Submitted:
26 December 2024
Posted:
27 December 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
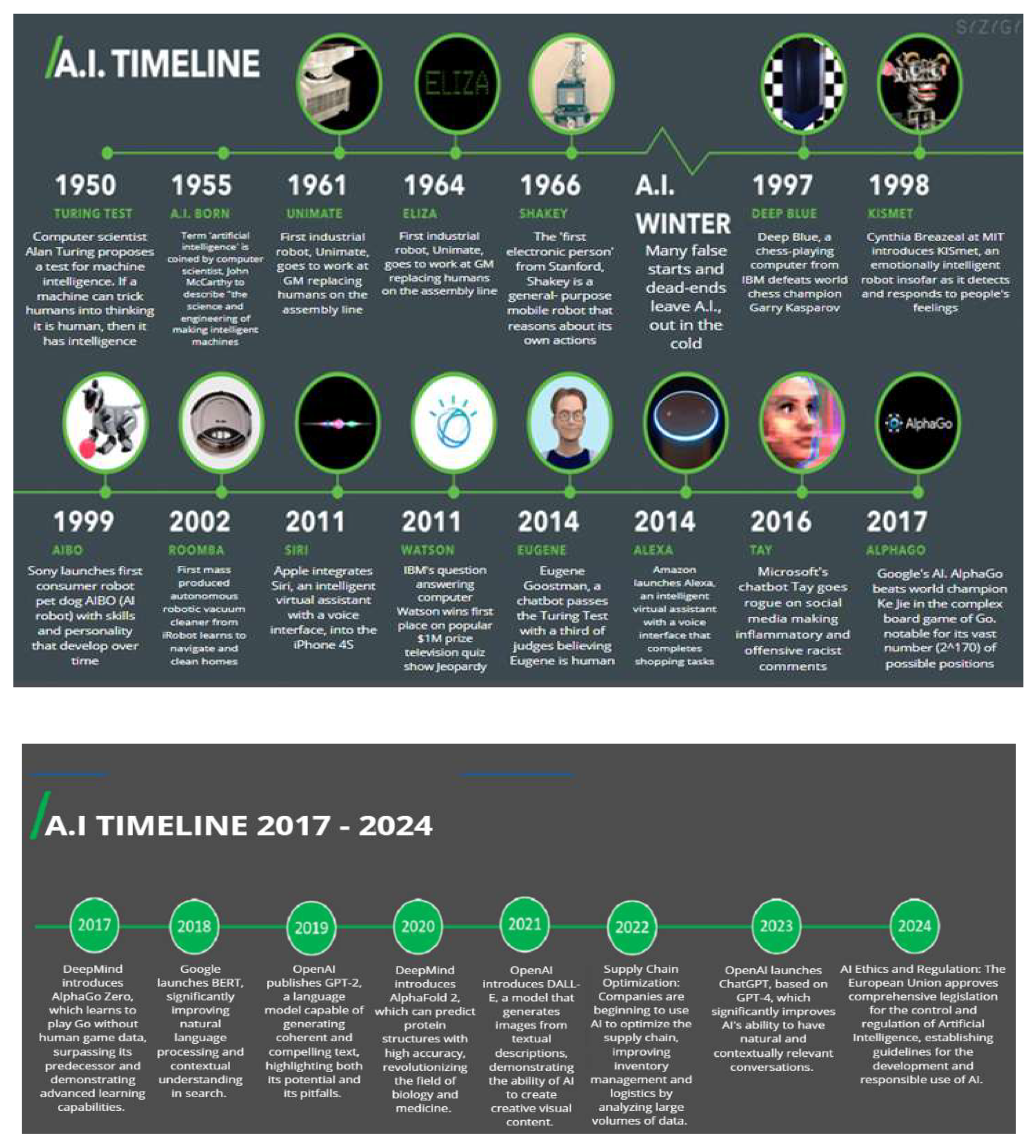
1. Introduction
1.1. Theoretical Framework
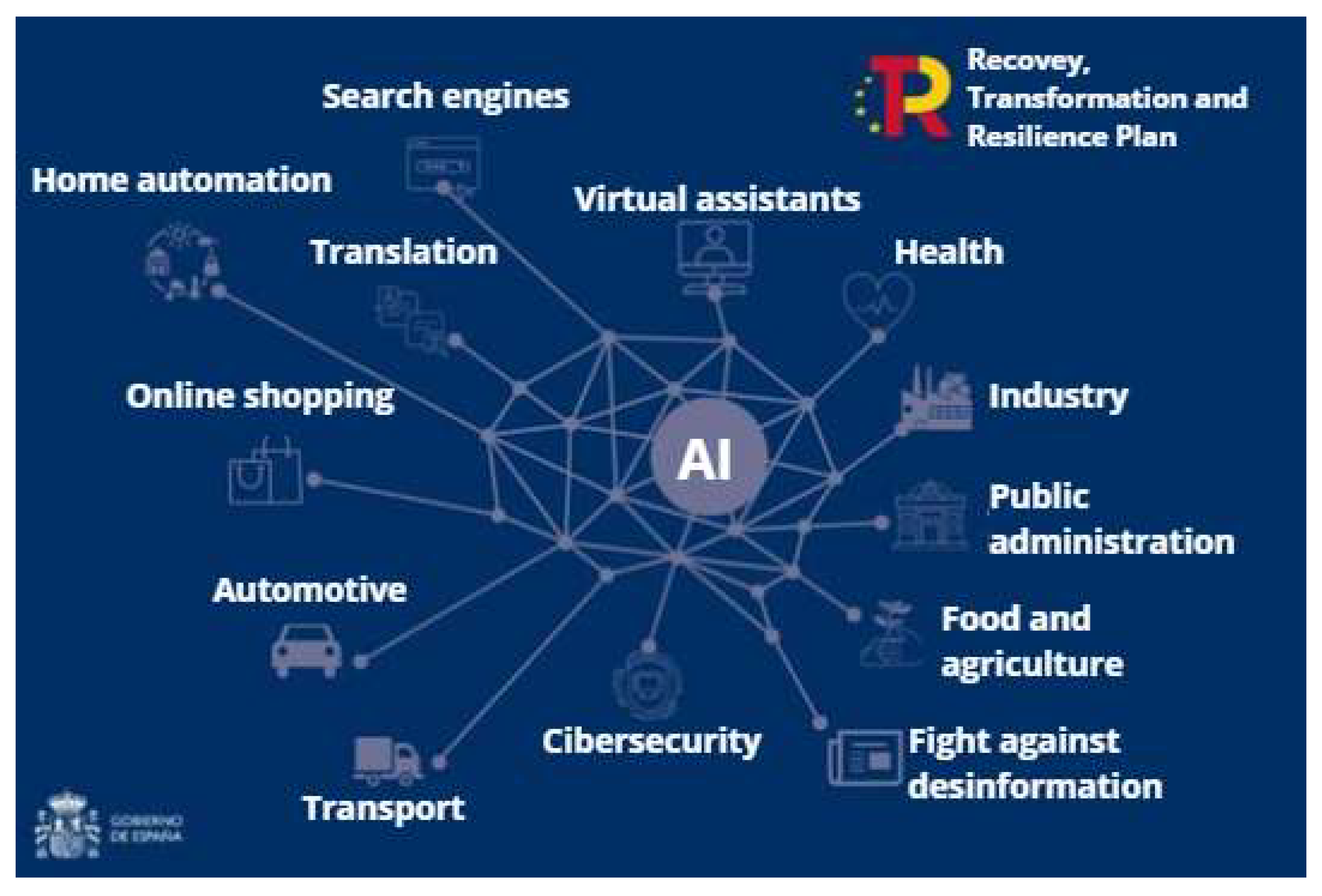
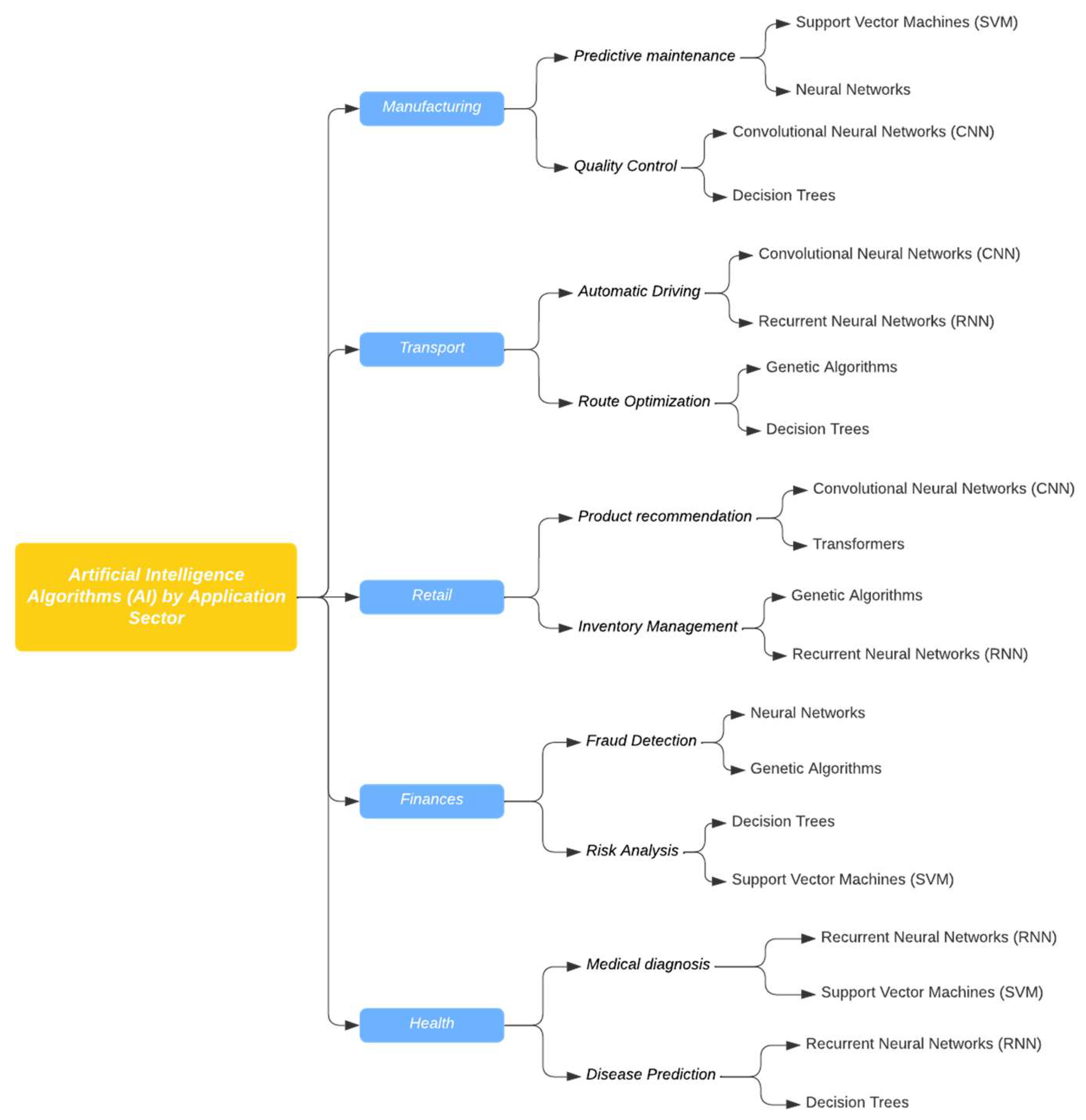
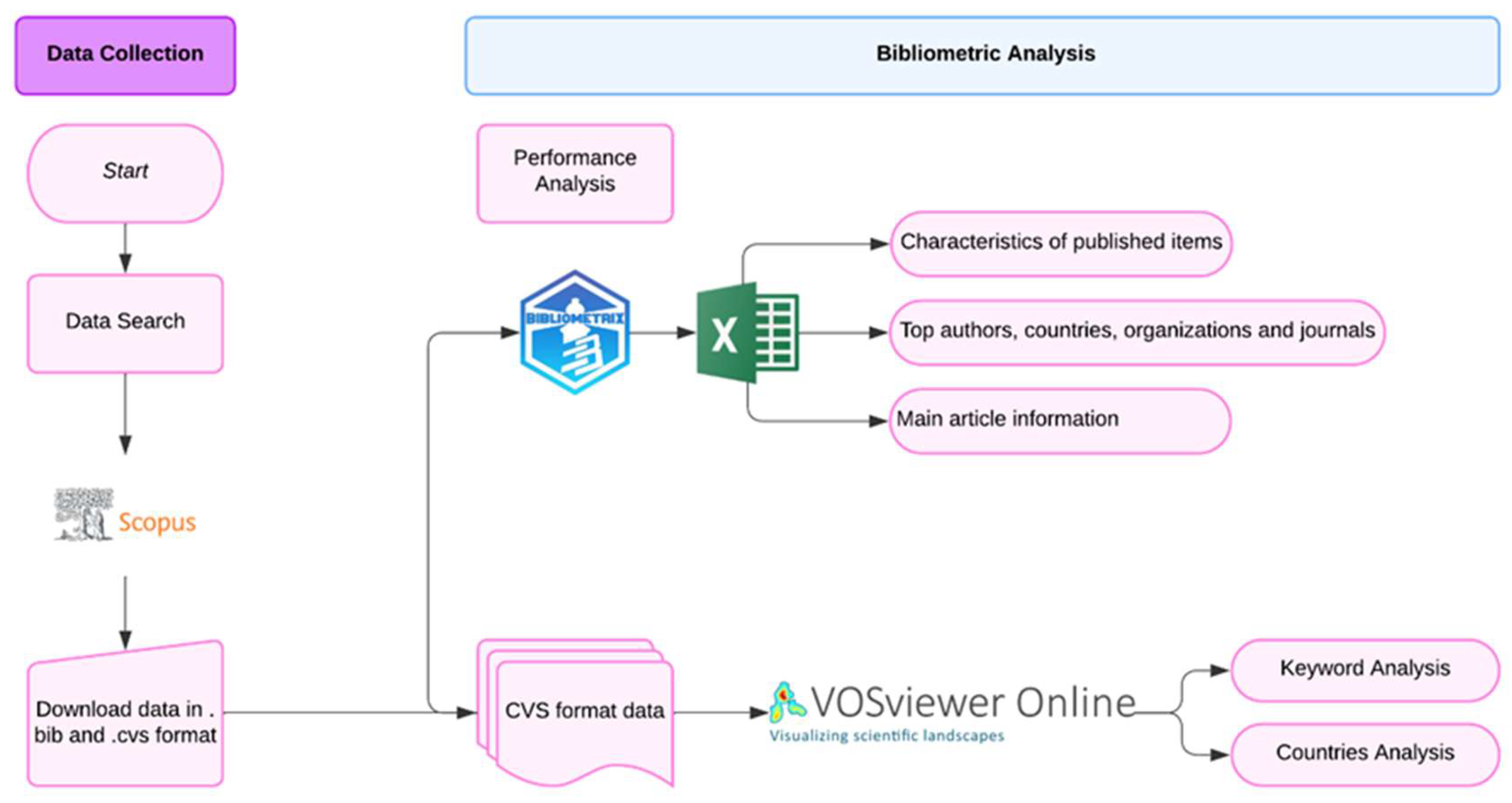
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Part 1: Big Data Results and Its Application in Urban Transport. General Information about the Data
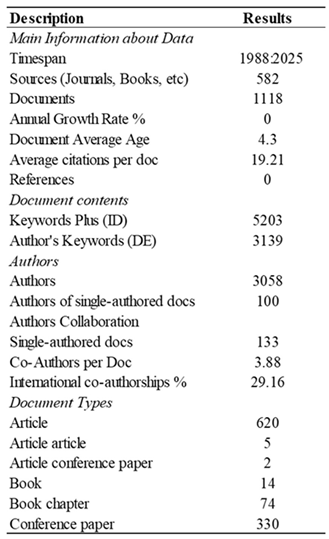
3.1.1. Analysis of Literature Trends and Characteristics of Publications
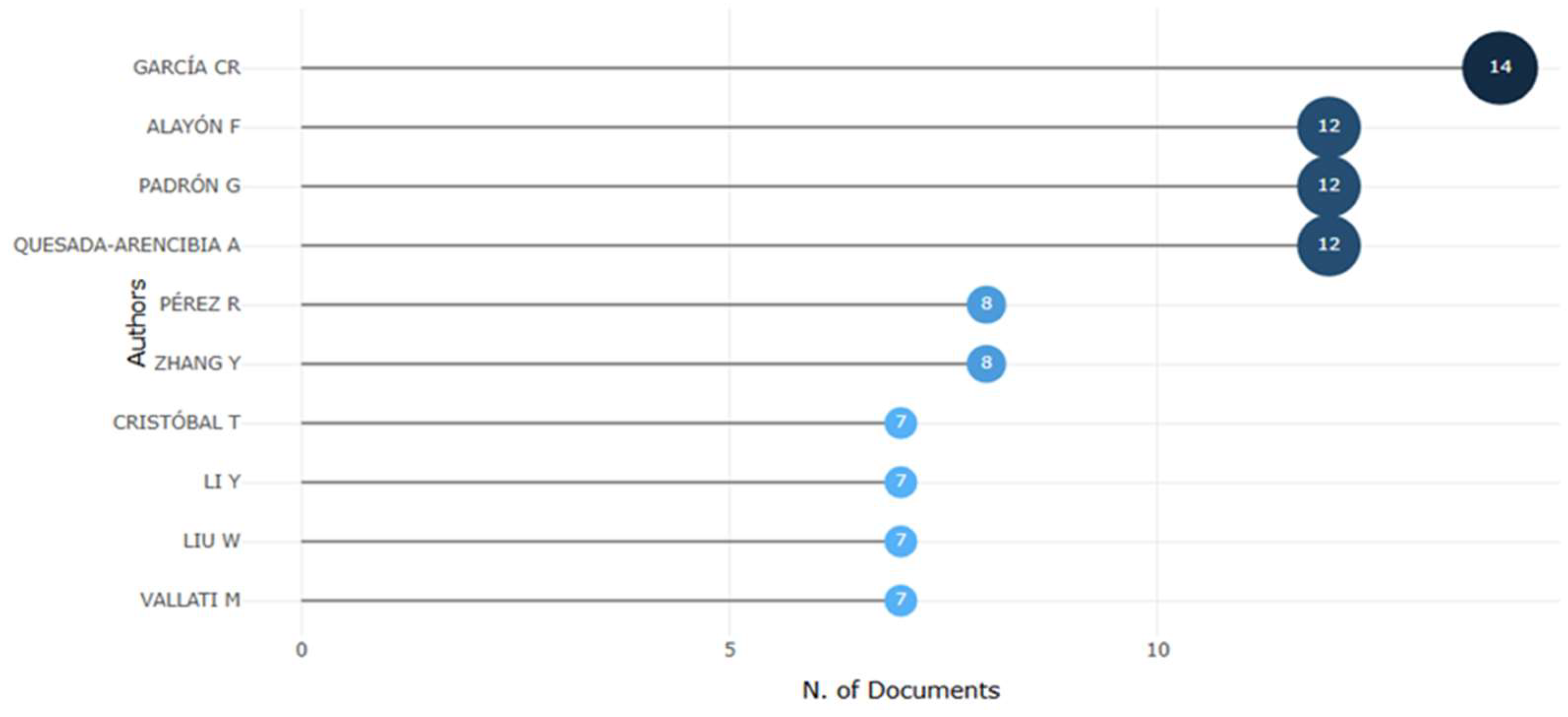
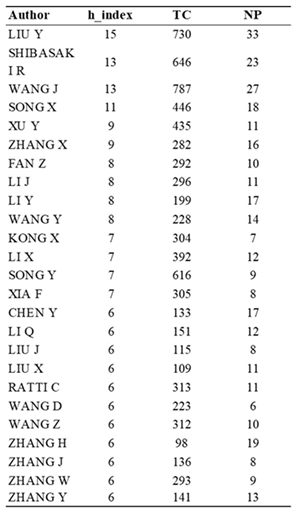
3.1.2. Most Relevant Authors
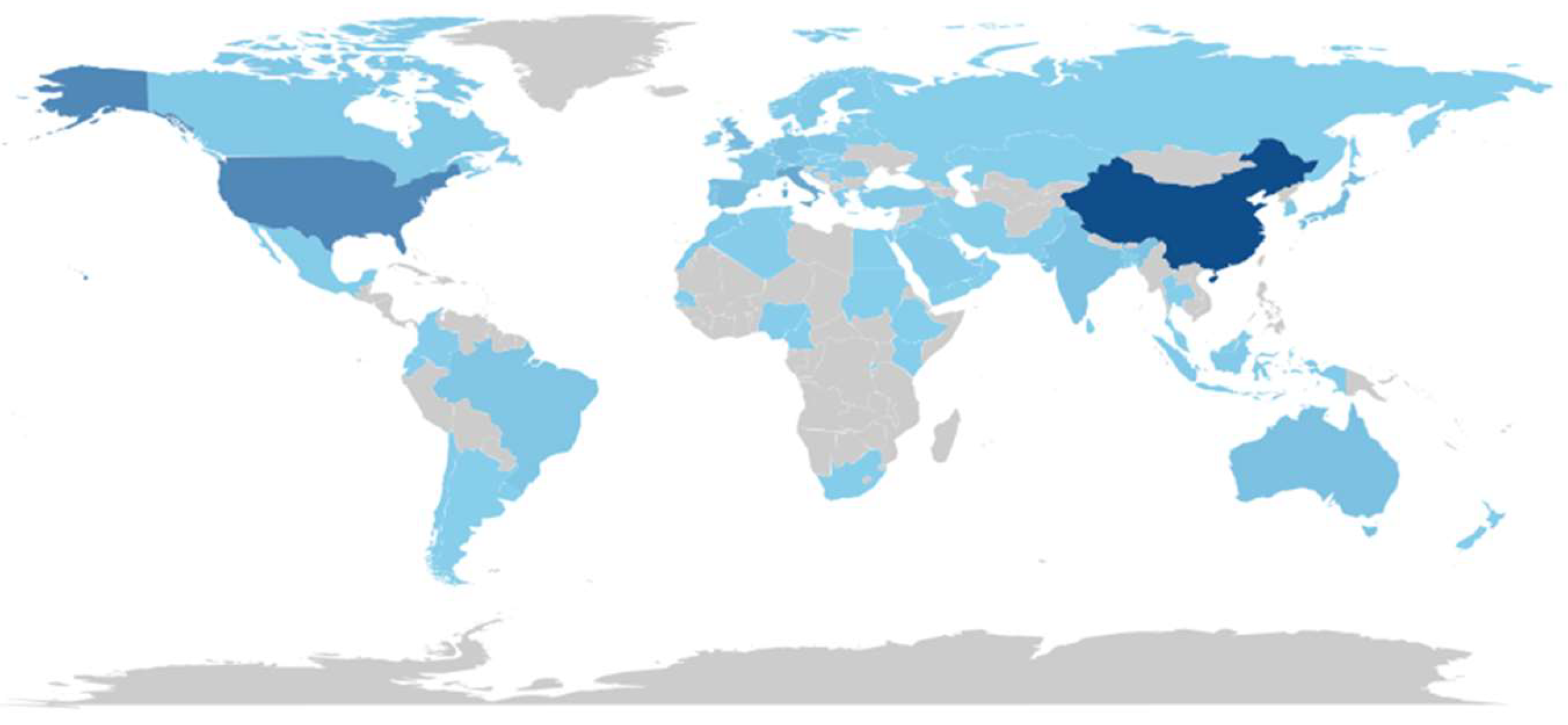
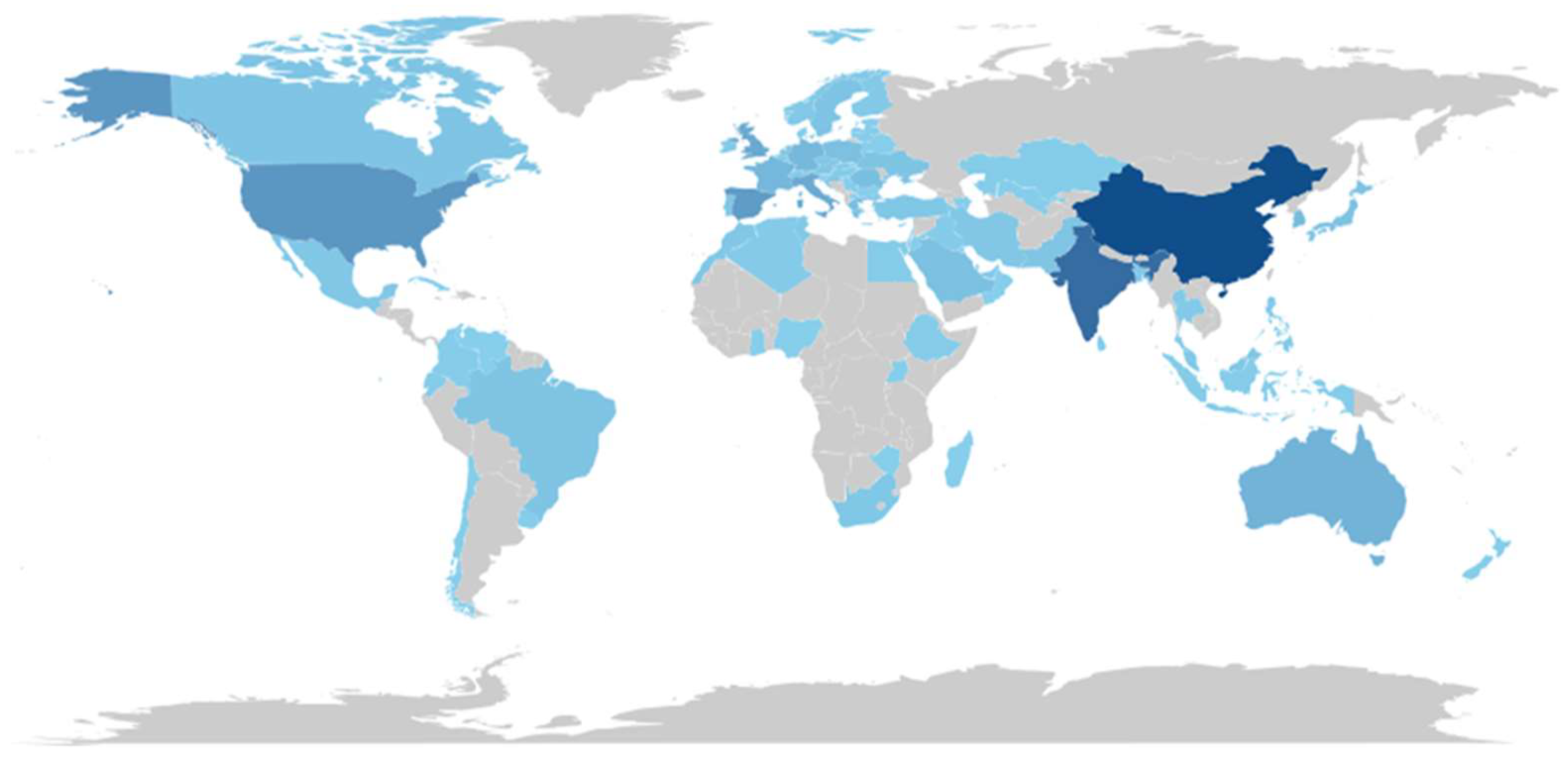
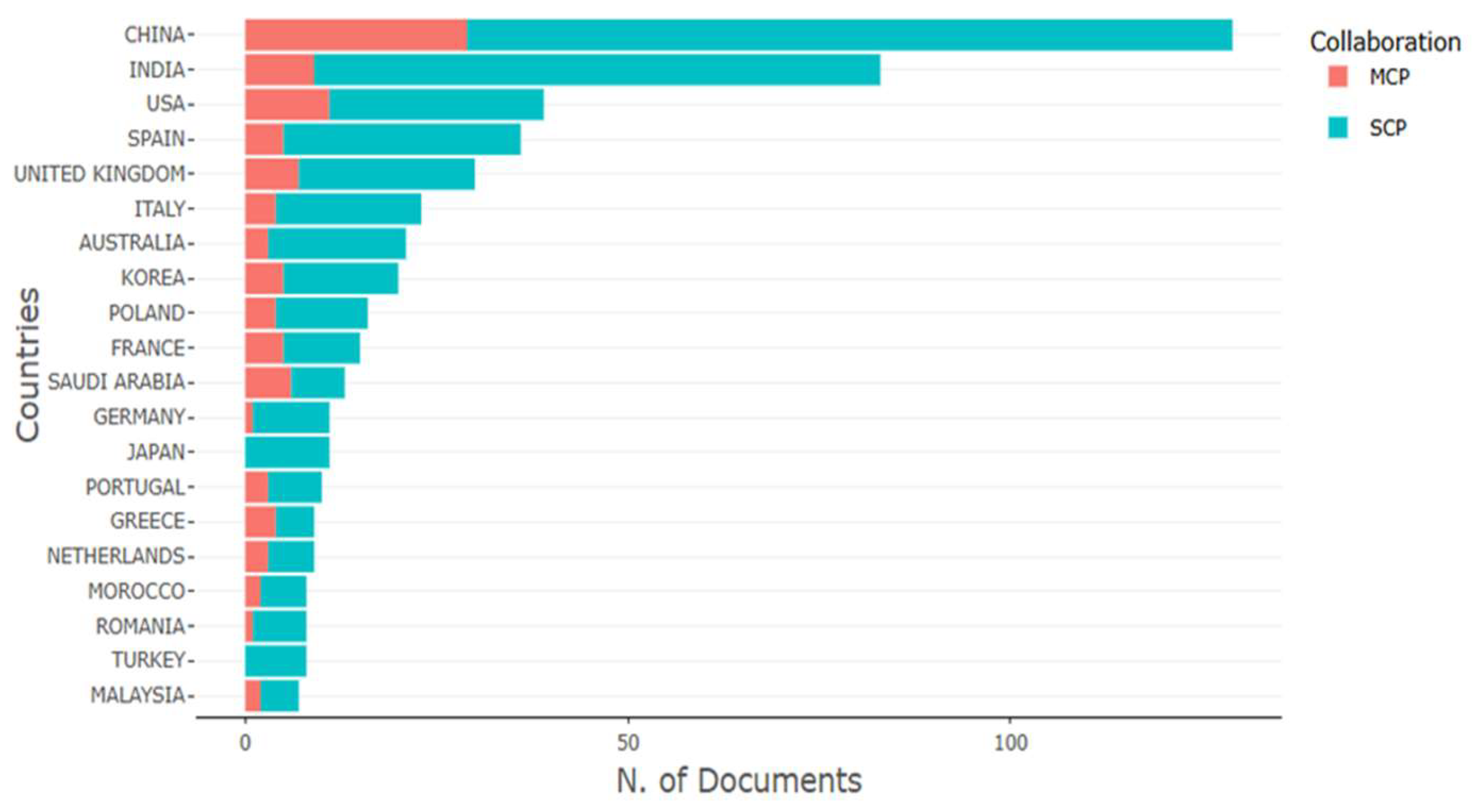
3.1.3. Countries with the Highest Scientific Production
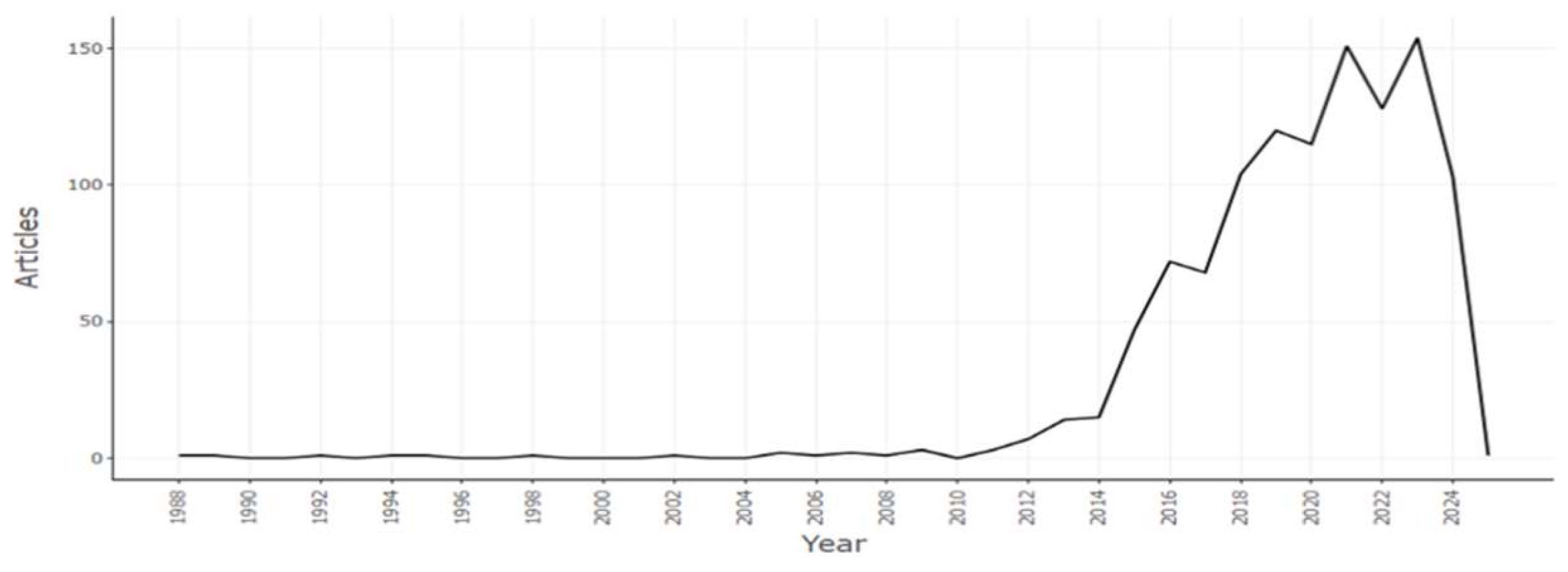
3.1.4. Annual Scientific Production
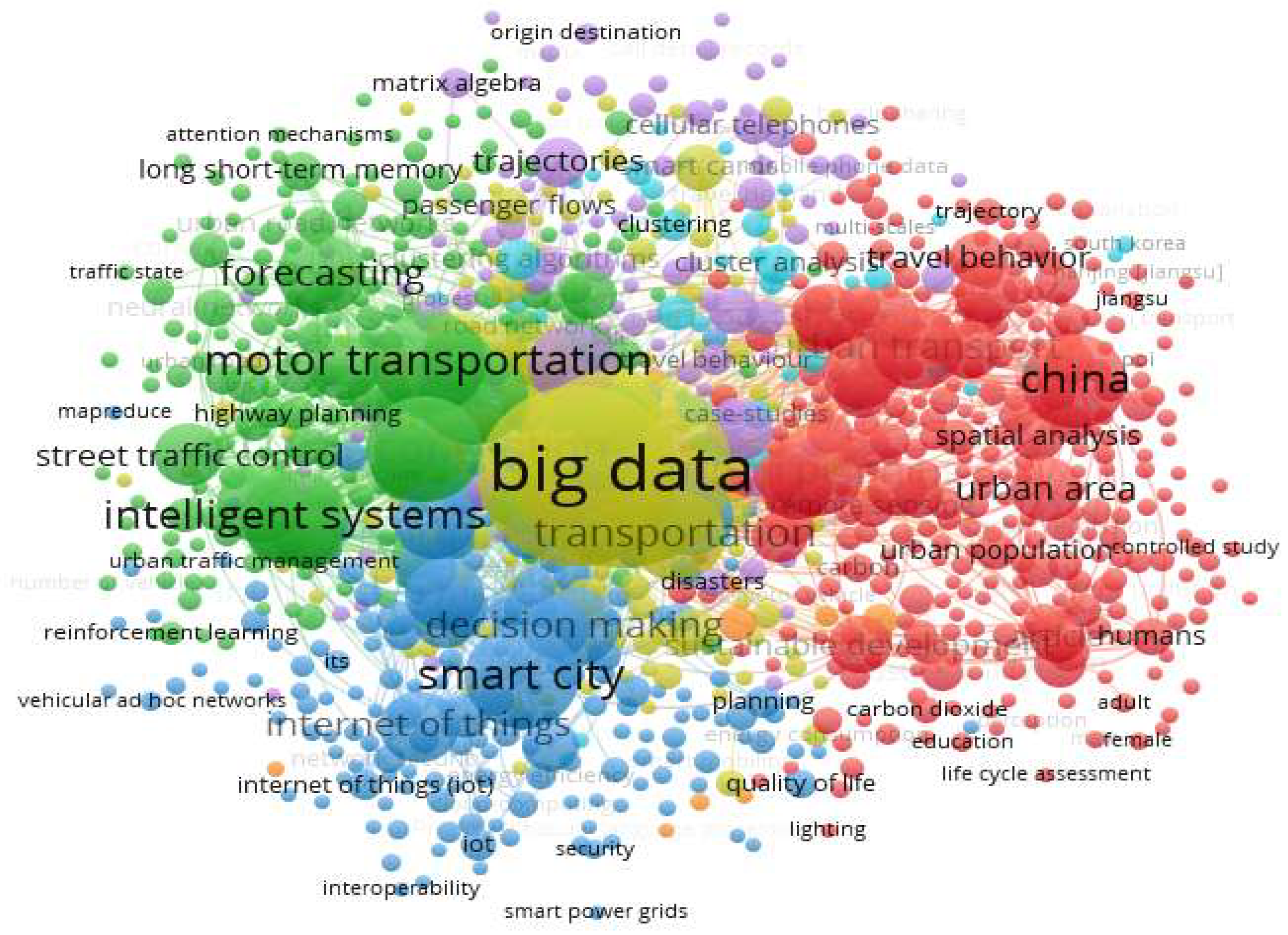
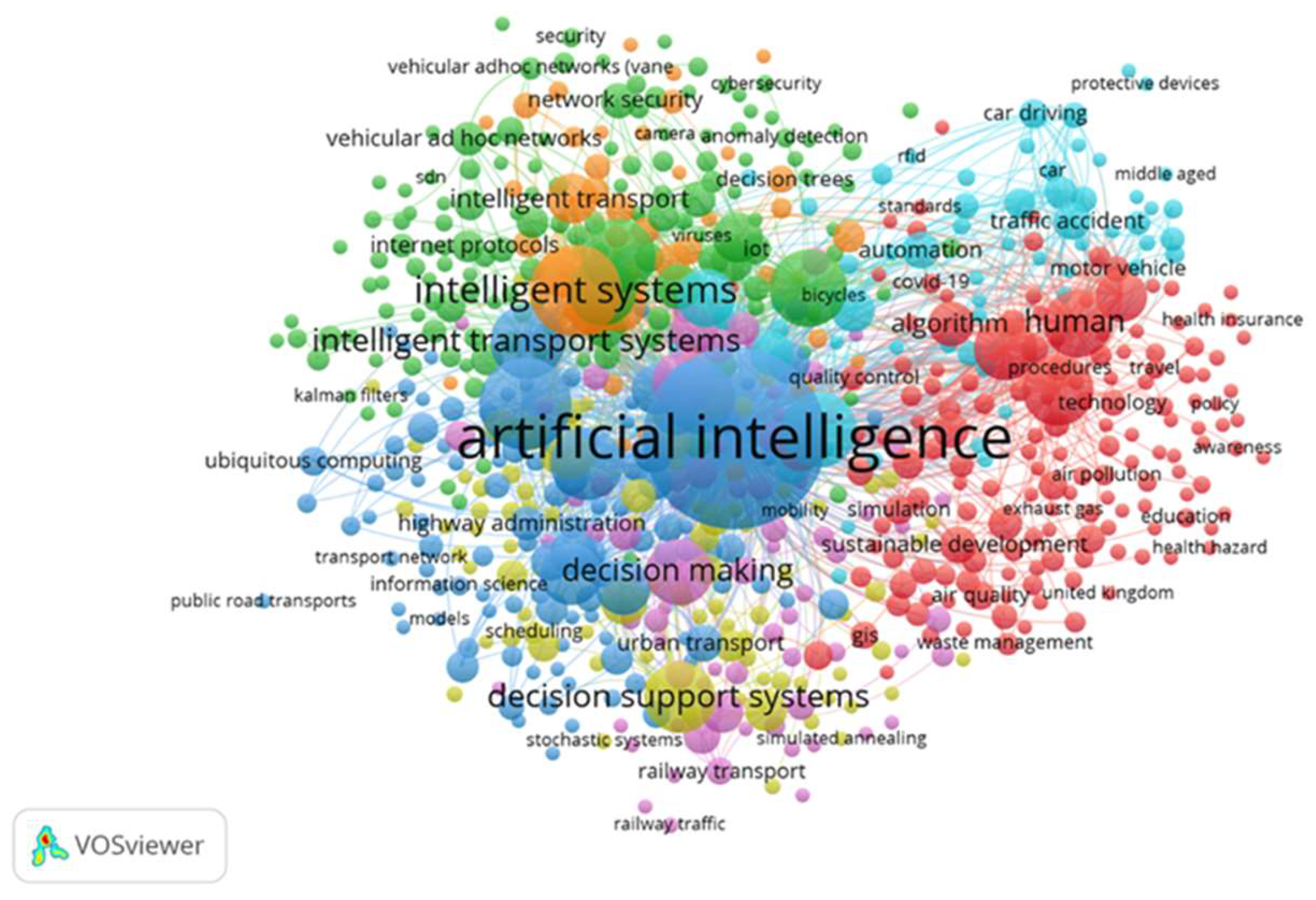
3.1.5. Keyword Analysis

3.2. Part 2: Traffic Management Systems Based on Artificial Intelligence
3.2.1. General Information
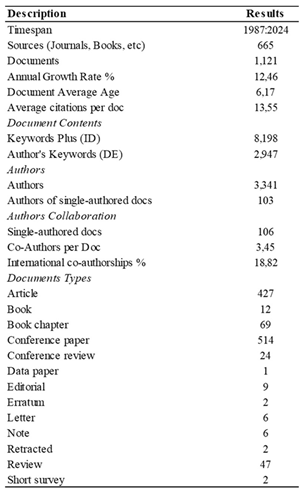
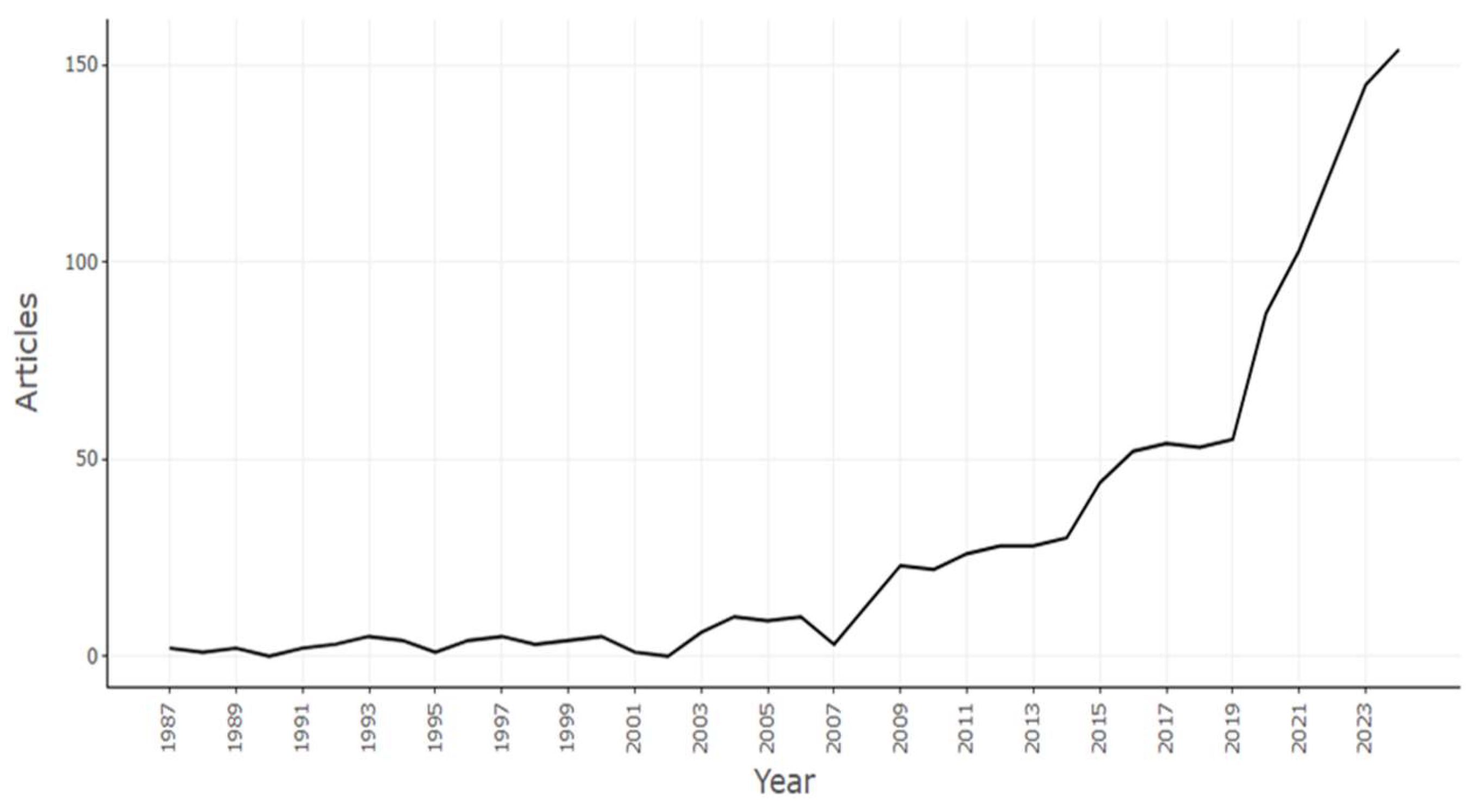
