Submitted:
07 August 2025
Posted:
08 August 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Rearing Under Fluctuating and Constant Temperature Regimes
Effect of Rearing Temperature Regimen on the Response of Parasitoids Under Contrasting Thermal Conditions: A Reciprocal Transplant Experiment
Data Analysis
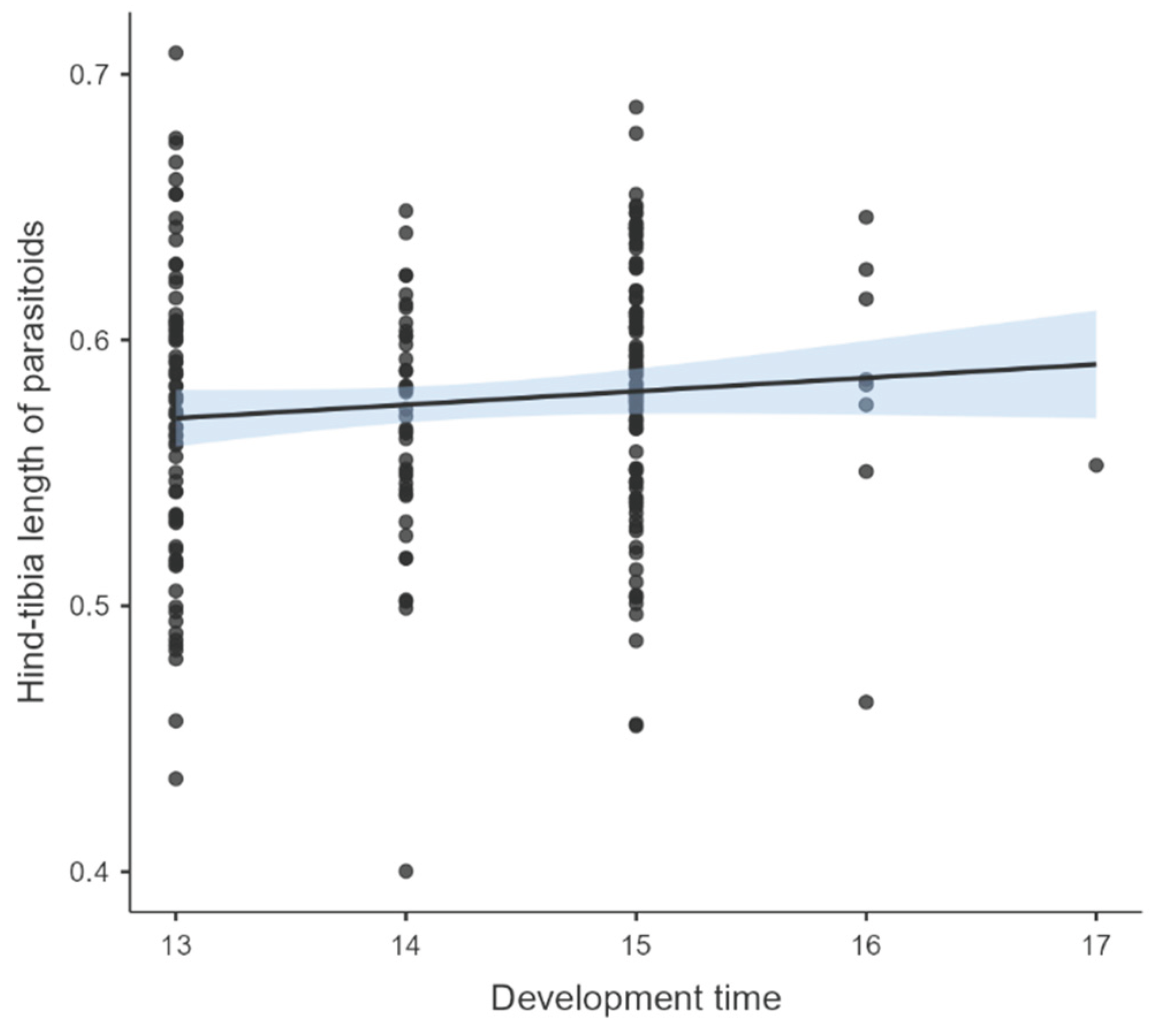
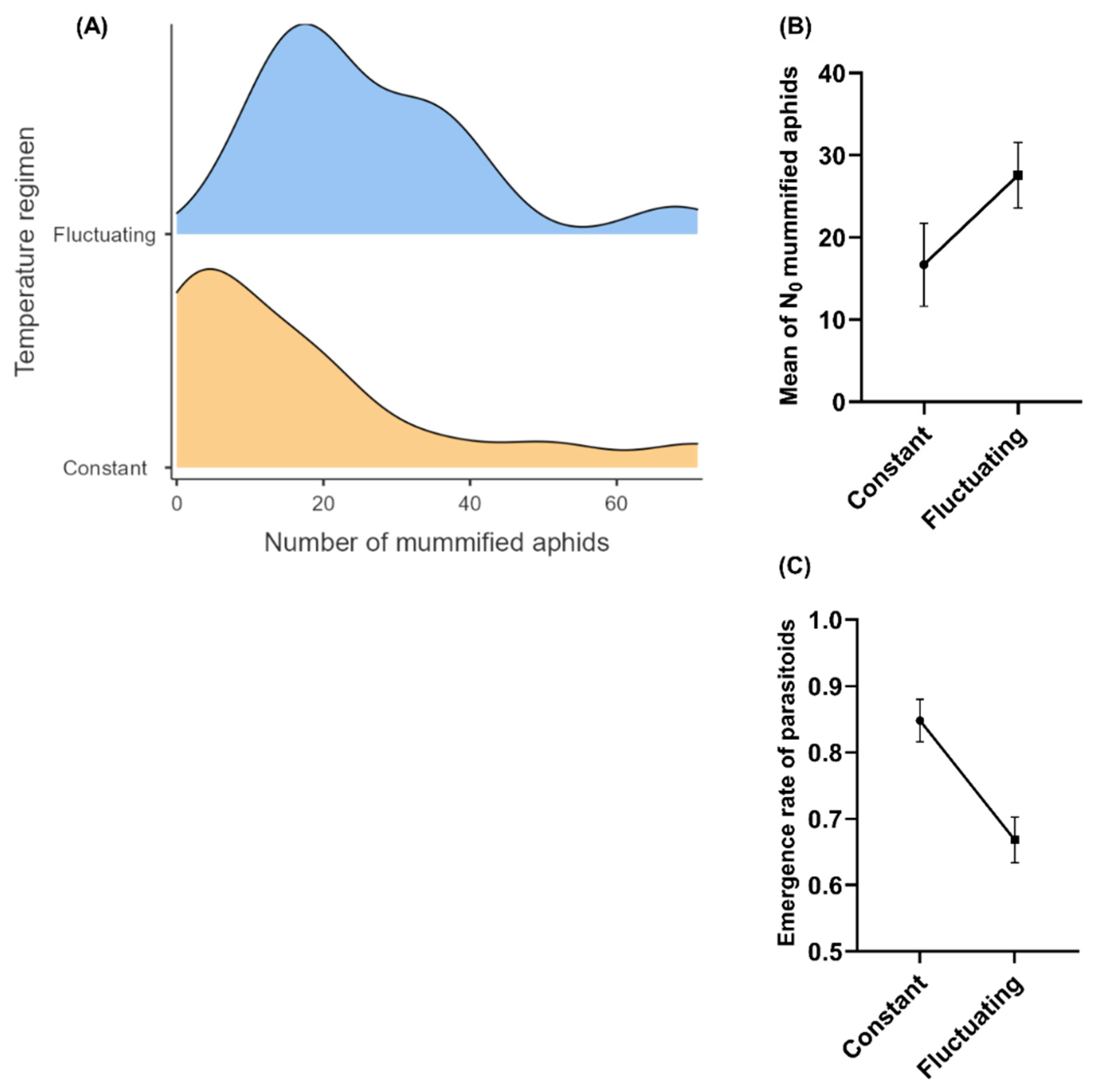
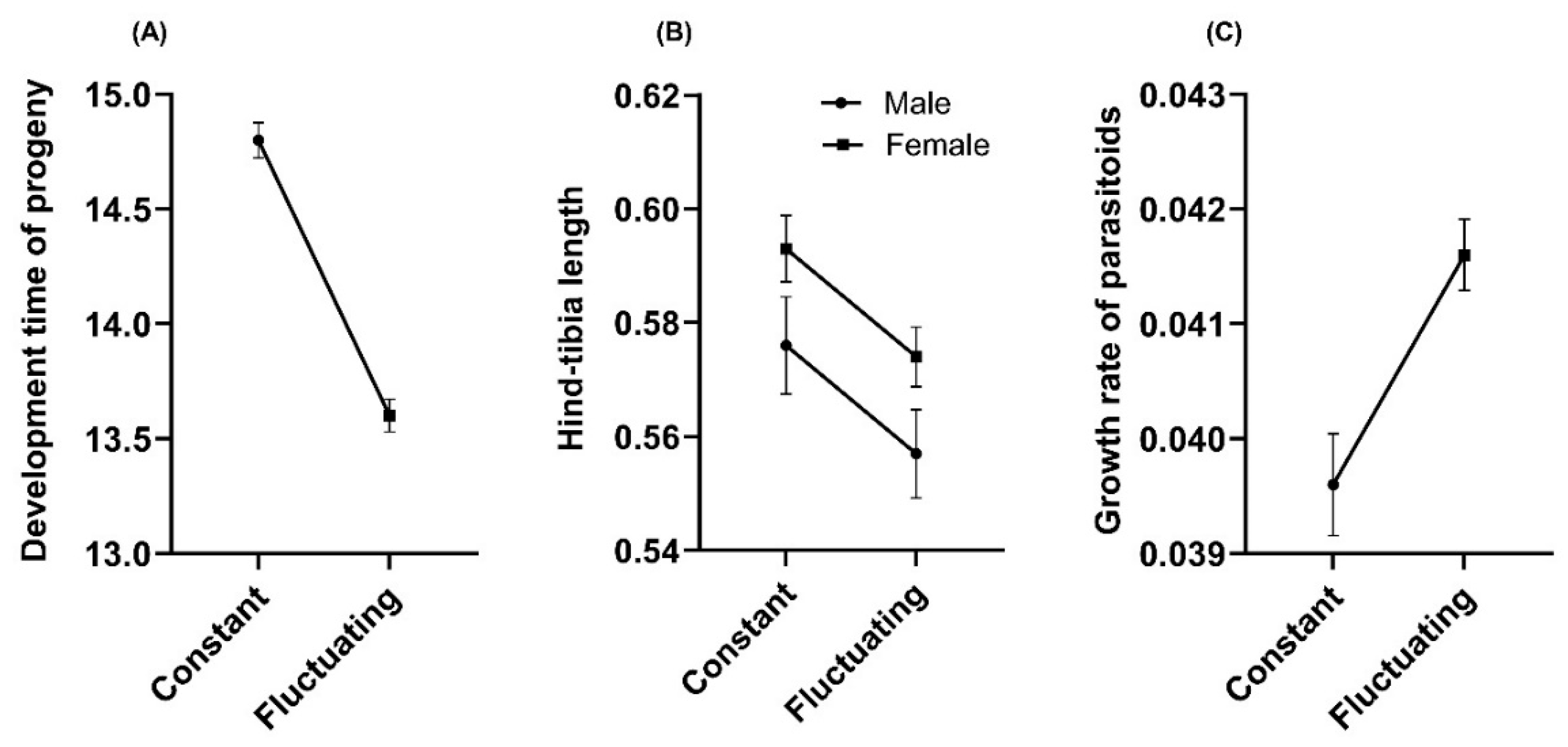
