Submitted:
11 March 2025
Posted:
12 March 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
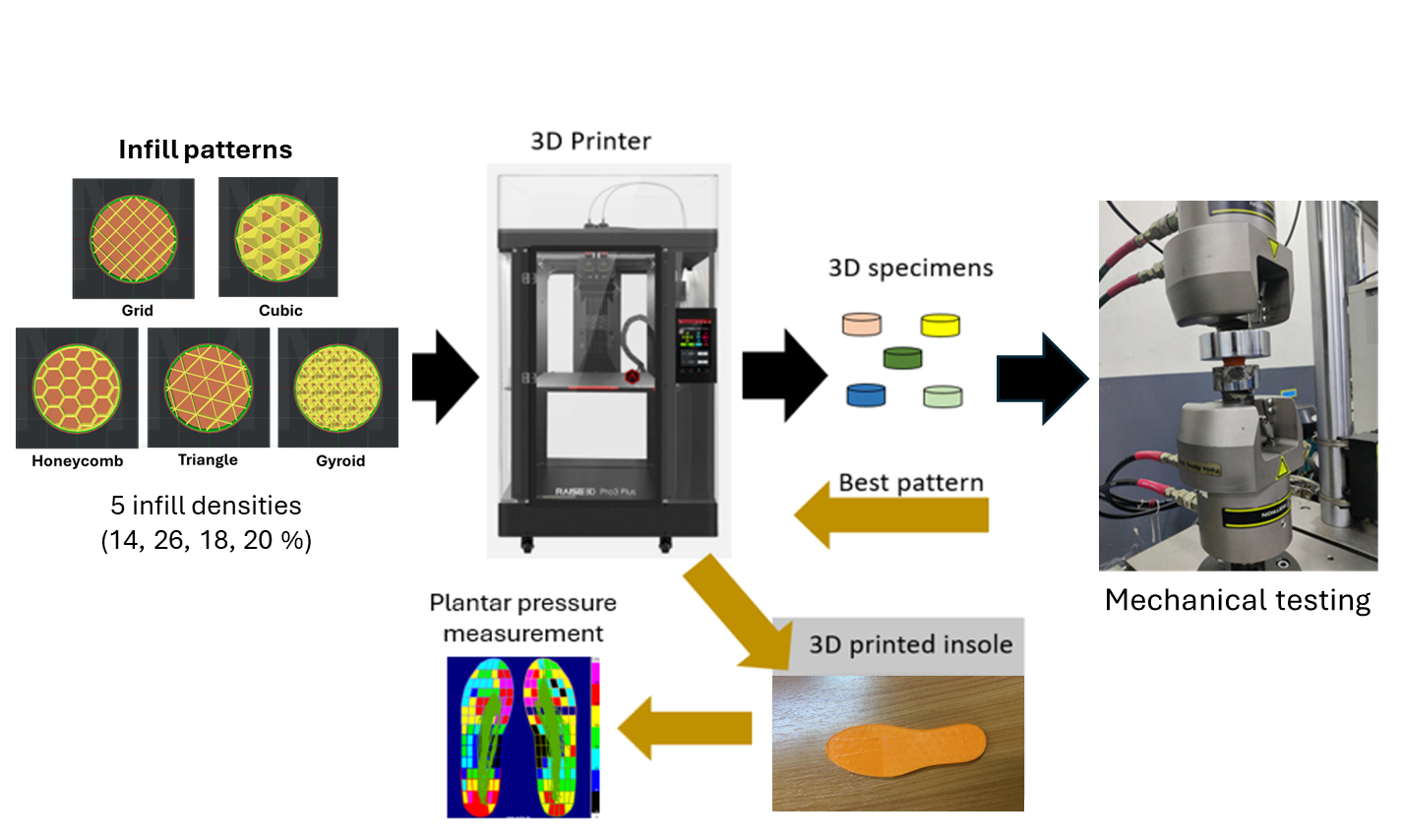
2. Materials and Methods
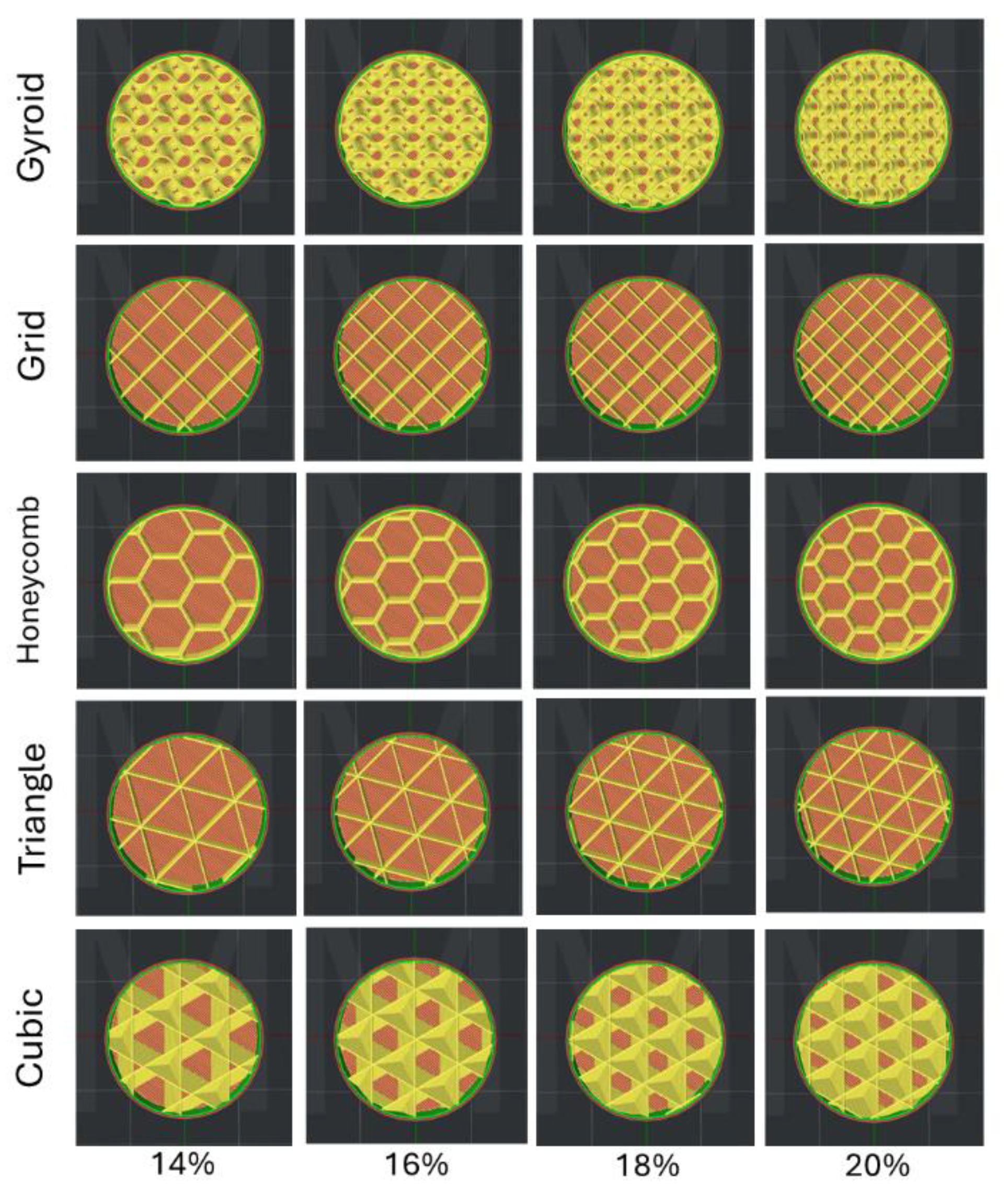
2.1. Specimen Preparation
2.2. Mechanical Properties Test
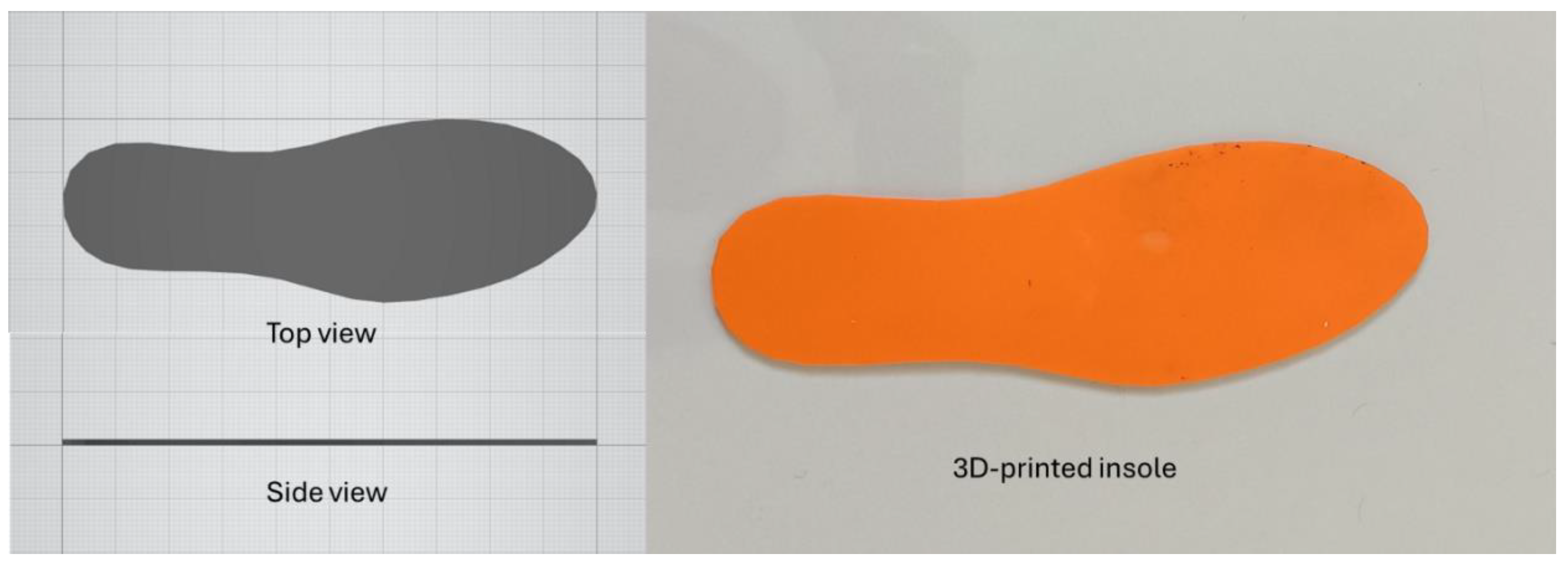
2.3. Insole Fabrication
2.4. Plantar Pressure Measurement
2.5. Gait Data Analysis
3. Results
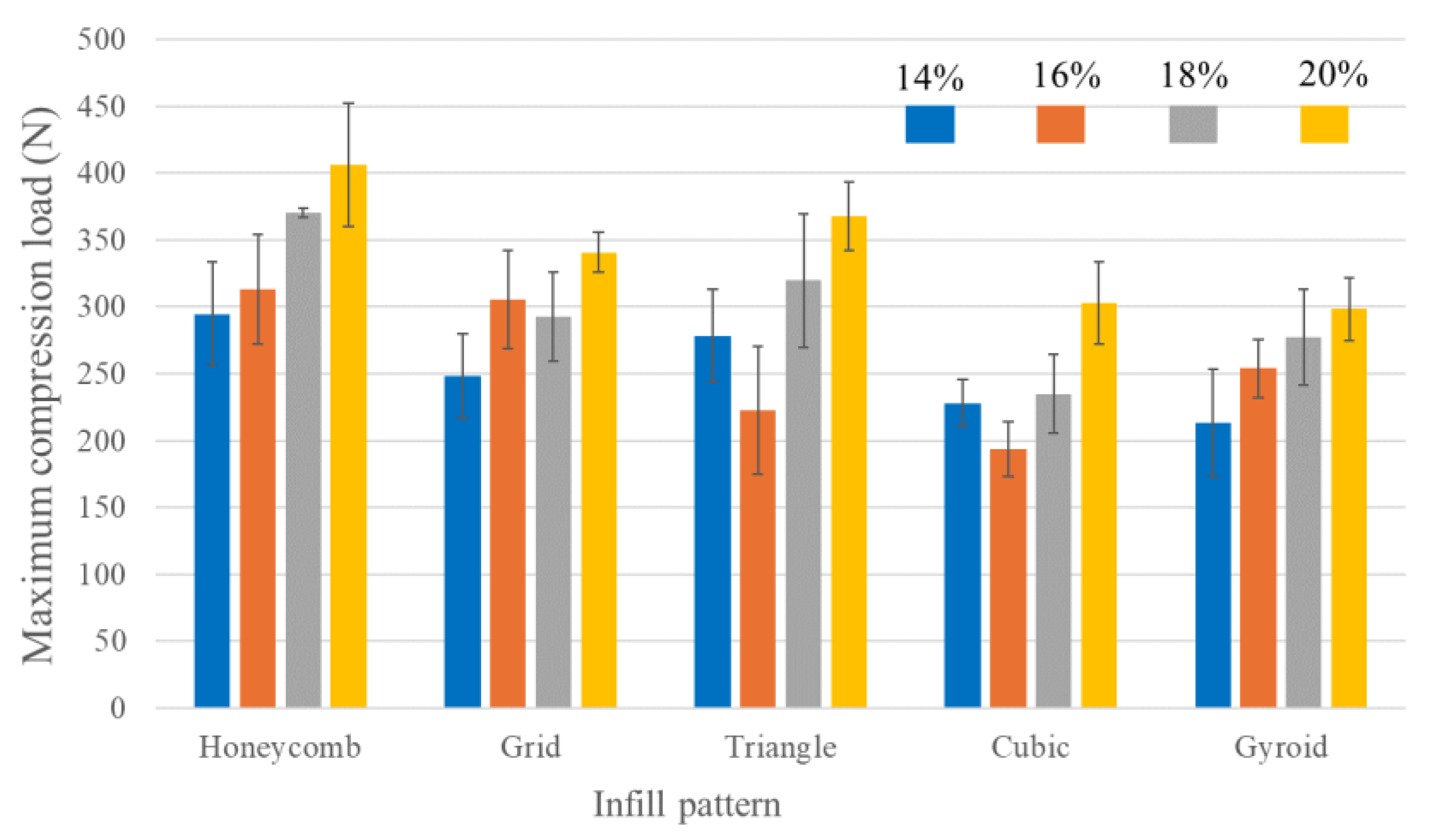
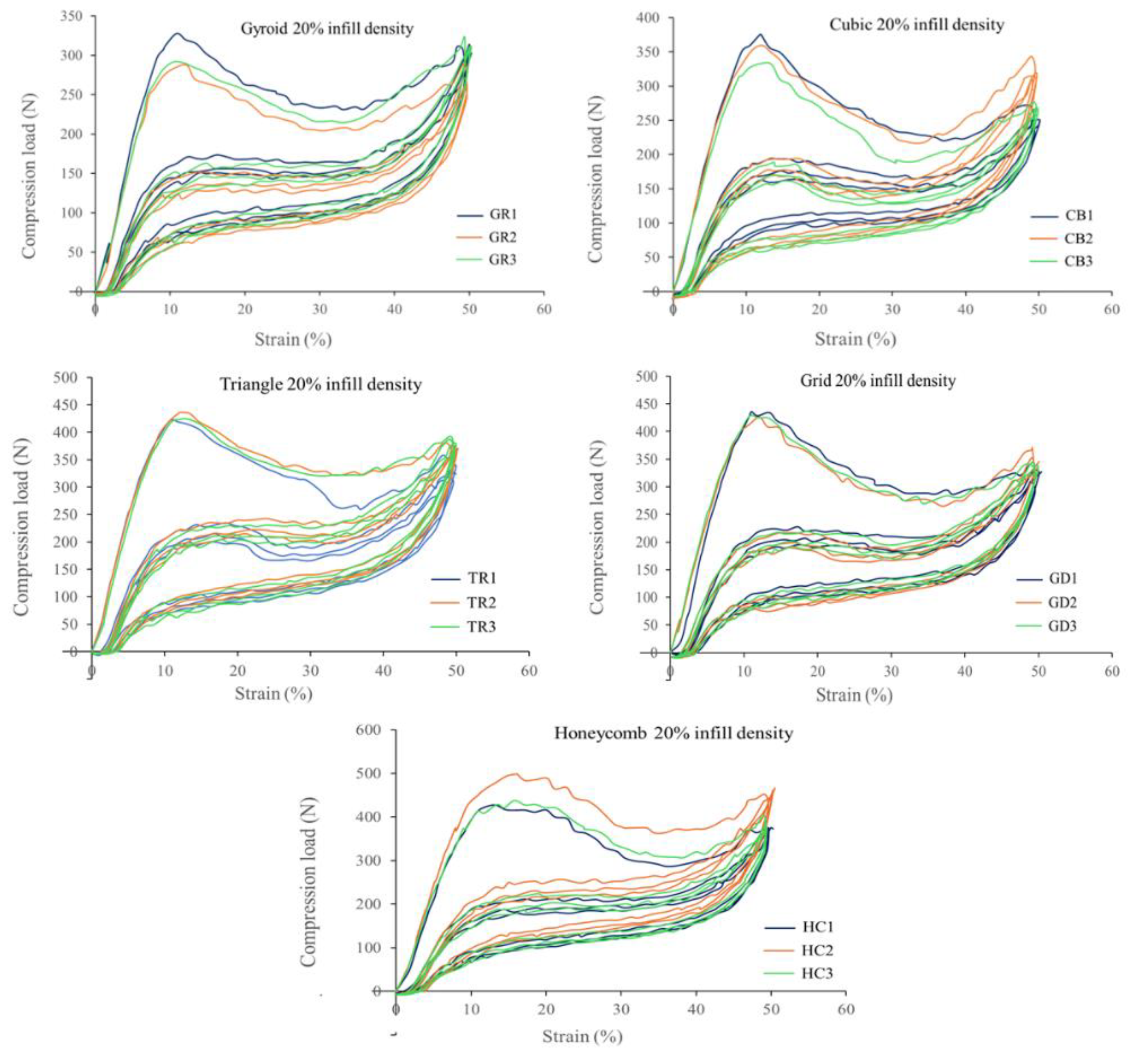
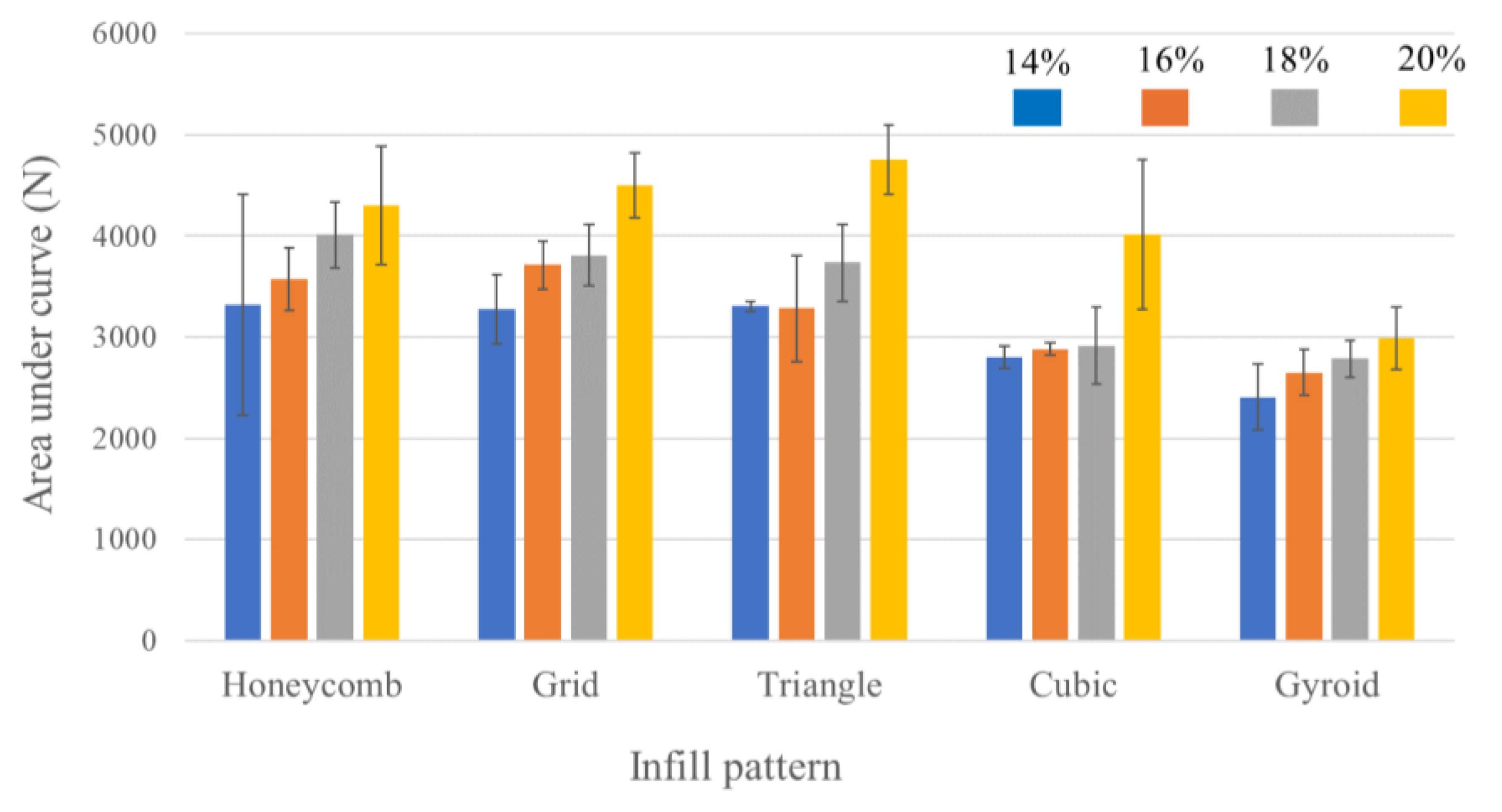
3.1. Mechanical Property Testing
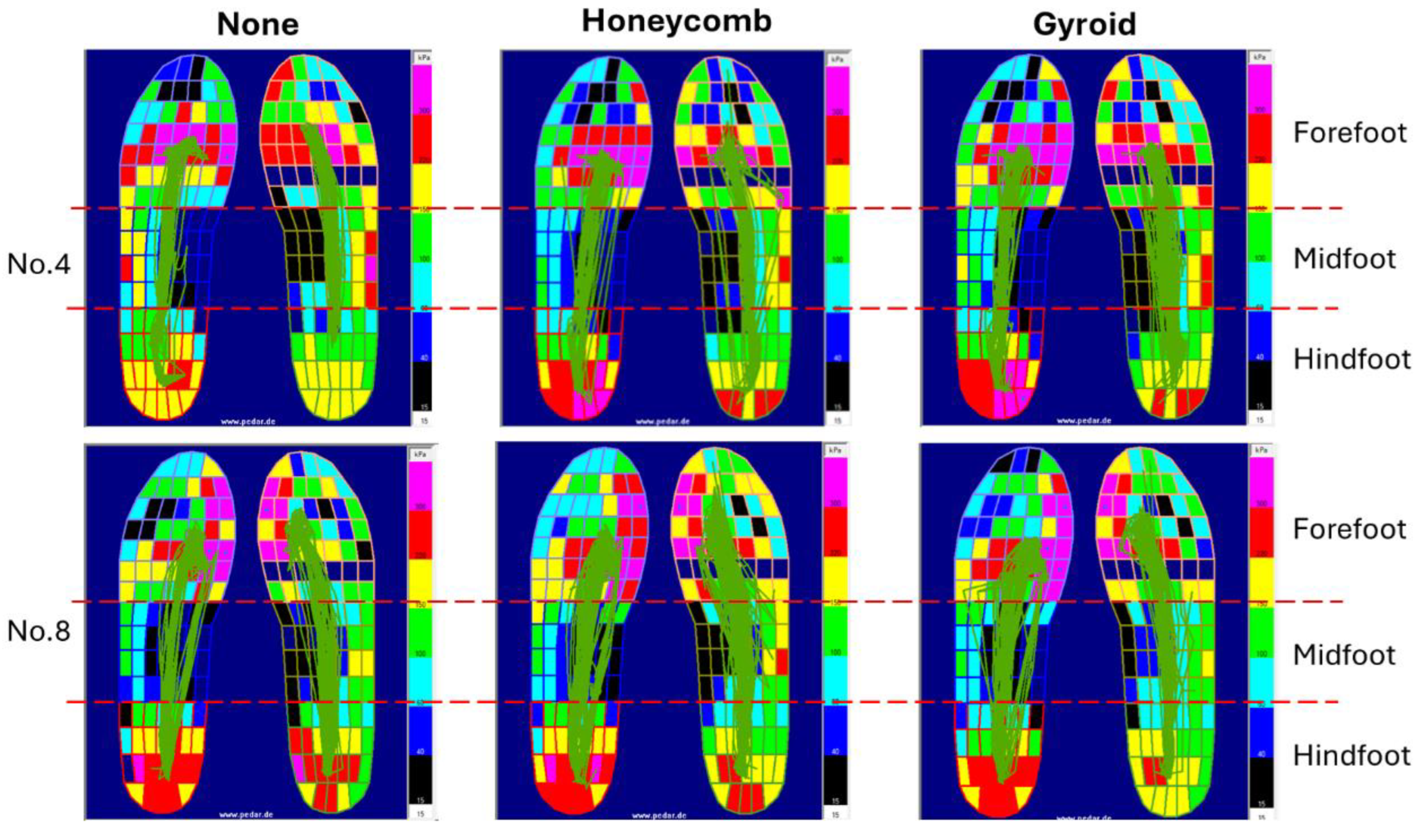
3.2. Plantar Pressure in Gait
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- P. Zhang, J. Lu, Y. Jing, S. Tang, D. Zhu, Y. Bi, Global epidemiology of diabetic foot ulceration: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Ann Med 49 (2017) 106–116. [CrossRef]
- K. Jones, M.R. Backhouse, J. Bruce, Rehabilitation for people wearing offloading devices for diabetes-related foot ulcers: a systematic review and meta-analyses, J Foot Ankle Res 16 (2023). [CrossRef]