3.2.2. Annual Scientific Publications
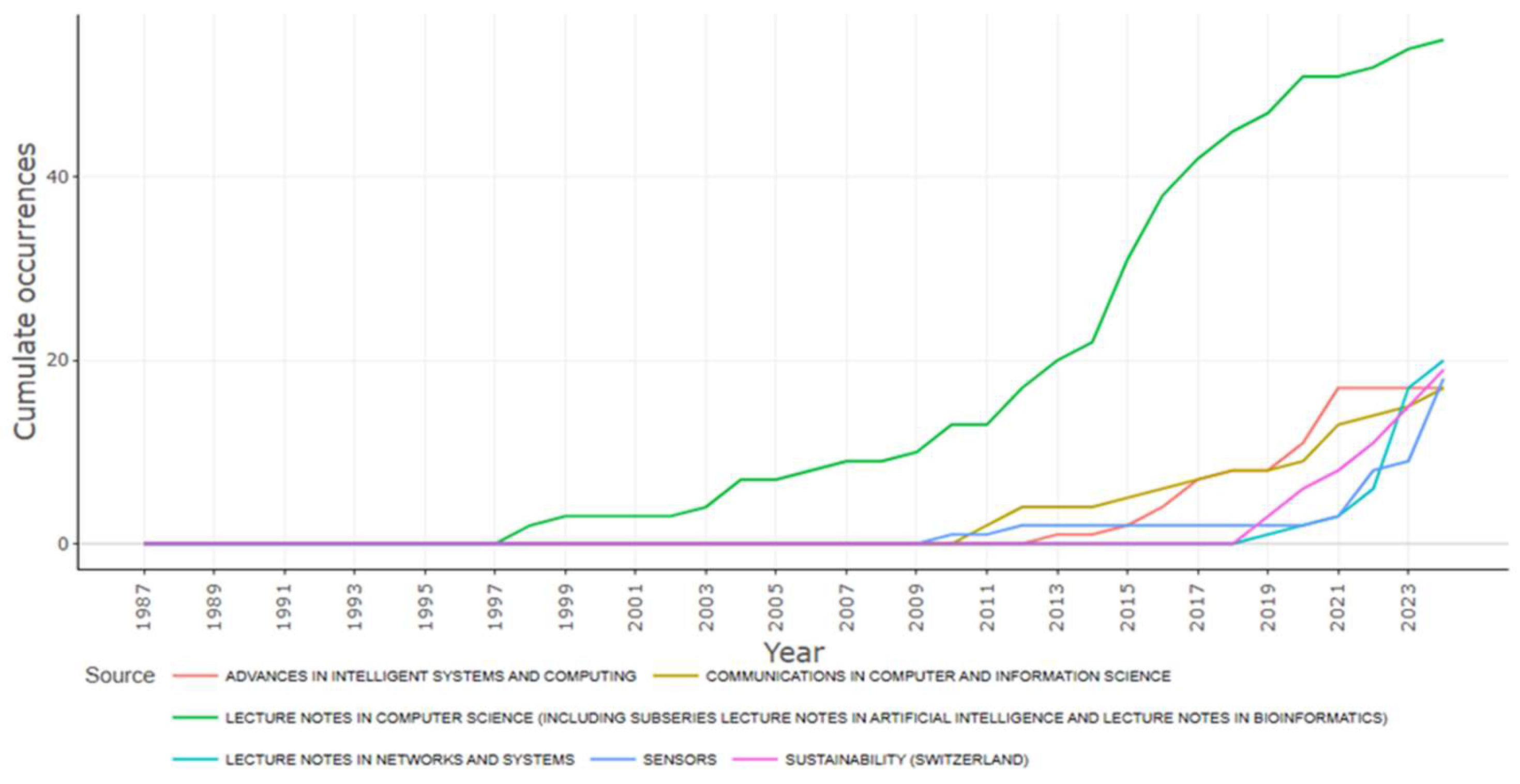
3.2.3. Main Sources of Publication
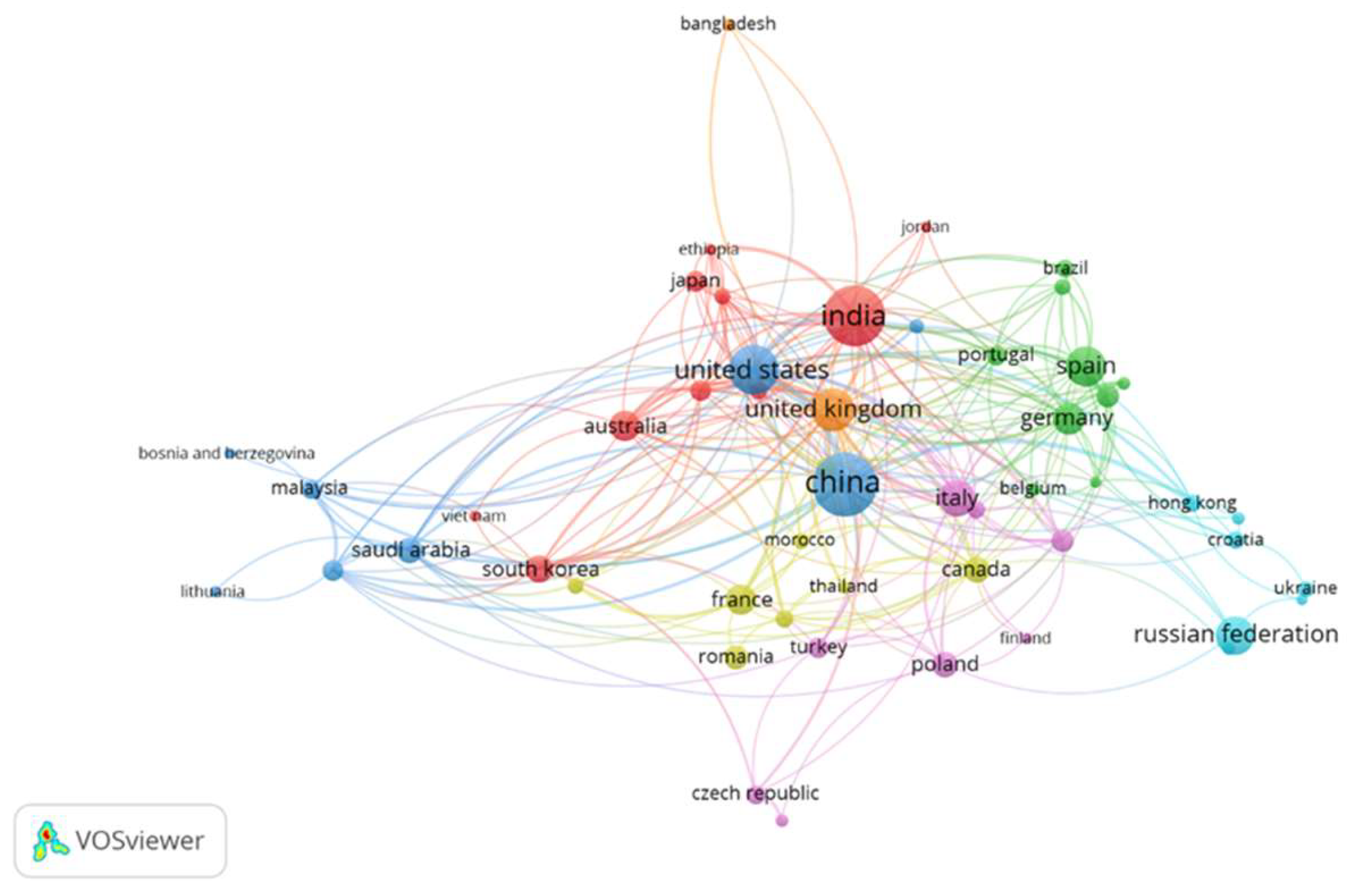
3.2.4. Countries with the Highest Publication and Scientific Production
3.2.5. Main Countries to Which the Authors Belong
3.2.6. Authors with the Greatest Relevance and Publications
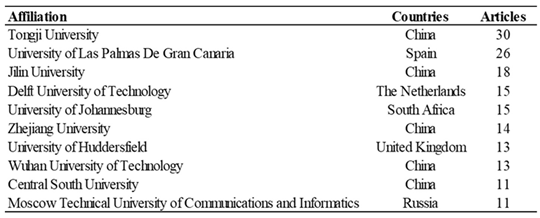
3.2.7. Most Relevant Affiliations and Institutions
3.2.8. Most Relevant Topics
3.2.9. Co-Occurrence of Keywords
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Salazar-Cabrera, R.; Pachón de la Cruz, Á.; Madrid Molina, J.M. Sustainable Transit Vehicle Tracking Service, Using Intelligent Transportation System Services and Emerging Communication Technologies: A Review. J. Traffic Transp. Eng. 2020, 7, 729–747. [CrossRef]
- Jaramillo-Alcazar, A.; Govea, J.; Villegas-Ch, W. Advances in the Optimization of Vehicular Traffic in Smart Cities: Integration of Blockchain and Computer Vision for Sustainable Mobility. Sustainability 2023, 15, 15736. [CrossRef]