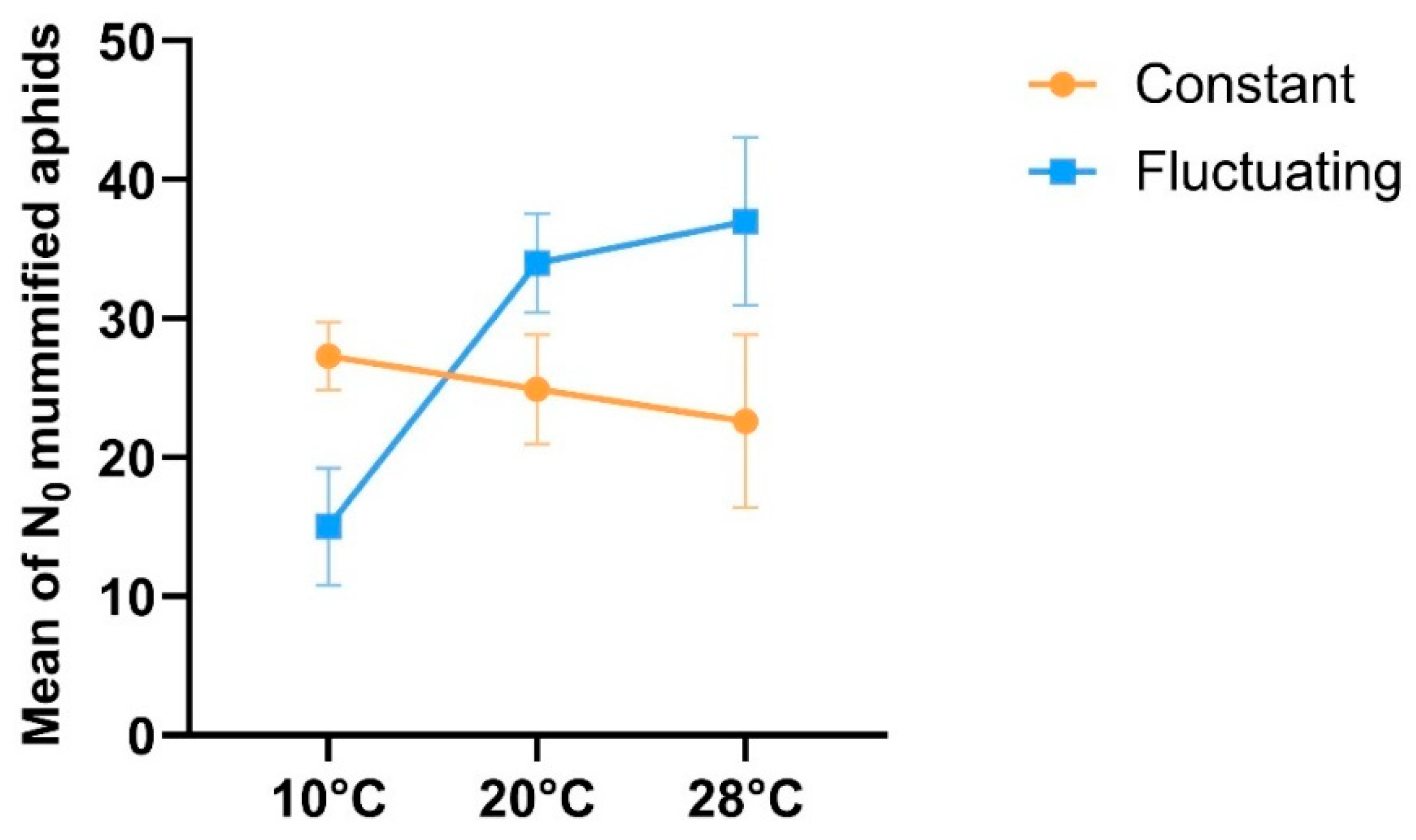
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Furlong, M.J., Zalucki, M.P. Climate change and biological control: the consequences of increasing temperatures on host–parasitoid interactions. Curr Opin Insect Sci. 2017; 20(1):39–44. [CrossRef]
- Tougeron, K., Brodeur, J., Le Lann, C., van Baaren, J. How climate change affects the seasonal ecology of insect parasitoids. Ecol Entomol. 2020; 45(2):167–181. [CrossRef]
- Monticelli, L.S., Bishop, J., Desneux, N., Gurr, G.M., Jaworski, C.C., McLean, A.H., Vanbergen, A.J. Multiple global change impacts on parasitism and biocontrol services in future agricultural landscapes. Adv Ecol Res. 2021; 65:245–304. [CrossRef]
- Barratt, B.I.P., Moran, V.C., Bigler, F., Van Lenteren, J.C. The status of biological control and recommendations for improving uptake for the future. BioControl. 2018; 63(1):155–167. [CrossRef]
- Baker, B.P., Green, T.A., Loker, A.J. Biological control and integrated pest management in organic and conventional systems. Biol Control. 2020; 140:104095. [CrossRef]
- Stenberg, J.A. A conceptual framework for integrated pest management. Trends Plant Sci. 2017; 22(10):759–769. DOI: 10.1016/j.tplants.2017.06.010 .