- J.Z.M. Lim, N.S.L. Ng, C. Thomas, Prevention and treatment of diabetic foot ulcers, J R Soc Med 110 (2017) 104–109. [CrossRef]
- V. Ramachandran, T. Mohanasundaram, D. Karunakaran, M. Gunasekaran, R. Tiwari, Physiological and Pathophysiological Aspects of Diabetic Foot Ulcer and its Treatment Strategies, Curr Diabetes Rev 19 (2023). [CrossRef]
- P.R. Cavanagh, S.A. Bus, Off-loading the diabetic foot for ulcer prevention and healing, J Vasc Surg 52 (2010). [CrossRef]
- A. Peker, L. Aydin, S. Kucuk, G. Ozkoc, B. Cetinarslan, Z. Canturk, A. Selek, Additive manufacturing and biomechanical validation of a patient-specific diabetic insole, Polym Adv Technol 31 (2020). [CrossRef]
- J. Cheng, J.-C. Wang, Exploring the Feasibility of Advanced Manufacturing for Mass Customization of Insoles in the Context of ESG, International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing-Green Technology 11 (2024) 815–832. [CrossRef]
- M. Mancuso, R. Bulzomì, M. Mannisi, F. Martelli, C. Giacomozzi, 3D-Printed Insoles for People with Type 2 Diabetes: An Italian, Ambulatory Case Report on the Innovative Care Model, Diabetology 4 (2023). [CrossRef]
- X. Zhang, P. Chu, X. Ma, W.M. Chen, 3D-Printed Insole Designs for Enhanced Pressure-Relief in Diabetic Foot Based on Functionally-Graded Stiffness Properties, in: IFMBE Proc, 2024. [CrossRef]
- K.R. Kumar, P. Vinothkumar, N. Soms, Investigation on the Development of Custom Foot Insole Using Soft Polylactic Acid by Fused Deposition Modelling Technique, J Mater Eng Perform 32 (2023) 1790–1796. [CrossRef]
- U.K. Jonnala, R. sankineni, Y. Ravi Kumar, Design and development of fused deposition modeling (FDM) 3D-Printed Orthotic Insole by using gyroid structure, J Mech Behav Biomed Mater 145 (2023). [CrossRef]
- S. Koteswari, S.N. Yeole, Development of 3D printed orthotic device for flat foot problem, Mater Today Proc 44 (2021) 2435–2441. [CrossRef]