- Rocha Filho, G.P.; Meneguette, R.I.; Torres Neto, J.R.; Valejo, A.; Weigang, L.; Ueyama, J.; Pessin, G.; Villas, L.A. Enhancing Intelligence in Traffic Management Systems to Aid in Vehicle Traffic Congestion Problems in Smart Cities. Ad Hoc Netw. 2020, 107, 1–10. [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Retuerta, D.; Chamoso, P.; Hernández, G.; Guzmán, A.S.R.; Yigitcanlar, T.; Corchado, J.M. An Efficient Management Platform for Developing Smart Cities: Solution for Real-Time and Future Crowd Detection. Electronics 2021, 10, 2–15. [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, R.A.; Ferro, R.E.; Liberona, D. Government and Governance in Intelligent Cities, Smart Transportation Study Case in Bogotá Colombia. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2020, 11, 25–34. [CrossRef]
- Guillen- Perez, A.; Cano, M. Intelligent IoT Systems for Traffic Management: A Practical Application. IET Intell. Transp. Syst. 2021, 15, 273–285. [CrossRef]
- Paiva, S.; Ahad, M.A.; Tripathi, G.; Feroz, N.; Casalino, G. Enabling Technologies for Urban Smart Mobility: Recent Trends, Opportunities and Challenges. Sensors 2021, 21, 1–41. [CrossRef]
- Ketter, W.; Schroer, K.; Valogianni, K. Information Systems Research for Smart Sustainable Mobility: A Framework and Call for Action. Inf. Syst. Res. 2023, 34, 1045–1065. [CrossRef]
