Submitted:
29 November 2024
Posted:
02 December 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Bridge foundation settlement monitoring is crucial for infrastructure safety management, as uneven settlement can lead to stress redistribution, structural damage, and potentially catastrophic collapse. While traditional contact sensors provide reliable measurements, their deployment is labor-intensive and costly, especially for long-span bridges. Current remote sensing methods have not been thoroughly evaluated for their capability to detect and analyze complex foundation settlement patterns in challenging environments with multiple influencing factors. Here, we applied Small Baseline Subsets Synthetic Aperture Radar Interferometry (SBAS-InSAR) technology to monitor foundation settlement of a long-span bridge. Our analysis revealed distinct deformation patterns: uplift in the north bank approach bridge foundation and the left-side main bridge foundation (maximum rate: 36.965 mm/year), concurrent with subsidence in the right-side main bridge foundation and south bank approach bridge foundation (maximum rate: 35.585 mm/year). We then investigated the relationship between these settlement patterns and various environmental factors, including geological conditions, Sediment Transport Index (STI), Topographic Wetness Index (TWI), relative humidity, and temperature. The observed settlement patterns were attributed to the combined effects of stratigraphic heterogeneity, dynamic hydrological conditions, and seasonal climate variations. These findings demonstrate that SBAS-InSAR technology can effectively capture complex bridge foundation deformation processes, offering a cost-effective alternative to traditional monitoring methods. This advancement in bridge monitoring technology could enable more widespread and