- Van Lenteren, J.C., Bolckmans, K., Köhl, J., Ravensberg, W.J., Urbaneja, A. Biological control using invertebrates and microorganisms: plenty of new opportunities. BioControl. 2018; 63(1):39–59. [CrossRef]
- Patel, H.R., Mandaliya, V.B. Biocontrol agents in agriculture: patent landscape, market dynamics, and recommendations for sustainable farming. In: Mitra, D., de los Santos Villalobos, S., Rani, A., Guerra Sierra, B.E., Andjelković, S., editors. Bio-control Agents for Sustainable Agriculture. Singapore: Springer; 2025. [CrossRef]
- Romo, C.M., Tylianakis, J.M. Elevated temperature and drought interact to reduce parasitoid effectiveness in suppressing hosts. PLoS ONE. 2013; 8(3):e58136. [CrossRef]
- Wakil, W., Kavallieratos, N.G., Eleftheriadou, N., Ghazanfar, M.U., El-Shafie, H.A., Blankson, A., Harvey, J.A. Climate change consequences for insect pest management, sustainable agriculture and food security. Entomol Gen. 2025; 45(1):37–51. [CrossRef]
- Bale, J.S., Masters, G.J., Hodkinson, I.D., Awmack, C., Bezemer, T.M., Brown, V.K., et al. Herbivory in global climate change research: direct effects of rising temperature on insect herbivores. Glob Change Biol. 2002; 8(1):1–16. [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, J.S., Kumari, M.K., Fand, B.B. Linking insect pest models with climate change scenarios to project against future risks of agricultural insect pests. CABI Rev. 2019; 2019:1–13. [CrossRef]
- Pardikes, N.A., Revilla, T.A., Lue, C.H., Thierry, M., Souto-Vilarós, D., Hrcek, J. Effects of phenological mismatch under warming are modified by community context. Glob Change Biol. 2022; 28(13):4013–4026. [CrossRef]
- Harvey, J.A., Tougeron, K., Gols, R., Heinen, R., Abarca, M., Abram, P.K., Chown, S.L. Scientists’ warning on climate change and insects. Ecol Monogr. 2023; 93(1):e1553. [CrossRef]
- Godfray, H.C.J. Parasitoids: behavioral and evolutionary ecology. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press; 1994.
- Le Lann, C., Lodi, M., Ellers, J. Thermal change alters the outcome of behavioural interactions between antagonistic partners. Ecol Entomol. 2014; 39(5):578–588. [CrossRef]
- Seehausen, M.L., Cusson, M., Régnière, J., Bory, M., Stewart, D., Djoumad, A., Martel, V. High temperature induces downregulation of polydnavirus gene transcription in lepidopteran host and enhances accumulation of host immunity gene transcripts. J Insect Physiol. 2017; 98:126–133. [CrossRef]
- Moore, M.E., Kester, K.M., Kingsolver, J.G. Rearing temperature and parasitoid load determine host and parasitoid performance in Manduca sexta and Cotesia congregata. Ecol Entomol. 2019; 44(5):519–528. [CrossRef]
- Schreven, S.J.J., Frago, E., Stens, A., de Jong, P.W., van Loon, J.J.A. Contrasting effects of heat pulses on different trophic levels: an experiment with a herbivore–parasitoid model system. PLoS ONE. 2017; 12(4):e0176704. [CrossRef]
- Machekano, H., Mvumi, B.M., Nyamukondiwa, C. Loss of coevolved basal and plastic responses to temperature may underlie trophic level host–parasitoid interactions under global change. Biol Control. 2018; 118:44–54. [CrossRef]
- Mutamiswa, R., Chidawanyika, F., Nyamukondiwa, C. Comparative assessment of the thermal tolerance of spotted stemborer and its larval parasitoid. Insect Sci. 2018; 25(5):847–860. [CrossRef]
- Moore, M.E., Hill, C.A., Kingsolver, J.G. Differing thermal sensitivities in a host–parasitoid interaction: high, fluctuating developmental temperatures produce dead wasps and giant caterpillars. Funct Ecol. 2021; 35:675–685. [CrossRef]
- Lange, S., Volkholz, J., Geiger, T., Zhao, F., Vega, I., Veldkamp, T., et al. Projecting exposure to extreme climate impact events across six event categories and three spatial scales. Earth’s Future. 2020; 8(11):e2020EF001616. [CrossRef]
- Ranasinghe, R., Ruane, A.C., Vautard, R., Arnell, N., Coppola, E., Dessai, S., et al. Climate change information for regional impact and risk assessment. Clim Change. 2021; 1767(14):1926. DOI: 10.1017/9781009157896.014.