- R. Kumar, S.K. Sarangi, 3D Printed customized diabetic foot insoles with architecture designed lattice structures – a case study, Biomed Phys Eng Express 10 (2024) 015019. [CrossRef]
- A. Zolfagharian, M. Lakhi, S. Ranjbar, M. Bodaghi, Custom Shoe Sole Design and Modeling Toward 3D Printing, Int J Bioprint 7 (2021). [CrossRef]
- Y.F. Hudak, J.S. Li, S. Cullum, B.M. Strzelecki, C. Richburg, G.E. Kaufman, D. Abrahamson, J.T. Heckman, B. Ripley, S. Telfer, W.R. Ledoux, B.C. Muir, P.M. Aubin, A novel workflow to a fabricate patient-specific 3D printed accommodative foot orthosis with personalized latticed metamaterial, Med Eng Phys 104 (2022). [CrossRef]
- P.E. Chatzistergos, A. Gatt, C. Formosa, K. Farrugia, N. Chockalingam, Optimised cushioning in diabetic footwear can significantly enhance their capacity to reduce plantar pressure, Gait Posture 79 (2020) 244–250. [CrossRef]
- R. Xu, Z. Wang, Z. Ren, T. Ma, Z. Jia, S. Fang, H. Jin, Comparative Study of the Effects of Customized 3D printed insole and Prefabricated Insole on Plantar Pressure and Comfort in Patients with Symptomatic Flatfoot, Medical Science Monitor 25 (2019) 3510–3519. [CrossRef]