frequent assessment of bridge foundation stability, ultimately improving infrastructure safety management.

Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data
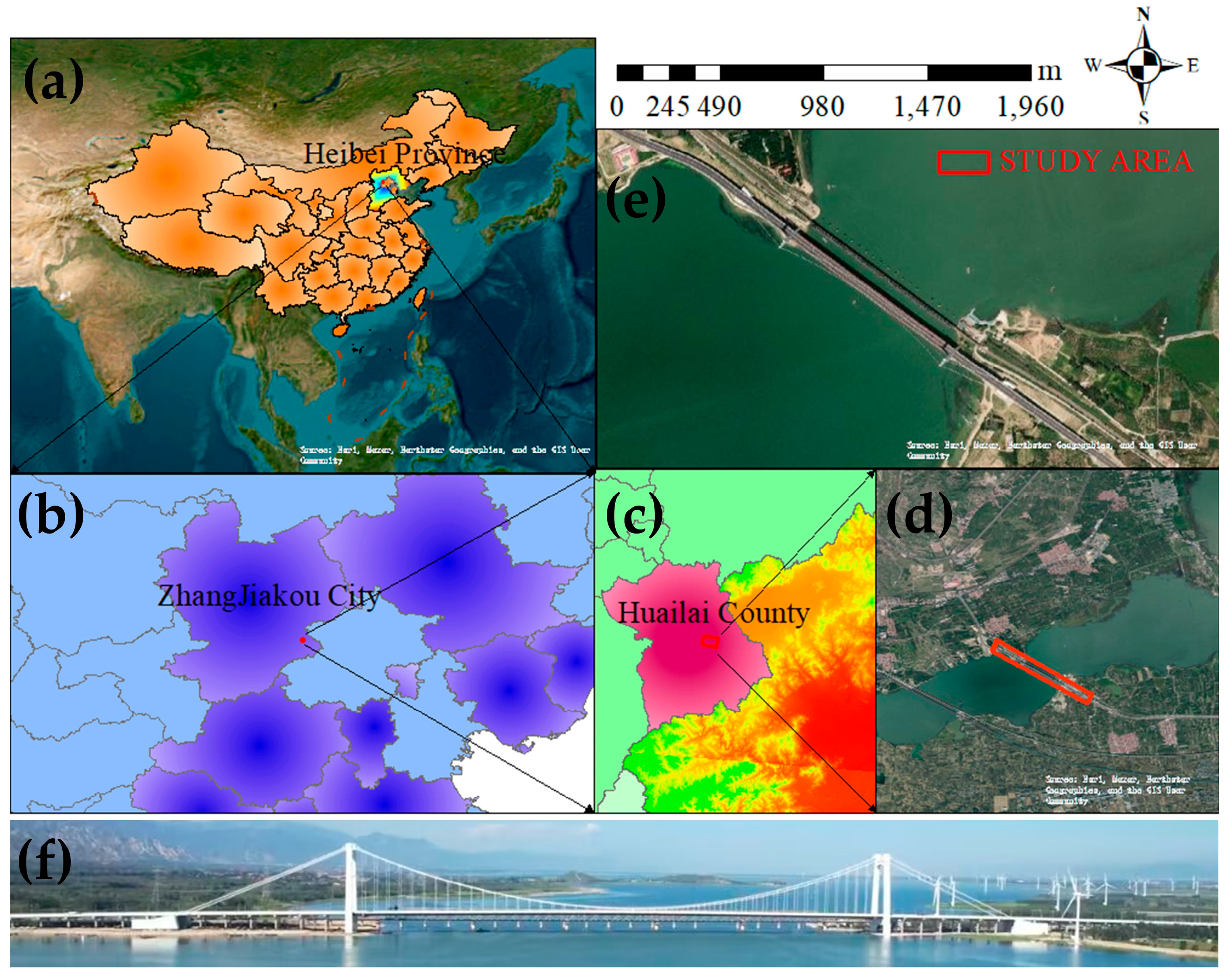
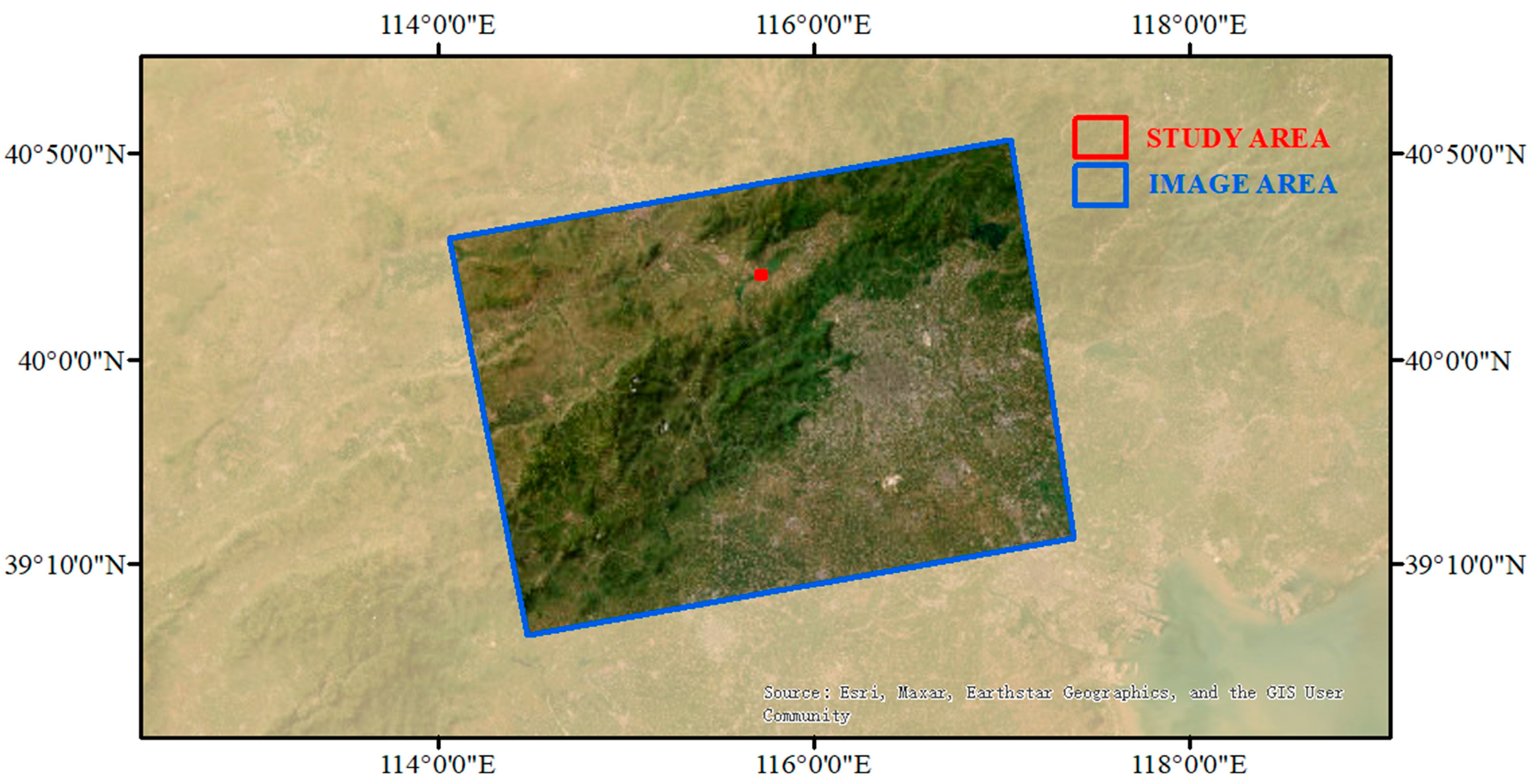
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sets
3. Methodology
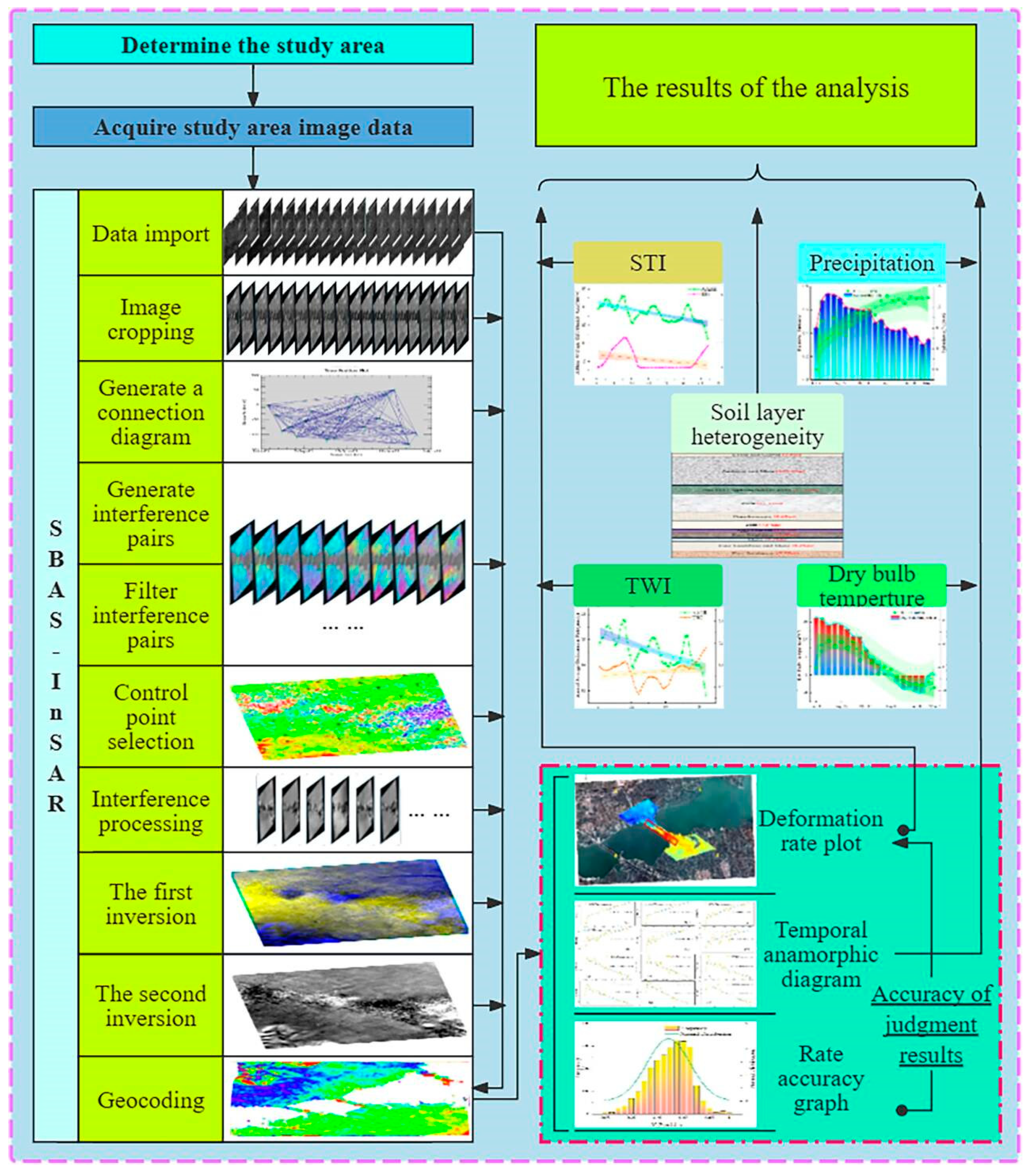
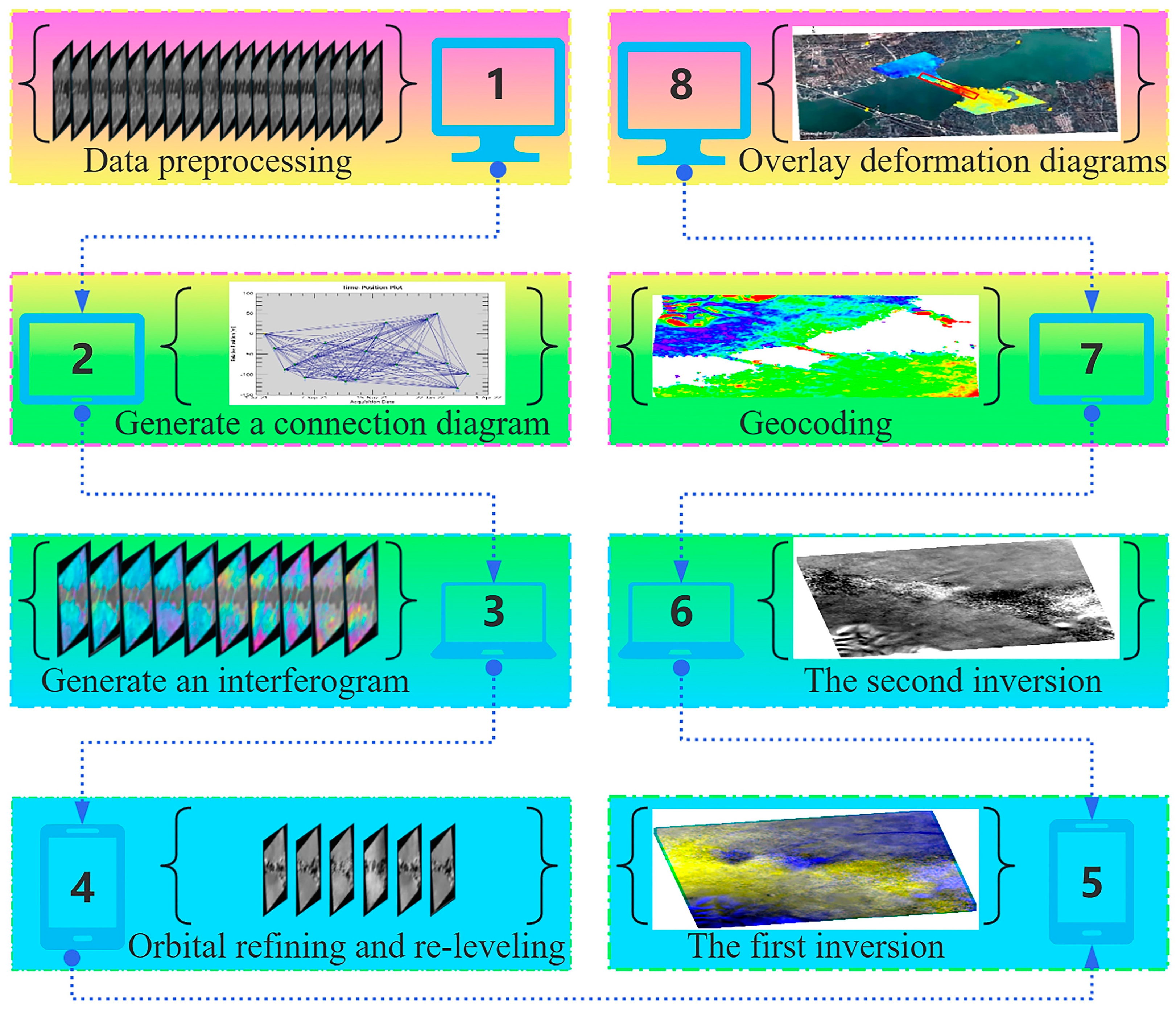
3.1. Principle of SBAS-InSAR
3.2. SBAS-InSAR Data Processing
3.3. The Topo-Hydrological Aspects
3.3.1. Topographic Wetness Index(TWI)
3.3.2. Sediment Transport Index(STI)
4. Result
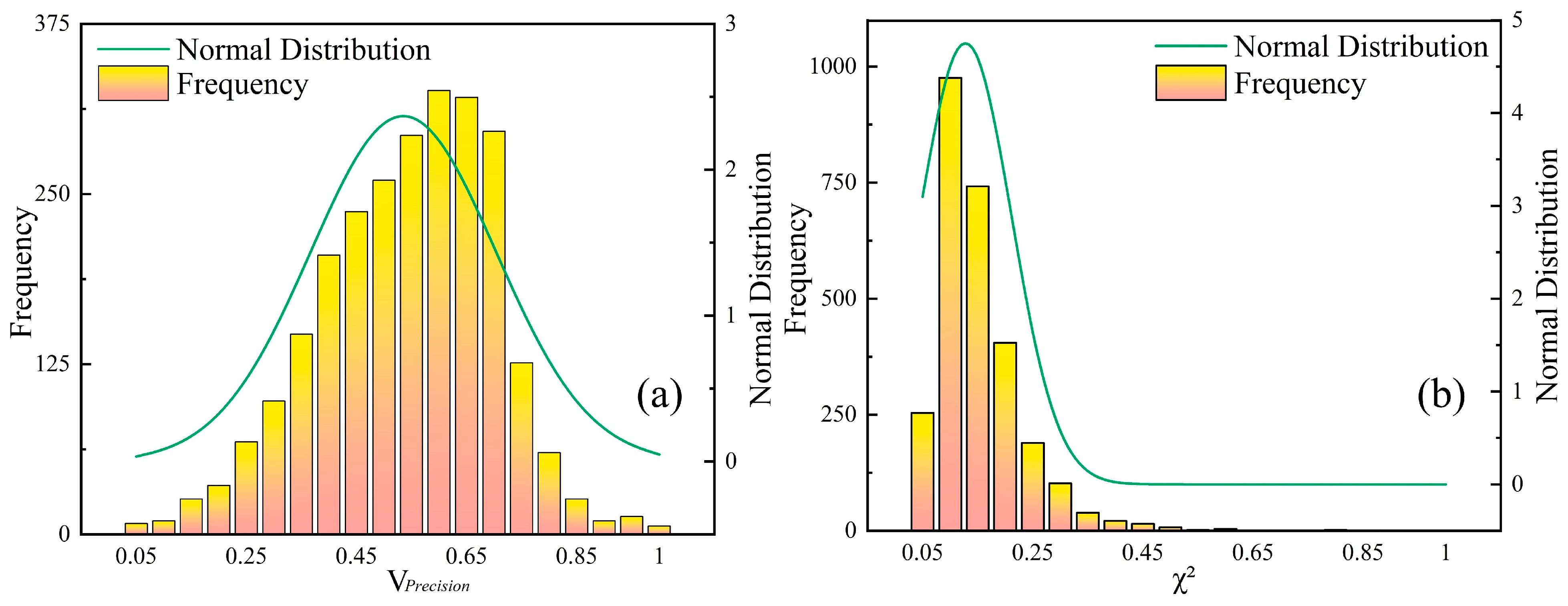