- Pörtner, H.O. Climate impacts on organisms, ecosystems and human societies: integrating OCLTT into a wider context. J Exp Biol. 2021; 224(Suppl_1):jeb238360. [CrossRef]
- Parmesan, C., Morecroft, M.D., Trisurat, Y., Adrian, R., Anshari, G.Z., Arneth, A., et al. Terrestrial and Freshwater Ecosystems and Their Services. In Climate Change 2022: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability: Working Group II Contribution to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (pp. 197-378). Cambridge University Press; 2023. pp. 197–377. [CrossRef]
- Martin, R.A., da Silva, C.R., Moore, M.P., Diamond, S.E. When will a changing climate outpace adaptive evolution?. WIREs Clim Change. 2023; 14(6):e852. [CrossRef]
- Sgrò, C.M., Terblanche, J.S., Hoffmann, A.A. What can plasticity contribute to insect responses to climate change?. Annu Rev Entomol. 2016; 61(1):433–451. [CrossRef]
- Logan, M.L., Cox, C.L. Genetic constraints, transcriptome plasticity, and the evolutionary response to climate change. Front Genet. 2020; 11:538226. [CrossRef]
- Bonamour, S., Chevin, L.-M., Charmantier, A., Teplitsky, C. Phenotypic plasticity in response to climate change: the importance of cue variation. Phil Trans R Soc B. 2019; 374:20180178. [CrossRef]
- Le Lann, C., Van Baaren, J., Visser, B. Dealing with predictable and unpredictable temperatures in a climate change context: the case of parasitoids and their hosts. J Exp Biol. 2021; 224(Suppl_1):jeb238626. [CrossRef]
- Jerbi-Elayed, M., Foray, V., Tougeron, K., Grissa-Lebdi, K., Hance, T. Developmental temperature affects life-history traits and heat tolerance in the aphid parasitoid Aphidius colemani. Insects. 2021; 12(10):852. [CrossRef]
- Kelly, M. Adaptation to climate change through genetic accommodation and assimilation of plastic phenotypes. Phil Trans R Soc B. 2019; 374(1768):20180176. [CrossRef]
- Armarego-Marriott, T. Climatic selection and gene expression plasticity. Nat Clim Chang. 2021; 11(1):4. [CrossRef]
- Castellanos, N.L., Bueno, A.F., Haddi, K., Silveira, E.C., Rodrigues, H.S., Hirose, E., Smagghe, G., Oliveira, E.E. The fitness and economic benefits of rearing the parasitoid Telenomus podisi under fluctuating temperature regime. Neotrop Entomol. 2019; 48:934–948. [CrossRef]
- Kawecki, T.D., Ebert, D. Conceptual issues in local adaptation. Ecol Lett. 2004; 7(12):1225–1241. [CrossRef]
- Tougeron, K., Van Baaren, J., Llopis, S., Ridel, A., Doyon, J., Brodeur, J., Le Lann, C. Disentangling plasticity from local adaptation in diapause expression in parasitoid wasps from contrasting thermal environments: a reciprocal translocation experiment. Biol J Linn Soc. 2018; 124(4):756–764. [CrossRef]
- Van Emden, H.F., Harrington, R., editors. Aphids as Crop Pests. Wallingford, UK: CABI; 2017.
- Wajnberg, E., Bernstein, C., Van Alphen, J., editors. Behavioral Ecology of Insect Parasitoids: From Theoretical Approaches to Field Applications. Chichester, UK: Wiley; 2008.
- Le Ralec, A., Anselme, C., Outreman, Y., Poirié, M., van Baaren, J., Le Lann, C., van Alphen, J.J.M. Evolutionary ecology of the interactions between aphids and their parasitoids. C R Biol. 2010; 333:554–565. [CrossRef]
- Rakhshani, E., Starý, P. Aphid parasitoids: Aphidiinae (Hym., Braconidae). In: Farazmand, H., editor. Biological Control of Insect and Mite Pests in Iran. Cham: Springer; 2021. p. 333–399.