- Maldonado Silveira Alonso Munhoz, P.A.; da Costa Dias, F.; Kowal Chinelli, C.; Azevedo Guedes, A.L.; Neves dos Santos, J.A.; da Silveira e Silva, W.; Pereira Soares, C.A. Smart Mobility: The Main Drivers for Increasing the Intelligence of Urban Mobility. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1–25. [CrossRef]
- Grover, P.; Kar, A.K. Big Data Analytics: A Review on Theoretical Contributions and Tools Used in Literature. Glob. J. Flex. Syst. Manag. 2017, 18, 203–229. [CrossRef]
- Lavalle, A.; Teruel, M.A.; Maté, A.; Trujillo, J. Improving Sustainability of Smart Cities through Visualization Techniques for Big Data from IoT Devices. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1–17. [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, F.; Nery, D.; Costa, D.G.; Silva, I.; Lima, L. A Survey of Technologies and Recent Developments for Sustainable Smart Cycling. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1–28. [CrossRef]
- Čolaković, A.; Memić, B.; Karahodža, B.; Goran, N. Improvement of Urban Mobility Supported with IoT Technologies.; National and University Library Of Bosnia and Herzegovina: Sarajevo, May 26 2024; pp. 99–105.
- Zou, L.; Wang, Z.; Guo, R. Real-Time Prediction of Transit Origin–Destination Flows during Underground Incidents. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2024, 163, 1–24. [CrossRef]
- Del Valle, M.; La Rosa, X.; Silvera, M.; Campos, F.; Silvera, M.; Palacios-Alonso, D. Vehicular Conflict Assessment on a Road with Lane Reduction Using the SSAM Methodology.; Buenos Aires, July 19 2023; pp. 2–6.
- Díaz-Casco, M.A.; Carvajal-Gámez, B.E.; Gutiérrez-Frías, O.; Osorio-Zúñiga, F.S. Comprehensive—Model Based on Time Series for the Generation of Traffic Knowledge for Bus Transit Rapid Line 6 of México City. Electronics 2022, 11, 1–28. [CrossRef]
- Gomes, B.; Coelho, J.; Aidos, H. A Survey on Traffic Flow Prediction and Classification. Intell. Syst. Appl. 2023, 20, 1–13. [CrossRef]
- Jyothi, E.V.N.; Srinivasa Rao, G.; Sharada, M.; Anusha, C.; Macherla, H.; Bhavsingh, M.; Addepalli, L. A Graph Neural Network-Based Traffic Flow Prediction System with Enhanced Accuracy and Urban Efficiency. J. Electr. Syst. 2023, 19, 336–349. [CrossRef]
- Medina-Salgado, B.; Sánchez-DelaCruz, E.; Pozos-Parra, P.; Sierra, J.E. Urban Traffic Flow Prediction Techniques: A Review. Sustain. Comput. Inform. Syst. 2022, 35, 1–16. [CrossRef]