4.1. Accuracy Verification
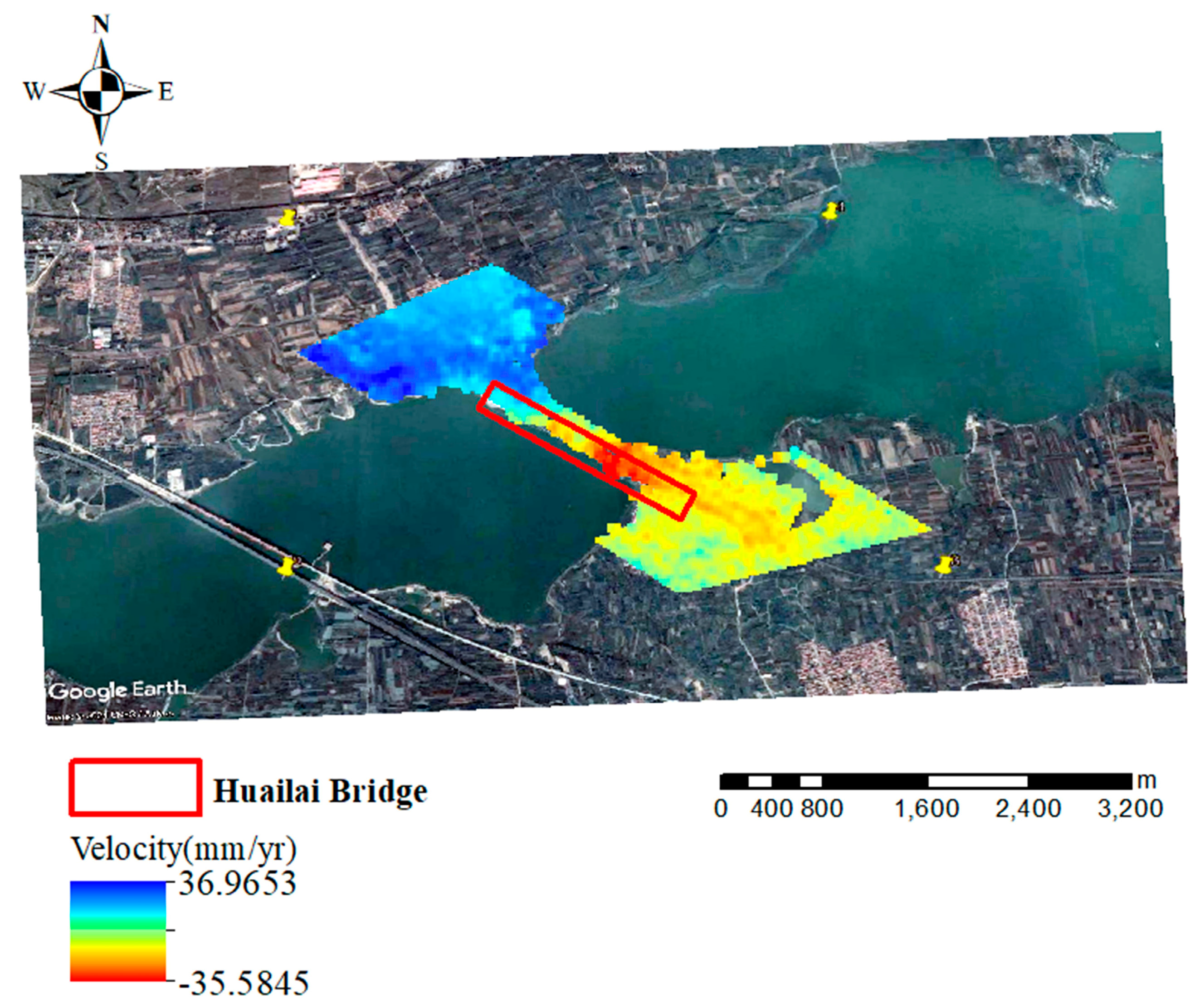
4.2. SBAS-InSAR Results
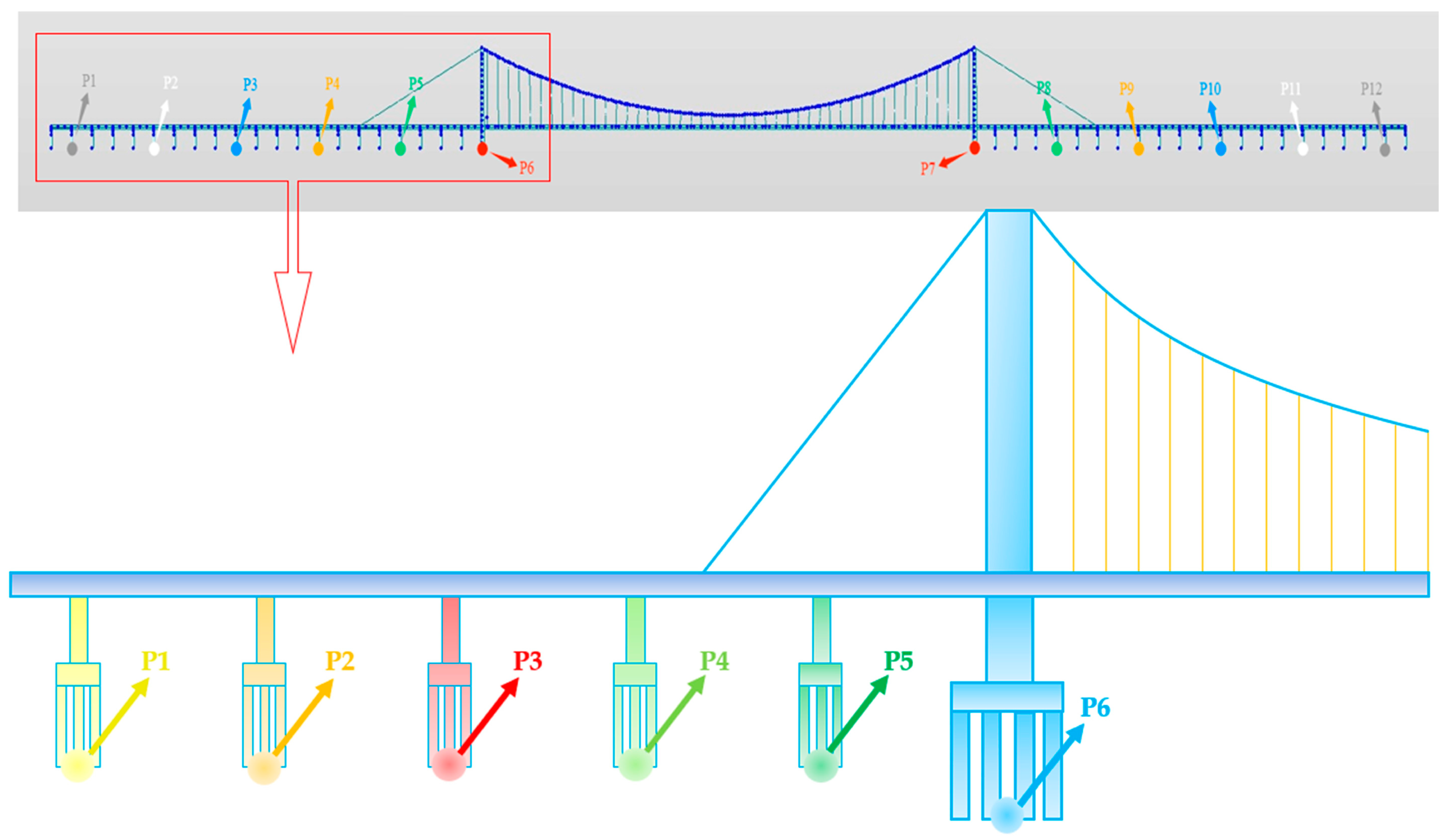
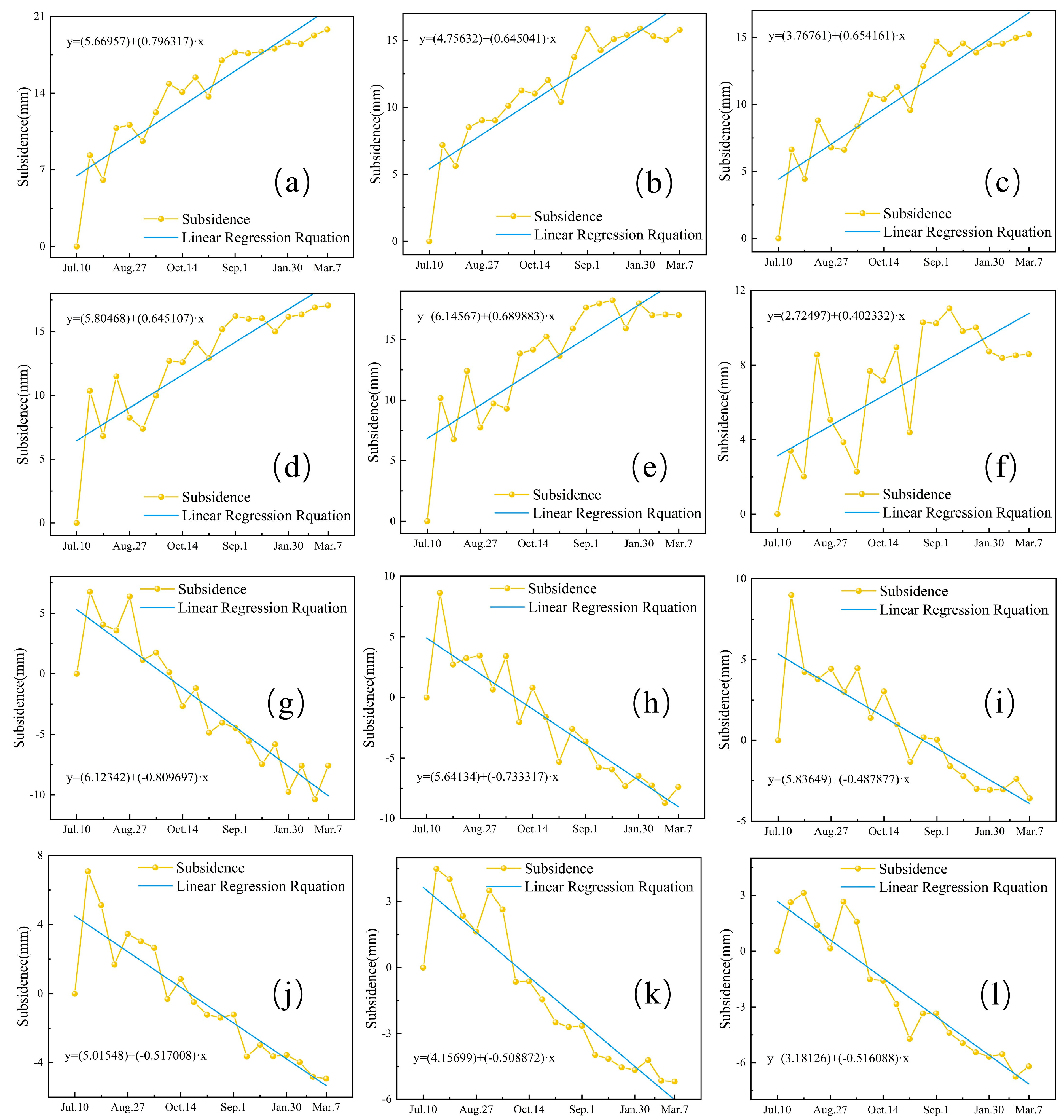
4.3. Time Series Cumulative Deformation
5. Discussion
5.1. Relationship Between Uneven Bridge Foundation Settlement and Soil Layer Heterogeneity
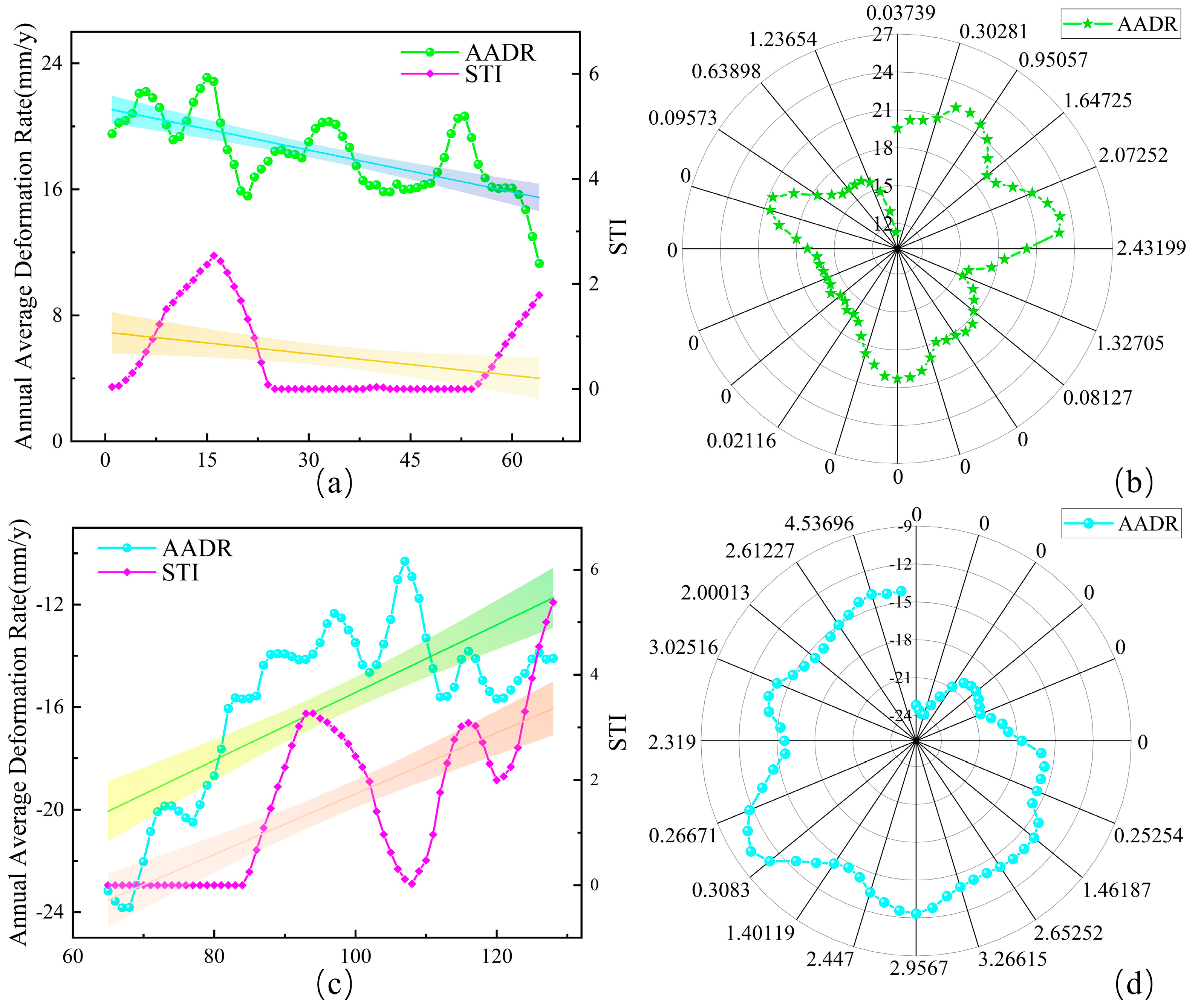
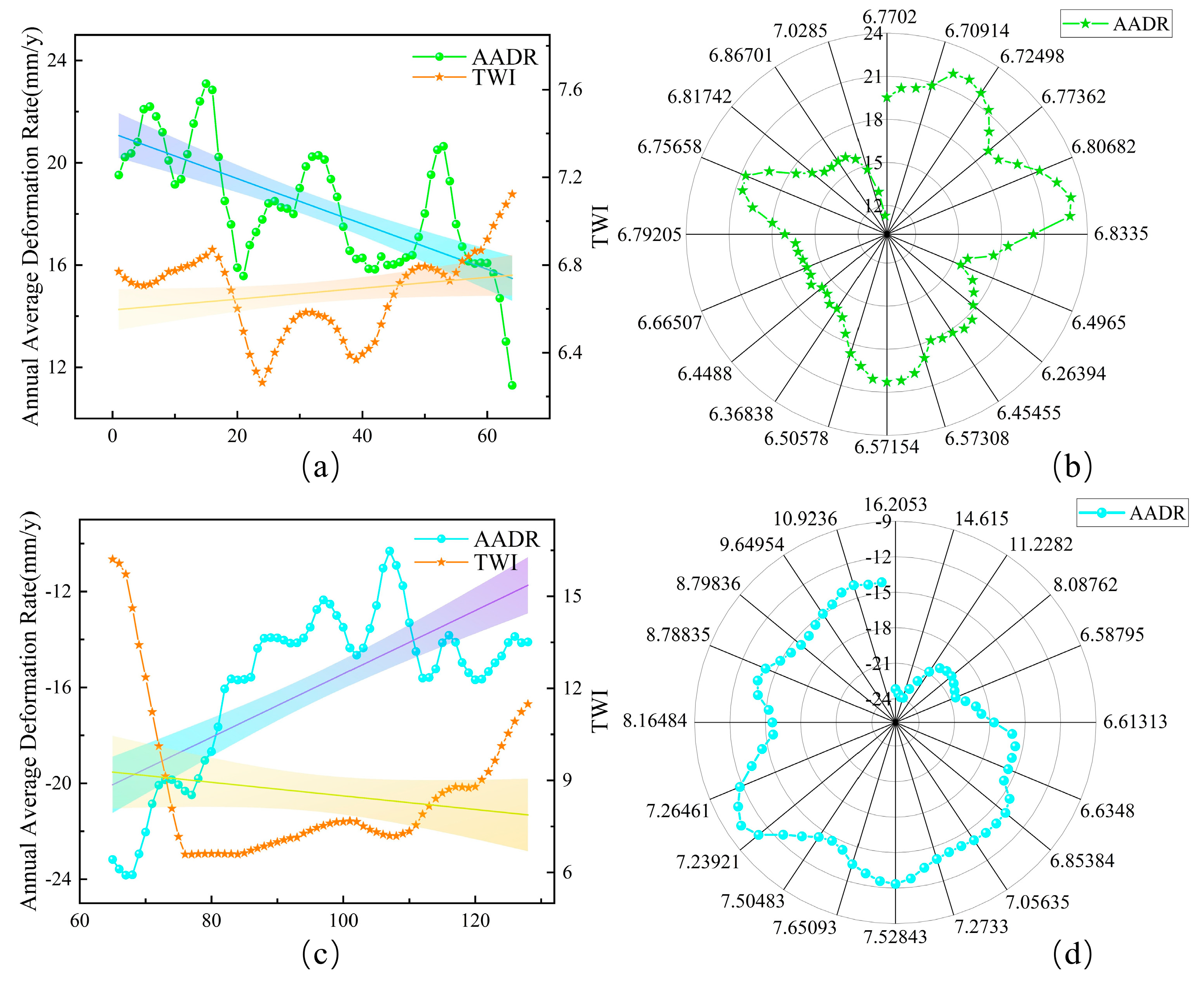
5.2. Relationship Between Uneven Bridge Foundation Settlement and STI
5.3. Relationship Between Uneven Bridge Foundation Settlement and TWI
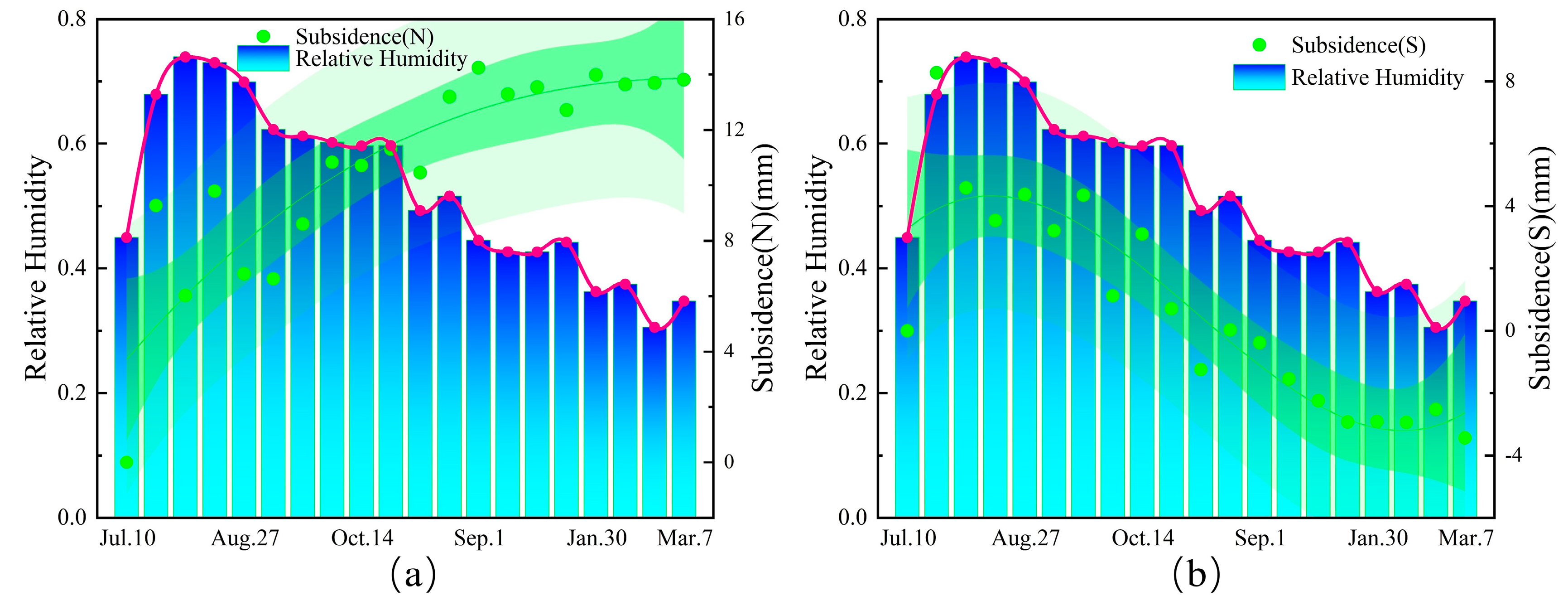