- A.C. Faulí, C.L. Andrés, N.P. Rosas, M.J. Fernández, E.M. Parreño, C.O. Barceló, Physical Evaluation of Insole Materials Used to Treat the Diabetic Foot, J Am Podiatr Med Assoc 98 (2008) 229–238. [CrossRef]
- F. Nilsen, M. Molund, E.M. Lium, K.H. Hvaal, Material Selection for Diabetic Custom Insoles: A Systematic Review of Insole Materials and Their Properties, JPO Journal of Prosthetics and Orthotics 34 (2022) e131–e143. [CrossRef]
- U. Hellstrand Tang, R. Zügner, V. Lisovskaja, J. Karlsson, K. Hagberg, R. Tranberg, Comparison of plantar pressure in three types of insole given to patients with diabetes at risk of developing foot ulcers - A two-year, randomized trial, J Clin Transl Endocrinol 1 (2014). [CrossRef]
- B. Orsu, Y.P. Shaik, Compression Strength Analysis of Customized Shoe Insole with Different Infill Patterns Using 3D Printing, OAlib 09 (2022) 1–13. [CrossRef]
- Y. Xiao, J. Yin, X. Zhang, X. An, Y. Xiong, Y. Sun, Mechanical performance and cushioning energy absorption characteristics of rigid polyurethane foam at low and high strain rates, Polym Test 109 (2022) 107531. [CrossRef]
- S.K. Reddy, D.B. Ferry, A. Misra, Highly compressible behavior of polymer mediated three-dimensional network of graphene foam, RSC Adv. 4 (2014) 50074–50080. [CrossRef]
- G. Melia, P. Siegkas, J. Levick, C. Apps, Insoles of uniform softer material reduced plantar pressure compared to dual-material insoles during regular and loaded gait, Appl Ergon 91 (2021). [CrossRef]
- M. Nouman, T. Dissaneewate, W. Leelasamran, S. Chatpun, The insole materials influence the plantar pressure distributions in diabetic foot with neuropathy during different walking activities, Gait Posture 74 (2019). [CrossRef]
- J. Zuñiga, M. Moscoso, P.G. Padilla-Huamantinco, M. Lazo-Porras, J. Tenorio-Mucha, W. Padilla-Huamantinco, J.P. Tincopa, Development of 3D-Printed Orthopedic Insoles for Patients with Diabetes and Evaluation with Electronic Pressure Sensors, Designs (Basel) 6 (2022). [CrossRef]
