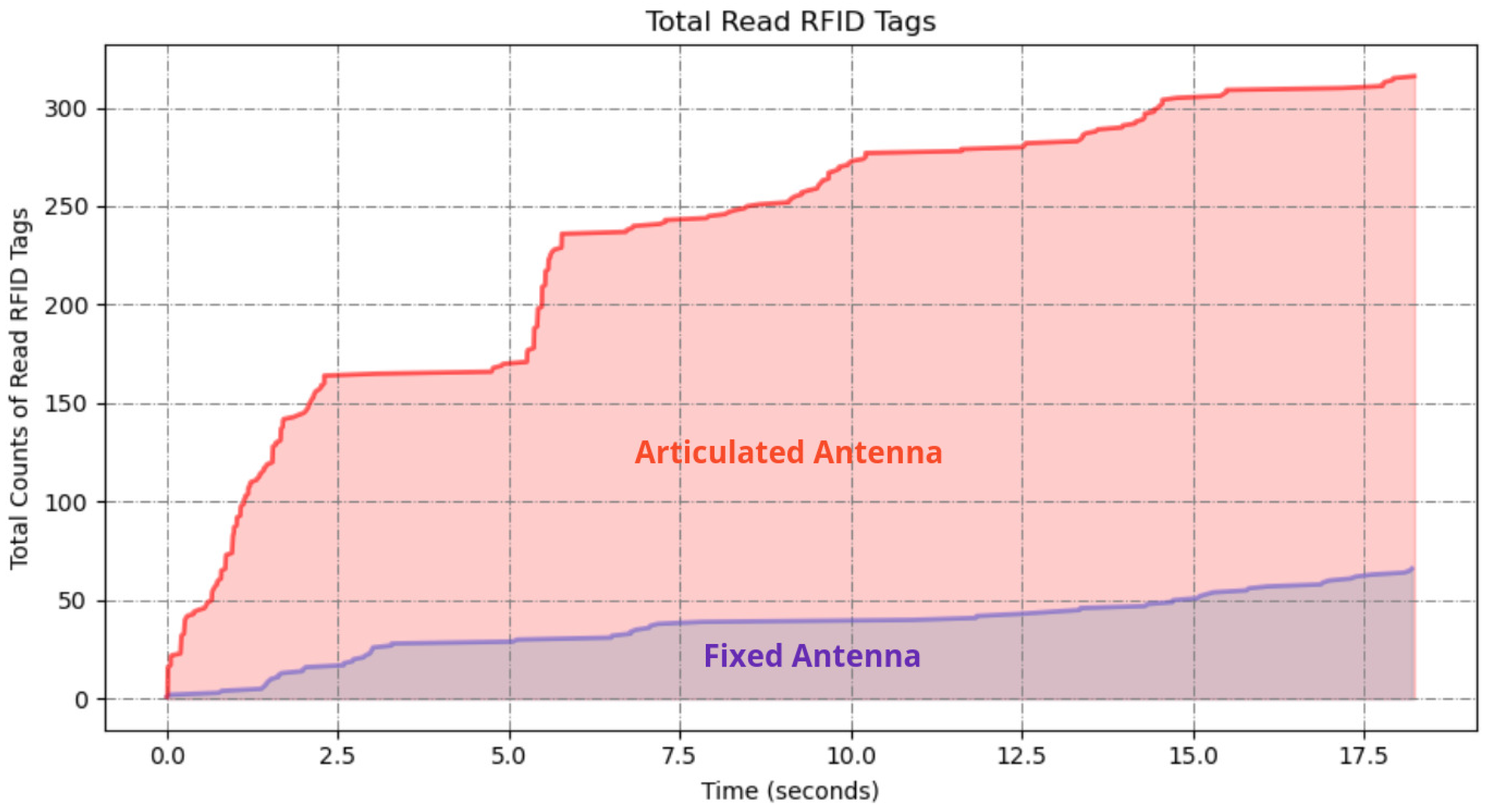
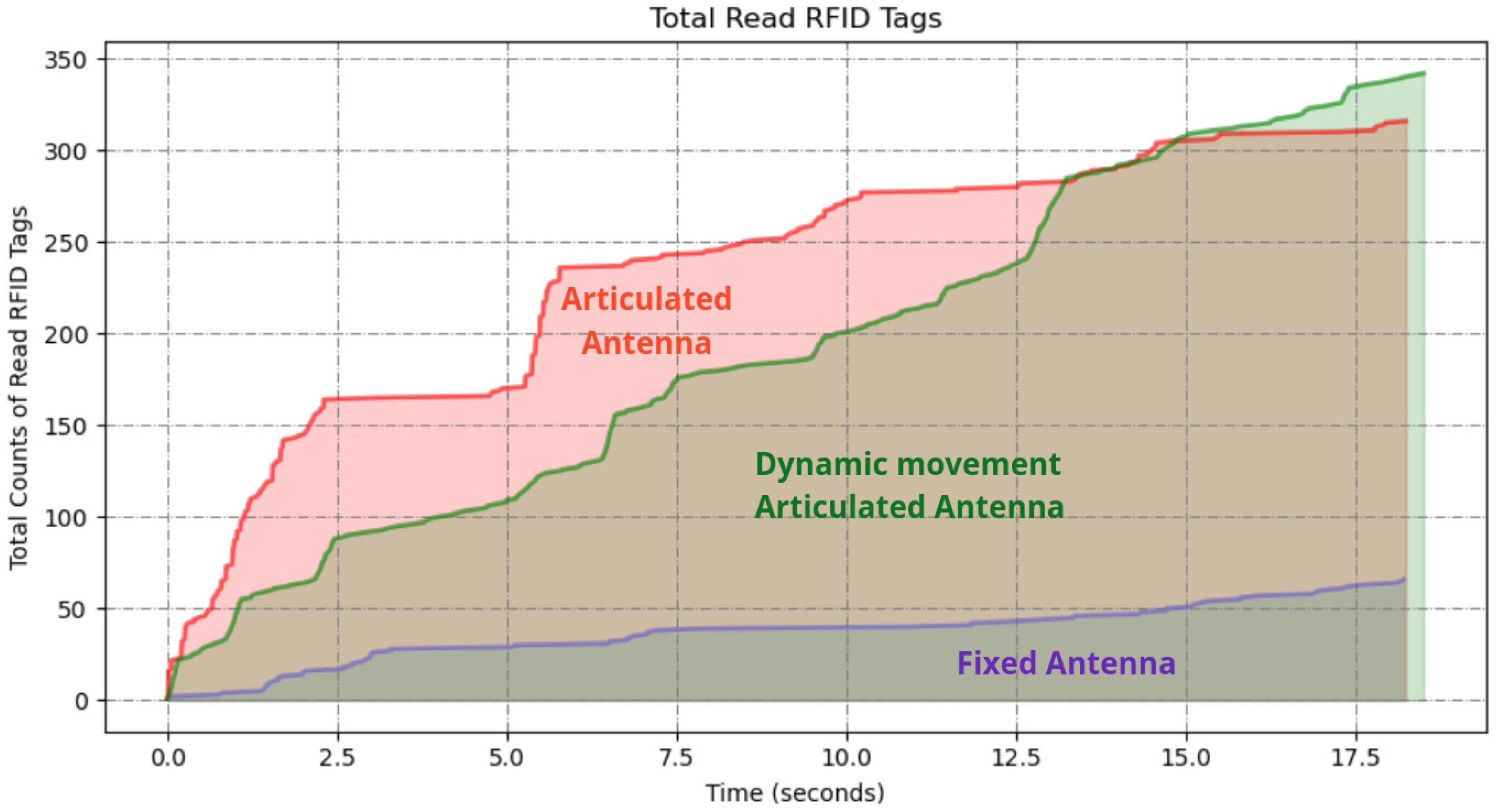
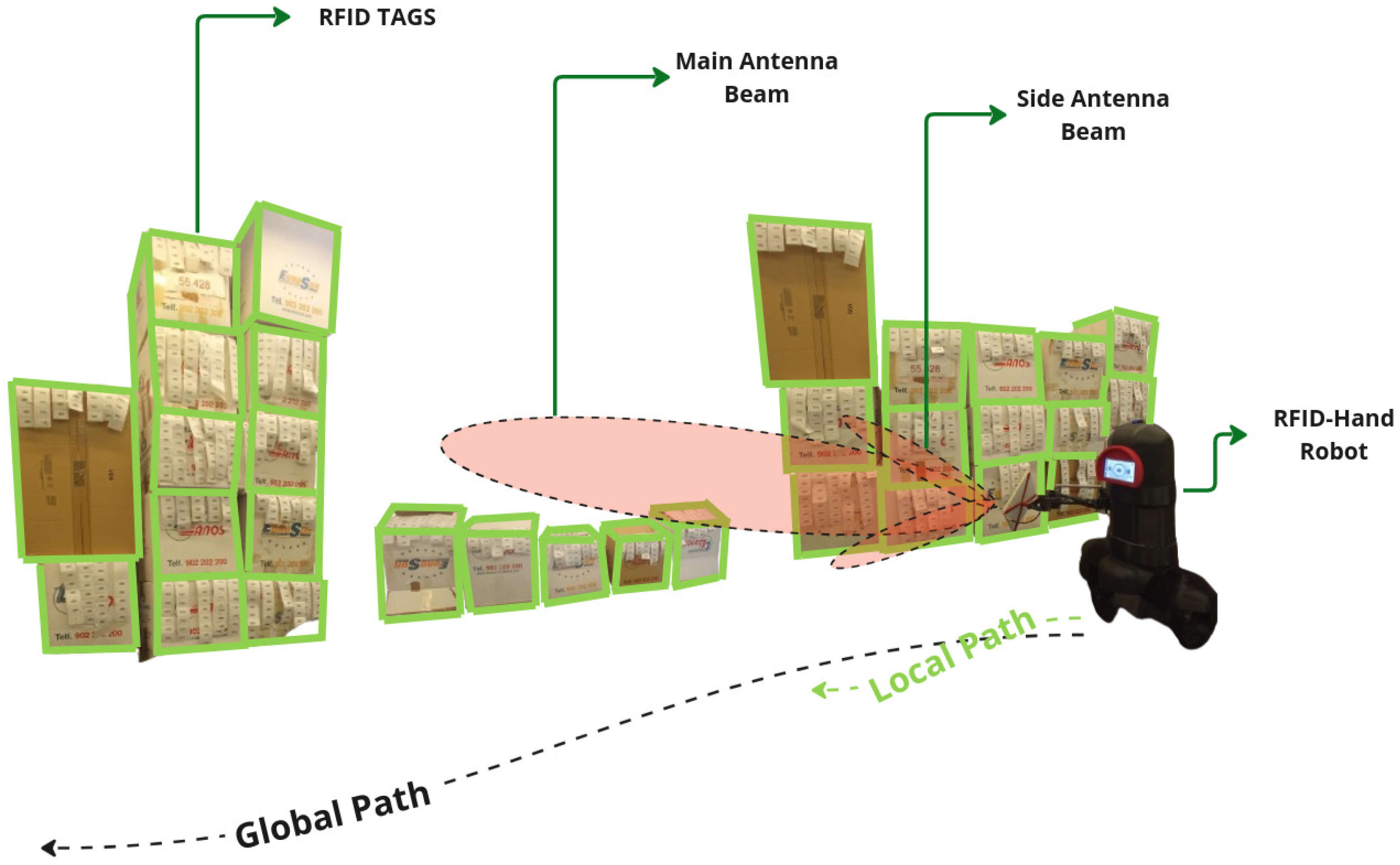
4.2. Tall Ailes High Shelves Scanning
4.2.1. Fixed Antenna
4.2.2. Articulated Antenna
4.2.3. Dynamic Movement Articulated Antenna
5. Conclusions
6. Future Work
References
- Motroni, A.; Buffi, A. RFID Robots and Vehicles for Item Inventory and Localization. In Proceedings of the 2023 17th European Conference on Antennas and Propagation (EuCAP), 2023, pp. 1–5. [CrossRef]
- Gareis, M.; Parr, A.; Trabert, J.; Mehner, T.; Vossiek, M.; Carlowitz, C. Stocktaking Robots, Automatic Inventory, and 3D Product Maps: The Smart Warehouse Enabled by UHF-RFID Synthetic Aperture Localization Techniques. IEEE Microwave Magazine 2021, 22, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morenza-Cinos, M.; Casamayor-Pujol, V.; Soler-Busquets, J.; Sanz, J.L.; Guzmán, R.; Pous, R. Development of an RFID inventory robot (AdvanRobot). Robot Operating System (ROS) The Complete Reference (Volume 2) 2017, pp. 387–417.