5.4. Relationship Between Uneven Bridge Foundation Settlement and Precipitation
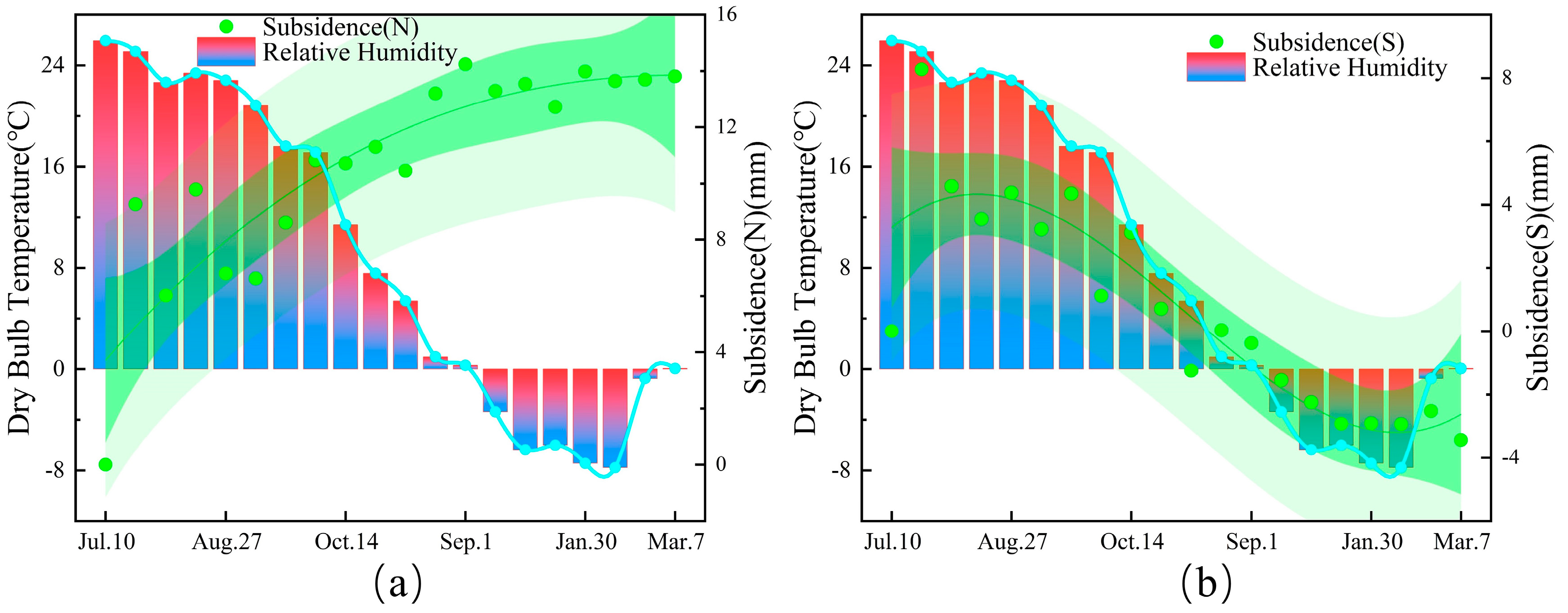
5.5. Relationship Between Uneven Bridge Foundation Settlement and Temperature
6. Conclusion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Z.; Leong, E. C.; Gong, W.; Dai, G.; Li, J. Foundation design of single-span arch bridges in China. Case Stud. Constr. Mater, 2023, 19: e02239. [CrossRef]
- Nolan, S.; Cadenazzi, T.; Rossini, M.; Nanni, A.; Knight, C.; Lasa, I. The 200-year bridge substructure: Resilience and sustainability. IABSE Congress: The Evolving Metropolis, New York, NY, USA, 4-6 September 2019.