- Starý, P. The Aphidiidae of Chile (Hymenoptera, Ichneumonoidea, Aphidiidae). Dtsch Entomol Z. 1995; 42(1):113–138. [CrossRef]
- Tomanović, Z., Petrović, A., Mitrović, M., Kavallieratos, N.G., Starý, P., Rakhshani, E., Popović, A., Shukshuk, A., Ivanović, A. Molecular and morphological variability within the Aphidius colemani group with redescription of Aphidius platensis Brethes. Bull Entomol Res. 2014; 104(1):1–14. [CrossRef]
- Nieto, J.M., Fuentes-Contreras, E., Castro, M.C., Aldea, M.P., Ortego, J., Mier, P.D. Catálogo de los áfidos (Hemiptera: Aphididae) de Chile, con plantas hospedadoras y distribuciones regional y provincial. Graellsia. 2016; 72:e050. [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Baca, J. K., Alfaro-Tapia, A., Lavandero, B., Le Lann, C., & Van Baaren, J. Suitability and profitability of a cereal aphid for the parasitoid Aphidius platensis in the context of conservation biological control of Myzus persicae in orchards. Insects, 2020. 11(6), 381. [CrossRef]
- Alfaro-Tapia A, Alvarez-Baca JK, Tougeron K et al Overwintering strategies and life-history traits of different populations of Aphidius platensis along a latitudinal gradient in Chile. Entomol. Gen. 2021. [CrossRef]
- Alfaro-Tapia, A., Alvarez-Baca, J. K., Tougeron, K., Van Baaren, J., Lavandero, B., & Le Lann, C. Composition and structure of winter aphid–parasitoid food webs along a latitudinal gradient in Chile. Oecologia 2022. 200(3), 425-440. [CrossRef]
- IPCC, Sections. In: Climate Change 2023: Synthesis Report. Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change [Core Writing Team, H. Lee and J. Romero (eds.)]. IPCC, 2023, Geneva, Switzerland, pp. 35-115. [CrossRef]
- ODEPA. Panorama de la agricultura chilena. Oficina de Estudios y Políticas Agrarias, Santiago, Chile; 2019. Disponible en: https://www.odepa.gob.cl/wp-content/uploads/2019/09/panorama2019Final.pdf.
- Nicol, C.M.Y., Mackauer, M. The scaling of body size and mass in a host–parasitoid association: influence of host species and stage. Entomol Exp Appl. 1999; 90(1):83–92. [CrossRef]
- Dion, E., Zélé, F., Simon, J.-C., Outreman, Y. Rapid evolution of parasitoids when faced with the symbiont-mediated resistance of their hosts. J Evol Biol. 2011; 24(4):741–750. [CrossRef]
- Jerbi-Elayed, M., Tougeron, K., Grissa-Lebdi, K., Hance, T. Effect of developmental temperatures on Aphidius colemani host-foraging behavior at high temperature. J Therm Biol. 2022; 103:103140. [CrossRef]
- Piticar, A. Changes in agro-climatic indices related to temperature in Central Chile. Int J Biometeorol. 2019; 63(4):499–510. [CrossRef]
- Harvey, J.A., Cloutier, J., Visser, B., et al. The effect of different dietary sugars and honey on longevity and fecundity in two hyperparasitoid wasps. J Insect Physiol. 2012; 58:816–823. [CrossRef]
- Charles, J.J., Paine, T.D. Fitness effects of food resources on the polyphagous aphid parasitoid, Aphidius colemani Viereck. PLoS ONE. 2016; 11(1):e0147551. [CrossRef]
- Benelli, G., Giunti, G., Tena, A., Desneux, N., Caselli, A., Canale, A. The impact of adult diet on parasitoid reproductive performance. J Pest Sci. 2017; 90:807–823. [CrossRef]
- Antolin, M.F., Bjorkstein, T.A., Vaughn, T.T. Host-related fitness trade-offs in a presumed generalist parasitoid, Diaeretiella rapae (Hymenoptera: Aphidiidae). Ecol Entomol. 2006; 31:242–254. [CrossRef]
- Charnov, E.L., Los-den Hartogh, R.L., Jones, W.T., van den Assem, J. Sex ratio evolution in a variable environment. Nature. 1981; 289(5793):27–33. [CrossRef]
- Colinet, H., Boivin, G., Hance, T. Manipulation of parasitoid size using the temperature-size rule: fitness consequences. Oecologia. 2007; 152:425–433. [CrossRef]
- Zepeda-Paulo, F.A., Ortiz-Martínez, S.A., Figueroa, C.C., Lavandero, B. Adaptive evolution of a generalist parasitoid: implications for the effectiveness of biological control agents. Evol Appl. 2013; 6(6):983–999. [CrossRef]
- Bolker, B. M., Brooks, M. E., Clark, C. J., Geange, S. W., Poulsen, J. R., Stevens, M. H. H., & White, J. S. S. Generalized linear mixed models: a practical guide for ecology and evolution. Trends in ecology & evolution, 2009. 24(3), 127-135. [CrossRef]
- Brooks ME, Kristensen K, van Benthem KJ, Magnusson A, Berg CW, Nielsen A, Skaug HJ, Maechler M, Bolker BM “glmmTMB Balances Speed and Flexibility Among Packages for Zero-inflated Generalized Linear Mixed Modeling.” The R Journal, 2017. 9(2), 378–400.