- Sharma, R.; Patange, A.D.; Padalghare, R.; Kale, R.C. Development of LiDAR operated inventory control and assistance robot. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part E: Journal of Process Mechanical Engineering 2024, 238, 192–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Lyu, Y.; Roppel, T.; Patton, J.; Senthilkumar, C. Mobile robot for retail inventory using RFID. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE international conference on Industrial technology (ICIT). IEEE, 2016, pp. 101–106.
- Alajami, A.A.; Moreno, G.; Pous, R. Design of a UAV for Autonomous RFID-Based Dynamic Inventories Using Stigmergy for Mapless Indoor Environments. Drones 2022, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beul, M.; Droeschel, D.; Nieuwenhuisen, M.; Quenzel, J.; Houben, S.; Behnke, S. Fast Autonomous Flight in Warehouses for Inventory Applications. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters 2018, 3, 3121–3128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alajami, A.A.; Santa Cruz, L.D.; Pous, R. Design of an Energy-Efficient Self-Heterogeneous Aerial-Ground Vehicle. In Proceedings of the 2023 9th International Conference on Automation, Robotics and Applications (ICARA). IEEE, 2023, pp. 213–218.
- Cao, M.; Xu, X.; Yuan, S.; Cao, K.; Liu, K.; Xie, L. DoubleBee: A Hybrid Aerial-Ground Robot with Two Active Wheels. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), 2023, pp. 6962–6969. [CrossRef]
- Alajami, A.A.; Perez, F.; Pous, R. The Design of an RFID-Based Inventory Hybrid Robot for Large Warehouses. In Proceedings of the 2024 9th International Conference on Control and Robotics Engineering (ICCRE), 2024, pp. 50–54. [CrossRef]
- Dexory. Dexory Inventory Robot. https://www.dexory.com/, 2024. Accessed: 2024-08-09.
- Bernardini, F.; Motroni, A.; Nepa, P.; Tripicchio, P.; Buffi, A.; Del Col, L. The MONITOR Project: RFID-based Robots enabling real-time inventory and localization in warehouses and retail areas. In Proceedings of the 2021 6th International Conference on Smart and Sustainable Technologies (SpliTech). IEEE, 2021, pp. 1–6.
- Macenski, S.; Foote, T.; Gerkey, B.; Lalancette, C.; Woodall, W. Robot Operating System 2: Design, architecture, and uses in the wild. Science Robotics 2022, 7, eabm6074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christoph Fröhlich. Ros2 control framework. 2022.
- S. Macenski, T. Moore, A.M. From the desks of ROS maintainers: A survey of modern & capable mobile robotics algorithms in the robot operating system 2. Robotics and Autonomous Systems 2023.
- M.Görner.; R.Haschke. “Moveit! task constructor for task-level motion planning. IEEE Intl. Conf. on Robotics and Automation 2019.
- Redmon, J.; Divvala, S.; Girshick, R.; Farhadi, A. You Only Look Once: Unified, Real-Time Object Detection. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR); 2016; pp. 779–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasubramanian, R. The Denavit Hartenberg Convention. USA: Robotics Insitute Carnegie Mellon University 2011.


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