- Ostenfeld, K. H. Evolution of bridge foundations for constructability, economy, substainability and safety. IABSE, 1999: 7-12.
- Hu, X.; Assaad, R. H.; Hussein, M. Discovering key factors and causalities impacting bridge pile resistance using Ensemble Bayesian networks: A bridge infrastructure asset management system. Expert Syst. Appl, 2024, 238: 121677. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Xiong, W.; Ma, X.; Cai, C. S. Fragility Evaluation of Bridge Pile Foundation Considering Scour Development under Floods. J. Bridge Eng, 2024, 29(8): 04024052. [CrossRef]
- Reumers, P.; Lombaert, G.; Degrande, G. The effect of foundation–soil–foundation interaction on the response of continuous, multi-span railway bridges. Eng. Struct, 2024, 299: 117096.
- Li, R.; He, Q.; Zhu, S.; Yan, J.; Zhai, W. A new methodology for pre-camber design of a long-span bridge considering dynamic train load and complex environmental effects. Eng. Struct, 2024, 302: 117349. [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Elgamal, A.; Lu, J. Seismic response of the Eureka Channel bridge-foundation system. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng, 2022, 152: 107015. [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Wang, D. J.; Peng, N. Numerical analysis of influencing factors of uneven settlement in abutment foundation. Adv Mat Res, 2012, 422: 864-868. [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Zheng, G.; Cui, G. Settlement deformation characteristics and control of soft soil through groundwater discharge zone. DESALIN WATER TREAT, 2021, 241: 282-287. [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Yang, X.; Zhang, S.; Kong, X.; Chen, W. Analysis of Deformation Characteristics of Long-Short Pile Composite Foundation in Salt Lake Area, Iran. Advances in Civil Engineering, 2019, 2019(1): 5976540. [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; He, X.; Wu, C.; Wu, W. Long-term monitoring and analysis of the longitudinal differential settlement of an expressway bridge–subgrade transition section in a loess area. Sci. Rep., 2022, 12(1): 19327. [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Hou, Y.; Jiang, L; Zhou, W.; Li, H; Yu, J. Failure mode of interlayer connection of longitudinally-connected ballastless track-bridge system under uneven pier settlement. Constr Build Mater., 2022, 351: 128805. [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Chen, A.; Shi, L.; Cai, Y. Iterative method for predicting uneven bridge approach settlement (BAS) caused by vehicle loads. MATH PROBL ENG, 2020, 2020(1): 8476746. [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Gong, H.; Chen, B.; Gao, M.; Zhou, C.; Guo, L. Understanding the influence of building loads on surface settlement: A case study in the central business district of Beijing combining multi-source data. Remote Sens., 2021, 13(16): 3063. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhou, H.; Wang, L. Settlement mode analysis for an immersed tube tunnel considering a nonuniform foundation under tidal load. China Ocean Eng, 2022, 36(3): 427-438. [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Ma, L. Research on Common Diseases and Construction Treatment Technologies in Road and Bridge Engineering. AJST, 2024, 10(3): 42-45. [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Li, J.; Liu, J.; Hu, Z.; Tang, C. Influence of Complex Hydraulic Environments on the Mechanical Properties of Pile-Soil Composite Foundation in the Coastal Soft Soil Area of Zhuhai. BUILDINGS-BASEL, 2023, 13(2): 563. [CrossRef]
- Wang, L. H.; Sun, G. Z.; Xu, J. B.; Wu, X.; Hou, X. M.; Han, Z. M. Study on Arching Mechanism of Bridge Pile Foundation: Taking the Shiyangtai No. 1 Bridge as an Example. BUILDINGS-BASEL, 2024, 14(1): 243. [CrossRef]
- Rakoczy, A. M.; Ribeiro, D.; Hoskere, V.; Narazaki, Y.; Olaszek, P.; Karwowski, W. Technologies and Platforms for Remote and Autonomous Bridge Inspection–Review. Struct. Eng. Int, 2024: 1-23. [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Ma, L. Research on Quality Inspection and Reinforcement Technology of Road Bridge. AJST, 2024, 10(2): 51-54. 5: 10(2). [CrossRef]
- Ozden, A.; Faghri, A.; Li, M.; Tabrizi, K. Evaluation of Synthetic Aperture Radar satellite remote sensing for pavement and infrastructure monitoring. Procedia Eng, 2016, 145: 752-759. [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, R.; Petryna, Y.; Lubitz, C.; Lang, O.; Wegener, V. Thermal deformation monitoring of a highway bridge: combined analysis of geodetic and satellite-based InSAR measurements with structural simulations. J. Civ. Struct. Health Monit., 2024, 14(5): 1237-1255. [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, A.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. Permanent scatterers in SAR interferometry. IEEE TRANS GEOSCI REMOTE SENS, 2001, 39(1): 8-20. [CrossRef]
- Hanssen, R. F. Satellite radar interferometry for deformation monitoring: a priori assessment of feasibility and accuracy. INT J APPL EARTH OBS, 2005, 6(3-4): 253-260. [CrossRef]
- Di Martino, G.; Esposito, M.; Festa, B.; Iodice, A.; Mancini, L. Poreh, D. Railway Bridge Monitoring with Sar: A Case Study. IEEE, 2018: 2952-2955. IGARSS 2018-2018 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Valencia, Spain, 22-27 July 2018.
- Cusson, D.; Stewart, H. Satellite Synthetic Aperture Radar, Multispectral, and Infrared Imagery for Assessing Bridge Deformation and Structural Health—A Case Study at the Samuel de Champlain Bridge. Remote Sens., 2024, 16(4): 614.
- Malinowska, D.; Milillo, P.; Briggs, K.; Reale, C.; Giardina, G. Coherence-Based Prediction of Multi-Temporal InSAR Measurement Availability for Infrastructure Monitoring. IEEE J Sel Top Appl Earth Obs Remote Sens, 2024, 16392. [CrossRef]
- Lazecky, M.; Perissin, D.; Bakon, M.; De Sousa, J. M.; Hlavacova, I.; Real, N. Potential of satellite InSAR techniques for monitoring of bridge deformations. 2015 Joint Urban Remote Sensing Event (JURSE), Lausanne, Switzerland, 30 March 2015 - 01 April 2015. [CrossRef]
- Selvakumaran, S.; Rossi, C.; Marinoni, A.; Webb, G.; Bennetts, J.; Barton, E. Combined InSAR and terrestrial structural monitoring of bridges. IEEE TRANS GEOSCI REMOTE SENS, 2020, 58(10): 7141-7153. [CrossRef]
- Nettis, A.; Massimi, V.; Nutricato, R.; Nitti, D. O.; Samarelli, S.; Uva, G. Satellite-based interferometry for monitoring structural deformations of bridge portfolios. AUTOMAT CONSTR, 2023, 147: 104707. [CrossRef]
- Matteo, D. S.; Roberto, T.; Javier, P. C.; Gerardo, H. G.; Juan Carlos, G. L. D.; Oscar, M. A multi-sensor approach for monitoring a road bridge in the Valencia harbor (SE Spain) by SAR Interferometry (InSAR). REND ONLINE SOC GEOL, 2016, 41: 235-238. 2: 41.