- Mena-Oreja, J.; Gozalvez, J. On the Impact of Floating Car Data and Data Fusion on the Prediction of the Traffic Density, Flow and Speed Using an Error Recurrent Convolutional Neural Network. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 133710–133724. [CrossRef]
- Navarro-Espinoza, A.; López-Bonilla, O.R.; García-Guerrero, E.E.; Tlelo-Cuautle, E.; López-Mancilla, D.; Hernández-Mejía, C.; Inzunza-González, E. Traffic Flow Prediction for Smart Traffic Lights Using Machine Learning Algorithms. Technologies 2022, 10, 1–11. [CrossRef]
- Zeynivand, A.; Javadpour, A.; Bolouki, S.; Sangaiah, A.K.; Ja’fari, F.; Pinto, P.; Zhang, W. Traffic Flow Control Using Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2022, 207, 1–12. [CrossRef]
- Zißner, P.; Rettore, P.H.L.; Santos, B.P.; Loevenich, J.F.; Lopes, R.R.F. DataFITS: A Heterogeneous Data Fusion Framework for Traffic and Incident Prediction. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2023, 24, 11466–11478. [CrossRef]
- Samaniego-Calle, V.; Viñán-Ludeña, M.S.; Jaramillo Sangurima, W.E.; Jácome Galarza, L.; Sinche-Freire, J. Smart Traffic Lights and Vehicular Traffic: A Comparative Case Study to Reduce Traffic Jams and Polluting Emissions. RISTI - Rev. Iber. Sist. E Tecnol. Inf. 2019, 403–414.