- B.C. Muir, J.-S. Li, Y.F. Hudak, G.E. Kaufman, S. Cullum, P.M. Aubin, Evaluation of novel plantar pressure-based 3-dimensional printed accommodative insoles - A feasibility study, Clinical Biomechanics 98 (2022) 105739. [CrossRef]
- Q.Q. Shi, P.L. Li, K.L. Yick, N.W. Li, J. Jiao, Effects of contoured insoles with different materials on plantar pressure offloading in diabetic elderly during gait, Sci Rep 12 (2022). [CrossRef]
- J.T.M. Cheung, M. Zhang, Parametric design of pressure-relieving foot orthosis using statistics-based finite element method, Med Eng Phys 30 (2008). [CrossRef]
- L. Tang, L. Wang, W. Bao, S. Zhu, D. Li, N. Zhao, C. Liu, Functional gradient structural design of customized diabetic insoles, J Mech Behav Biomed Mater 94 (2019). [CrossRef]
- L. Jin, The Influence of Different Footwear Insole Stiffness on Center of Pressure and Ankle Kinematics during Walking: A Case Report, Biomechanics (Switzerland) 2 (2022). [CrossRef]
- M.C. Iacob, D. Popescu, D. Petcu, R. Marinescu, Assessment of the Flexural Fatigue Performance of 3D-Printed Foot Orthoses Made from Different Thermoplastic Polyurethanes, Applied Sciences (Switzerland) 13 (2023). [CrossRef]
| Demographics | |
| Age (years) | 23.10 ± 3.25 |
| Gender (male/female) | 10/0 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 22.93 ± 1.43 |
| Foot length (cm) | 25.52 ± 0.97 |
| Side of dominant (left/right) | 0/10 |
| Mean plantar pressure (kPa) | ||||||
| Infill pattern | Hindfoot | Midfoot | Forefoot | |||
| Left | Right | Left | Right | Left | Right | |
| None | 58.21±10.64 | 52.97±5.10 | 16.43±3.45 | 21.84±8.46 | 58.06±7.99 | 38.51±11.15 |
| Honeycomb | 51.80±10.33 | 47.26±8.31 | 19.26±4.19 | 27.57±10.75 | 56.99±7.81 | 45.00±14.82 |
| Gyroid | 54.56±9.67 | 46.27±6.84 | 18.53±2.54 | 26.81±7.47 | 62.27±8.96 | 40.46±9.91 |
| Insole | AUC (N·s) |
| None | 337.75 ± 45.31 |
| Honeycomb | 377.40 ± 49.52 |
| Gyroid | 374.43 ± 48.73 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