- The jamovi project (2024). jamovi. (Version 2.6) [Computer Software]. Retrieved from https://www.jamovi.org.
- R Core Team (2024). R: A Language and environment for statistical computing. (Version 4.4) [Computer software]. Retrieved from https://cran.r-project.org. (R packages retrieved from CRAN snapshot 2024-08-07).
- Box, G.E.P., Cox, D.R. An analysis of transformations. J R Stat Soc B. 1964; 26:211–243. [CrossRef]
- Venables, W.N., Ripley, B.D. Modern Applied Statistics with S. 4th ed. New York: Springer; 2002.
- Pinheiro, J., Bates, D., DebRoy, S., Sarkar, D., R Core Team. nlme: Linear and Nonlinear Mixed Effects Models. R package version 3.1-162; 2021.
- Lenth R (2025). emmeans: Estimated Marginal Means, aka Least-Squares Means. R package version1.10.6090003. https://rvlenth.github.io/emmeans/, https://rvlenth.gith b.io/emmeans/.
- Fox, J., Weisberg, S. An R Companion to Applied Regression. 3rd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage; 2019.
- Lüdecke, D., Ben-Shachar, M., Patil, I., Waggoner, P., Makowski, D. performance: An R Package for Assessment, Comparison and Testing of Statistical Models. J Open Source Softw. 2021; 6(60):3139. [CrossRef]
- Cohen, A.C. Ecology of insect rearing systems: a mini-review of insect rearing papers from 1906–2017. Adv Entomol. 2018; 6(2):86. doi: 10.4236/ae.2018.62008.
- Herren, P., Hesketh, H., Meyling, N.V., Dunn, A.M. Environment–host–parasite interactions in mass-reared insects. Trends Parasitol. 2023; 39(7):588–602. [CrossRef]
- Lommen, S.T., de Jong, P.W., Pannebakker, B.A. It is time to bridge the gap between exploring and exploiting: prospects for utilizing intraspecific genetic variation to optimize arthropods for augmentative pest control—a review. Entomol Exp Appl. 2017; 162(2):108–123. [CrossRef]
- Buckley, L.B., Schoville, S.D., Williams, C.M. Shifts in the relative fitness contributions of fecundity and survival in variable and changing environments. J Exp Biol. 2021; 224(Suppl_1):jeb228031. [CrossRef]
- Le Lann, C, Wardziak, T, van Baaren, J, van Alphen, JJM. Thermal plasticity of metabolic rates linked to life-history traits and foraging behaviour in a parasitic wasp. Functional Ecology 2011. 25:641-651. [CrossRef]
- Logan, M.L., Cox, R.M., Calsbeeka, R. Natural selection on thermal performance in a novel thermal environment. PNAS 2014; 33:14165–14169. doi/10.1073/pnas.1404885111.
- Ismaeil, I., Doury, G., Desouhant, E., Dubois, F., Prevost, G. and Couty, A. (2013). Trans-generational effects of mild heat stress on the life history traits of an aphid parasitoid. PLOS One 8, 1-9. [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, D. (1994) Temperature and organism size—a biological law for ectotherms. Advances in Ecological Research, 25, 1–58. [CrossRef]
- Sinclair, B.J., Marshall, K.E., Sewell, M.A., Levesque, D.L., Willett, C.S., Slotsbo, S., et al. Can we predict ectotherm responses to climate change using thermal performance curves and body temperatures?. Ecol Lett. 2016; 19(11):1372–1385. [CrossRef]
- Giri, M.K., Pass, B.C., Yeargan, K.V., Parr, J.C. Behavior, net reproduction, longevity, and mummy-stage survival of Aphidius matricariae. Entomophaga. 1982; 27:147–153. [CrossRef]
- Zamani, A.A., Talebi, A., Fathipour, Y., Baniameri, V. Effect of temperature on life history of Aphidius colemani and Aphidius matricariae, two parasitoids of Aphis gossypii and Myzus persicae. Environ Entomol. 2007; 36(2):263–271. [CrossRef]
- Deutsch, C.A.; Tewksbury, J.J.; Tigchelaar, M.; Battisti, D.S.; Merrill, S.C.; Huey, R.B.; Naylor, R.L. Increase in crop losses to insect pests in a warming climate. Science 2018, 361, 916–919. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