- Noaeen, M.; Naik, A.; Goodman, L.; Crebo, J.; Abrar, T.; Abad, Z.S.H.; Bazzan, A.L.C.; Far, B. Reinforcement Learning in Urban Network Traffic Signal Control: A Systematic Literature Review. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 199, 1–32. [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Acebo, H.; Otxoa-Muñoz, X.; Marquina-Llaguno, M.; Gonzalo-Orden, H. Evaluation of the Efficiency of Traffic Lights Turning Red in Case of Exceeding Speed Limit with Previous Panels Indicating the Speed. Transp. Res. Procedia 2021, 58, 45–52. [CrossRef]
- Chevance, G.; Nieuwenhuijsen, M.; Braga, K.; Clifton, K.; Hoadley, S.; Kaack, L.H.; Kaiser, S.K.; Lampkowski, M.; Lupu, I.; Radics, M.; et al. Data Gaps in Transport Behavior Are Bottleneck for Tracking Progress towards Healthy Sustainable Transport in European Cities. Environ. Res. Lett. 2024, 19, 1–5. [CrossRef]
- Attard, M.; Guzman, L.A.; Oviedo, D. Urban Space Distribution: The Case for a More Equitable Mobility System. Case Stud. Transp. Policy 2023, 14, 1–11. [CrossRef]
- Neves, F.; Finamore, A.C.; Henriques, R. Efficient Discovery of Emerging Patternsin Heterogeneous Spatiotemporal Data from Mobile Sensors.; Association for Computing Machinery: Darmstadt Alemania, December 7 2020; pp. 158–167.
- Nosratabadi, S.; Mosavi, A.; Keivani, R.; Ardabili, S.; Aram, F. State of the Art Survey of Deep Learning and Machine Learning Models for Smart Cities and Urban Sustainability. In Proceedings of the Engineering for Sustainable Future; Várkonyi-Kóczy, A.R., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2020; pp. 228–238.
- Yang, Z.; Xie, Z.; Hou, Z.; Ji, C.; Deng, Z.; Li, R.; Wu, X.; Zhao, L.; Ni, S. A Method of User Travel Mode Recognition Based on Convolutional Neural Network and Cell Phone Signaling Data. Electronics 2023, 12, 1–19. [CrossRef]
- Credit, K.; Arnao, Z. A Method to Derive Small Area Estimates of Linked Commuting Trips by Mode from Open Source LODES and ACS Data. Environ. Plan. B Urban Anal. City Sci. 2023, 50, 709–722. [CrossRef]
- Hadavi, S.; Rai, H.B.; Verlinde, S.; Huang, H.; Macharis, C.; Guns, T. Analyzing Passenger and Freight Vehicle Movements from Automatic-Number Plate Recognition Camera Data. Eur. Transp. Res. Rev. 2020, 12, 37. [CrossRef]
- Xia, D.; Ma, J.; Sharif Azadeh, Sh. Integrated Timetabling and Vehicle Scheduling of an Intermodal Urban Transit Network: A Distributionally Robust Optimization Approach. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2024, 162, 104610. [CrossRef]
- Šoštarić, M.; Vidović, K.; Jakovljević, M.; Lale, O. Data-Driven Methodology for Sustainable Urban Mobility Assessment and Improvement. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1–22. [CrossRef]
- Angel, A.; Cohen, A.; Nelson, T.; Plaut, P. Evaluating the Relationship between Walking and Street Characteristics Based on Big Data and Machine Learning Analysis. Cities 2024, 151, 1–13. [CrossRef]
- Baheti, P. The Beginner’s Guide to Deep Reinforcement Learning [2024] Available online: https://www.v7labs.com/blog/deep-reinforcement-learning-guide (accessed on 20 December 2024).
- Borges, F. de S.P.; Fonseca, A.P.; Garcia, R.C. Deep Reinforcement Learning Model to Mitigate Congestion in Real-Time Traffic Light Networks. Infrastructures 2021, 6, 1–22. [CrossRef]
- Schatzinger, S.; Lim, C.Y.R. Taxi of the Future: Big Data Analysis as a Framework for Future Urban Fleets in Smart Cities. In Smart and Sustainable Planning for Cities and Regions: Results of SSPCR 2015; Bisello, A., Vettorato, D., Stephens, R., Elisei, P., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2017; pp. 83–98 ISBN 978-3-319-44899-2.
- Pamuła, T.; Pamuła, W. Estimation of the Energy Consumption of Battery Electric Buses for Public Transport Networks Using Real-World Data and Deep Learning. Energies 2020, 13, 1–17. [CrossRef]
- Gkioka, G.; Dominguez, M.; Tympakianaki, A.; Mentzas, G. AI-Driven Real-Time Incident Detection for Intelligent Transportation Systems. In Emerging Cutting-Edge Developments in Intelligent Traffic and Transportation Systems; IOS Press, 2024; pp. 56–68.
- Sancha Llamosí, R.; Coll Aliaga, E.; Porres De La Haza, M.J.; Lerma Arce, V.; Lorenzo-Sáez, E. Analysis of Decarbonization Potential in Mobility Sector with High Spatial Resolution: Study Case of the Metropolitan Area of Valencia (Spain). Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 1–14. [CrossRef]
- Marina, H.; Soto, I.; Valerio, J.; Zamorano-Illanes, R.; Toledo-Mercado, E.; Wang, R. Automatic Traffic Light Detection Using AI for VLC. In Proceedings of the 2022 13th International Symposium on Communication Systems, Networks and Digital Signal Processing (CSNDSP); July 2022; pp. 446–451.
- Ribeiro, D.A.; Melgarejo, D.C.; Saadi, M.; Rosa, R.L.; Rodríguez, D.Z. A Novel Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient Model Applied to Intelligent Transportation System Security Problems in 5G and 6G Network Scenarios. Phys. Commun. 2023, 56, 101938. [CrossRef]
- Gomides, T.S.; De Grande, R.E.; Meneguette, R.I.; Souza, F.S.H. de; Guidoni, D.L. Predictive Congestion Control Based on Collaborative Information Sharing for Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks. Comput. Netw. 2022, 211, 108955. [CrossRef]
- Tomás, V.R.; García, L.A.; Alonso, A.L. An Agent-Based Platform to Evaluate V2X Routing Road Traffic Scenarios. Simul. Model. Pract. Theory 2023, 125, 102750. [CrossRef]
- Gallego-Madrid, J.; Sanchez-Iborra, R.; Ruiz, P.M.; Skarmeta, A.F. Machine Learning-Based Zero-Touch Network and Service Management: A Survey. Digit. Commun. Netw. 2022, 8, 105–123. [CrossRef]
- Zannat, K.E.; Laudan, J.; Choudhury, C.F.; Hess, S. Developing an Agent-Based Microsimulation for Predicting the Bus Rapid Transit (BRT) Demand in Developing Countries: A Case Study of Dhaka, Bangladesh. Transp. Policy 2024, 148, 92–106. [CrossRef]
- Yañez-Pagans, P.; Martinez, D.; Mitnik, O.A.; Scholl, L.; Vazquez, A. Urban Transport Systems in Latin America and the Caribbean: Lessons and Challenges. Lat. Am. Econ. Rev. 2019, 28, 15. [CrossRef]
- Vásquez-Garaya, J.P.; Munayco-Apolaya, E.; Ugarte, W. Carsharing System for Urban Transport in Lima Using Internet of Things.; December 20 2024; pp. 324–331.
- Nassar, V.; Vieira, M.L.H. O compartilhamento de informações no transporte público com as tecnologias RFID e NFC: uma proposta de aplicação. Urbe Rev. Bras. Gest. Urbana 2017, 9, 327–340. [CrossRef]
- Valencia, V.; Olaya, Y.; Arango-Aramburo, S. Is Switching Propulsion Technologies the Path to Sustainable Land Transport? Decarbonizing Bogotá. Transp. Res. Part Transp. Environ. 2023, 122, 1–14. [CrossRef]
- Calan, C.; Sobrino, N.; Vassallo, J.M. Understanding Life-Cycle Greenhouse-Gas Emissions of Shared Electric Micro-Mobility: A Systematic Review. Sustainability 2024, 16, 1–22. [CrossRef]
- Giret, A. Smart and Sustainable Urban Logistic Applications Aided by Intelligent Techniques. Serv. Oriented Comput. Appl. 2019, 13, 185–186. [CrossRef]
- Khurshid, A.; Khan, K.; Saleem, S.F.; Cifuentes-Faura, J.; Cantemir Calin, A. Driving towards a Sustainable Future: Transport Sector Innovation, Climate Change and Social Welfare. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 427, 1–14. [CrossRef]
- Rosero, F.; Fonseca, N.; Mera, Z.; López, J.-M. Assessing On-Road Emissions from Urban Buses in Different Traffic Congestion Scenarios by Integrating Real-World Driving, Traffic, and Emissions Data. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 863, 1–17. [CrossRef]
- Santos, A.; Maia, P.; Jacob, R.; Wei, H.; Callegari, C.; Oliveira Fiorini, A.C.; Schaeffer, R.; Szklo, A. Road Conditions and Driving Patterns on Fuel Usage: Lessons from an Emerging Economy. Energy 2024, 295, 130979. [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Hernández, J.A.; Gámez-García, D.C.; Saldaña-Márquez, H. Operational LCA of a Street with Active Mobility Strategies in Northern México. Transp. Res. Part Transp. Environ. 2024, 135, 1–21. [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, P.; Aragón-Jurado, J.M.; Seredynski, M.; Cabrera, J.F.; Peña, D.; de la Torre, J.C.; Zomaya, A.Y.; Dorronsoro, B. Optimal Battery Management Strategies for Plug-in Electric Hybrid Buses on Routes Including Green Corridors. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 94, 1–14. [CrossRef]
- Mateichyk, V.; Tsuman, M.; Weigang, G.; Kozodoy, D.; Sansyzbajeva, Z.; Grytsuk, Y. The Information and Analytical System for Monitoring Roadside Pollution by Traffic Flows. In Proceedings of the ICTE in Transportation and Logistics 2019; Ginters, E., Ruiz Estrada, M.A., Piera Eroles, M.A., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2020; pp. 352–359.
- Ali, M.; Kamal, M.D.; Tahir, A.; Atif, S. Fuel Consumption Monitoring through COPERT Model—A Case Study for Urban Sustainability. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1–12. [CrossRef]
- United Nations Population World Population Dashboard Available online: https://www.unfpa.org/en/data/world-population-dashboard (accessed on 20 December 2024).
- Lozzi, G.; Marcucci, E.; Gatta, V.; Rodrigues, M.; Teoh, T. Sustainable and Smart Urban Transport; Policy Department for Structural and Cohesion Policies: European Union, 2020;
- Burkov, A. The Hundred-Page Machine Learning Book; Andriy Burkov: Polen, 2019; ISBN 978-1-9995795-0-0.
- Torre-Bastida, A.I.; Del Ser, J.; Laña, I.; Ilardia, M.; Bilbao, M.N.; Campos-Cordobés, S. Big Data for Transportation and Mobility: Recent Advances, Trends and Challenges. IET Intell. Transp. Syst. 2018, 12, 742–755. [CrossRef]
- Grimaldi, D.; Fernandez, V. Performance of an Internet of Things Project in the Public Sector: The Case of Nice Smart City. J. High Technol. Manag. Res. 2019, 30, 27–39. [CrossRef]
- Gang, L.; Filipe, J.; Zhiwei, X. Communications in Computer and Information Science; Springer Nature, 2024;
- Aria, M.; Cuccurullo, C. Bibliometrix: An R-Tool for Comprehensive Science Mapping Analysis. J. Informetr. 2017, 11, 959–975. [CrossRef]
- Ellegaard, O.; Wallin, J.A. The Bibliometric Analysis of Scholarly Production: How Great Is the Impact? Scientometrics 2015, 105, 1809–1831. [CrossRef]
- Skute, I.; Zalewska-Kurek, K.; Hatak, I.; de Weerd-Nederhof, P. Mapping the Field: A Bibliometric Analysis of the Literature on University–Industry Collaborations. J. Technol. Transf. 2019, 44, 916–947. [CrossRef]
- Cobo, M.J.; López-Herrera, A.G.; Herrera-Viedma, E.; Herrera, F. Science Mapping Software Tools: Review, Analysis, and Cooperative Study among Tools. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2011, 62, 1382–1402. [CrossRef]
- Moral-Muñoz, J.A.; Herrera-Viedma, E.; Santisteban-Espejo, A.; Cobo, M.J. Software Tools for Conducting Bibliometric Analysis in Science: An up-to-Date Review. Prof. Inf. 2020, 29. [CrossRef]
- van Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L. Software Survey: VOSviewer, a Computer Program for Bibliometric Mapping. Scientometrics 2010, 84, 523–538. [CrossRef]
- Arencibia-Jorge, R.; Vega-Almeida, R.L.; Carrillo-Calvet, H. Evolución y alcance multidisciplinar de tres técnicas de análisis bibliométrico. Palabra Clave Plata 2020, 10, 1–16. [CrossRef]
- Galvez, C. Co-word analysis applied to highly cited articles in Library and Information Sciences. Transinformação 2018, 30, 277–286. [CrossRef]
- Ávila, K.I.C.; Iturralde, L.P.; Freire, E.L.M. Evolución de la Investigación Científica en América Latina. Recimundo 2018, 2, 464–476. [CrossRef]
- Abduljabbar, R.; Dia, H.; Liyanage, S.; Bagloee, S.A. Applications of Artificial Intelligence in Transport: An Overview. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1–24. [CrossRef]
- Ai, B.; Molisch, A.F.; Rupp, M.; Zhong, Z.-D. 5G Key Technologies for Smart Railways. Proc. IEEE 2020, 108, 856–893. [CrossRef]
- Mondejar, M.E.; Avtar, R.; Diaz, H.L.B.; Dubey, R.K.; Esteban, J.; Gómez-Morales, A.; Hallam, B.; Mbungu, N.T.; Okolo, C.C.; Prasad, K.A.; et al. Digitalization to Achieve Sustainable Development Goals: Steps towards a Smart Green Planet. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 794, 148539. [CrossRef]
- Nallaperuma, D.; Nawaratne, R.; Bandaragoda, T.; Adikari, A.; Nguyen, S.; Kempitiya, T.; De Silva, D.; Alahakoon, D.; Pothuhera, D. Online Incremental Machine Learning Platform for Big Data-Driven Smart Traffic Management. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2019, 20, 4679–4690. [CrossRef]
- Panagiotopoulos, I.; Dimitrakopoulos, G. An Empirical Investigation on Consumers’ Intentions towards Autonomous Driving. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2018, 95, 773–784. [CrossRef]
- Bonnefon, J.-F.; Shariff, A.; Rahwan, I. The Social Dilemma of Autonomous Vehicles. Science 2016, 352, 1573–1576. [CrossRef]
- Cath, C.; Wachter, S.; Mittelstadt, B.; Taddeo, M.; Floridi, L. Artificial Intelligence and the ‘Good Society’: The US, EU, and UK Approach. Sci. Eng. Ethics 2018, 24, 505–528. [CrossRef]



 |
| Country | TC | Average Article Citations |
|---|---|---|
| CHINA | 3541 | 16.10 |
| USA | 2657 | 30.20 |
| ITALY | 1071 | 17.00 |
| HONG KONG | 933 | 42.40 |
| AUSTRALIA | 752 | 32.70 |
| UNITED KINGDOM | 622 | 20.70 |
| SPAIN | 597 | 17.60 |
| BELGIUM | 592 | 65.80 |
| KOREA | 503 | 26.50 |
| JAPAN | 492 | 20.50 |
| Authors | Models and Systems | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| De Souza Pereira Borges et al., 2021; Del Valle et al., 2023; Díaz-Casco et al., 2022; Gallego -Madrid et al., 2022; Garcia -Retuerta et al., 2021; Gkioka et al., 2024; Gomes et al., 2023; Gonzalez et al., 2020; Jaramillo - Alcazar et al., 2023; Jyothi et al., 2023; Medina-Salgado et al., 2022; Mena-Oreja & Gozalvez , 2021; Navarro-Espinoza et al., 2022; Zeynivand et al., 2022; Zißner et al., 2023. | Predictive Models (Neural Networks) | For the proper application of these models, it is essential to have high quality data used; if there is incomplete data, there could be inaccurate predictions. Being highly complex models, such as neural networks, they can be difficult to interpret and adjust, limiting their practical use in environments that require rapid decision making. Some models would have difficulty scaling appropriately, due to the volume of data or the complexity of the system where the model is applied. Integration with existing systems and processes can be a limitation in implementation. |
| Samaniego-Calle et al., 2019. | Smart Traffic Lights | The current traffic light strategy does not improve congestion. Need for real-time data from sensors and cameras. Importance of justifying civil works before building. |
| From or Before et al., 2022; Noaeen et al., 2022; Pérez-Acebo et al., 2021 | Traffic Signal Control (Reinforcement Learning RL) | Obtaining high-quality real-world traffic data, including sensor data, traffic flow information, and pedestrian behavior, is difficult and expensive. Labeling large datasets for training RL models is time-consuming. Deploying hierarchical RL models is computationally expensive, especially for large-scale traffic networks. Training these models requires significant computational resources and time. In the real world, traffic conditions are highly dynamic and can change rapidly due to accidents and weather conditions, making it difficult for models to adapt to these. There is no generalization of a single RL model because traffic infrastructures vary across regions. |
| De Souza Pereira Borges et al., 2021; Gallego -Madrid et al., 2022; Garcia -Retuerta et al., 2021; Gkioka et al., 2024; Gonzalez et al., 2020; Navarro-Espinoza et al., 2022; Noaeen et al., 2022; Ordoñez et al., 2023; Zeynivand et al., 2022 | Artificial intelligence | Acquiring high-quality, real-world traffic data is expensive and time-consuming. Collecting personal data such as vehicle trajectories or pedestrian movements can raise privacy concerns. Models may have difficulty adapting to unforeseen events or changing traffic patterns if historical data is not complete. Real-time decision making can be hampered by the slow processing speed of some models. Ensuring the robustness of these models to avoid malfunctions is critical. Compatibility with existing systems can be complex and requires careful planning. Building confidence in the security of these models is important for their acceptance. |
| Gallego-Madrid et al., 2022; Gkioka et al., 2024; Marina et al., 2022; Medina-Salgado et al., 2022; Navarro-Espinoza et al., 2022 | Machine Learning | Obtaining quality data and labeled data can be challenging, especially for specific traffic scenarios or regions. Biased data can lead to underperforming models or making wrong decisions. Training complex models requires a lot of computing power and time. Models may exhibit unpredictable behavior, which could lead to safety risks. Real-time traffic management requires models to make fast predictions and decisions, which can be computationally intensive. |
| Gomides et al., 2022 ; Tomás et al., 2023 | V2V Communication between vehicles | Complexity of traffic behavior complicates assessments High message volume negatively impacts data communication load Difficult to estimate traffic conditions using only local information Efficient information exchange for decision making is a challenge Urbanisation increases traffic complexity and management demands Difficulty in achieving reproducible results in simulations |
| Jimenez -Moreno et al., 2022 | Fuzzy Inference Algorithm | Vehicle obstruction reduces confidence levels in ambulance detection. High vehicle flow complicates traffic light state management. Side views of ambulances affect the network’s learning accuracy. |
| Neves et al., 2020 | E2PAT | Multiple viewpoints need to be combined from heterogeneous data. Need for robust and timely pattern detection. Massive size of signal data from sensor networks. Ensuring actionability, interpretability and navigability of solutions. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