- Selvakumaran, S.; Rossi, C.; Marinoni, A.; Webb, G.; Bennetts, J. Barton, E. Combined InSAR and terrestrial structural monitoring of bridges. IEEE TRANS GEOSCI REMOTE SENS, 2020, 58(10): 7141-7153. [CrossRef]
- Macchiarulo, V.; Milillo, P.; Blenkinsopp, C.; Reale, C.; Giardina, G. Multi-temporal InSAR for transport infrastructure monitoring: recent trends and challenges. PROC INST CIV ENG-BR, 2021, 176(2): 92-117. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zhu, S.; Sun, W.; Huang, Z. Application of PS-InSAR technology in bridge settlement deformation monitoring. CN11-4527/TU,2023,41(7): 54-60.
- Wang, C.; Zhou, L.; Ma, J.; Shi, A.; Li, X.; Liu, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, D. GB-RAR deformation information estimation of high-speed railway bridge in consideration of the effects of colored noise. Appl. Sci, 2022, 12(20): 10504. [CrossRef]
- Selvakumaran, S.; Plank, S.; Geiß C.; Rossi, C.; Middleton, C. Remote monitoring to predict bridge scour failure using Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar (InSAR) stacking techniques. INT J APPL EARTH OBS, 2018, 73: 463-470. [CrossRef]
- Guzman-Acevedo, G. M.; Quintana-Rodriguez, J. A.; Gaxiola-Camacho, J. R.; Vazquez-Becerra, G. E.; Torres-Moreno, V.; Monjardin-Quevedo, J. G. The Structural Reliability of the Usumacinta Bridge Using InSAR Time Series of Semi-Static Displacements. Infrastructures, 2023, 8(12): 173. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Balz, T.; Cigna, F.; Tapete, D.; Li, J.; Han, Y. Multi-sensor InSAR time series fusion for long-term land subsidence monitoring. Geo Spat Inf Sci, 2023: 1-17 27(5), 1424–1440. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Peng, M.; Zhu, J. Application of Persistent Scatterer Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar in Bridge Settlement Monitoring. Road Machinery & Construction Mechanization,2019,36(07):115-120.
- Lasri, O.; Giordano, P. F.; Limongelli, M. P.; Previtali, M. Remote monitoring of a concrete bridge using PSInSAR. ce/papers, 2023, 6(5): 893-899. [CrossRef]
- Ma, P.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Au, F. T. K. SAR-Transformer-based decomposition and geophysical interpretation of InSAR time-series deformations for the Hong Kong-Zhuhai-Macao Bridge. Remote Sens. Environ, 2024, 302: 113962. [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Yan, S.; Zhao, F.; Chen, D.; Zhang, H. DS-InSAR based long-term deformation pattern analysis in the mining region with an improved phase optimization algorithm. Front. Environ. Sci., 2022, 10: 799946.
- Li, S.; Xu, W.; Li, Z. Review of the SBAS InSAR Time-series algorithms, applications, and challenges. Geod Geodyn, 2022, 13(2): 114-126. [CrossRef]
- Berardino, P.; Fornaro, G.; Lanari, R.; Sansosti, E. A new algorithm for surface deformation monitoring based on small baseline differential SAR interferograms. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens, 2002, 40(11): 2375-2383. [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Feng, Y.; Tong, X.; Li, P.; Wang, J.; Tang, P.; Tang, X.; Xi, M.; Zhou, Y. Large-Scale Surface Deformation Monitoring Using SBAS-InSAR and Intelligent Prediction in Typical Cities of Yangtze River Delta. Remote Sens. 2023, 15(20), 4942.
- Han, Z. Research on Surface Deformation Monitoring Using SBAS-InSAR: A Case Study of Zhujiang Bridge in Nansha District, Guangzhou. J. ACM. 2023: 1-6.
- Zhou, L.; Li, X.; Pan, Y.; Ma, J; Wang, W.; Shi, A; Chen, Y. Deformation monitoring of long-span railway bridges based on SBAS-InSAR technology. Geod Geodyn, 2024, 15(2): 122-132.
- The Provincial Highway S228 Langzhen Line Huailai Bridge officially opened to traffic today! Available online: https://www.thepaper.cn/newsDetail_forward_13344674(accessed on 6 October 2024).
- Yu, Z.; Zhang, G.; Huang, G.; Cheng, C.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, C. SSBAS-InSAR: A Spatially Constrained Small Baseline Subset InSAR Technique for Refined Time-Series Deformation Monitoring. Remote Sens., 2024, 16(18): 3515. [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Y.; Chen, B.; He, X.; Zhao, Z. An identification method of potential landslide zones using InSAR data and landslide susceptibility. GEOMAT NAT HAZ RISK, 2023, 14(1): 2185120. [CrossRef]
- Gaurav Singh, V.; Singh S. K. Analysis of geo-morphometric and topo-hydrological indices using COP-DEM: a case study of Betwa River Basin, Central India. Geol. ecol. landsc, 2024, 8(2): 101-128. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wu, X.; Chen, Q.; Skibniewski, M. J.; Hsu, S. C. Towards a safety management approach for adjacent buildings in tunneling environments: Case study in China. Build. Environ, 2014, 75: 222-235. [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, J. K.; Soga, K. Fundamentals of soil behavior, 3rd ed.; Wiley & Sons Ltd: Hoboken, New Jersey, USA, 2005; pp. 18–25. Available online: https://istasazeh-co.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/04/Fundamentals-Of-Soil-Behavior-K-Mitchel.pdf (accessed on 11 November 2024).
- Nujid, M. M.; Tholibon, D. A.; Mukhlisin, M. Geotechnical and structural assessment on estimated bearing capacity of strip footing resting on silty sand incorporating moisture content effect. Case Stud. Constr. Mater., 2024, 20: e03106. [CrossRef]
- Hosseinpour, I.; Almeida, M. S. S.; Riccio, M.; Baroni, M. Strength and compressibility characteristics of a soft clay subjected to ground treatment. Geotech. Geol. Eng., 2017, 35: 1051-1066. [CrossRef]
- Mrad, D.; Boukhari, S.; Dairi, S.; Djebbar, Y. Mapping the Potential for Erosion Gullies Using Frequency Ratio and Fuzzy Analytical Hierarchy Process: Case Study Medjerda Basin, Northeast Algeria. Eurasian Soil Sci, 2024: 1-17. [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, C.; Ren, J.; Li, H.; Wang, H.; Wu, F. Response of sediment transport capacity to soil properties and hydraulic parameters in the typical agricultural regions of the Loess Plateau. Sci. Total Environ., 2023, 879: 163090. [CrossRef]
- Hagiwara, T.; Aita, S.; Kazama, S. Impact of Filter Unit Placement on Suspended Sediment Deposition Promotion in Rivers. J Hydraul Eng, 2024, 150(6): 04024043. [CrossRef]
- Leopold, L. B.; Wolman, M. G.; Miller, J. P.; Wohl, E. E. Fluvial processes in geomorphology, 2nd ed. Courier Dover Publications, Mineola, New York, USA, 2020; pp. 284-304. Available online: https://books.google.com.hk/books?hl=en&lr=&id=vnb2DwAAQBAJ&oi=fnd&pg=PA3&dq=fluvial+processes+in+geomorphology+2020&ots=znSNXNoq7g&sig=ZdNWbUiZjlWVul7IjMyUtxOmpjw&redir_esc=y#v=onepage&q=fluvial%20processes%20in%20geomorphology%202020&f=false (accessed on 11 November 2024).
- Hesterah, H.; Plantak, M.; Gernhardt, D. Correlations Between Topographic Wetness Index and Soil Moisture in The Pannonian Region of Croatia. Geogr. Tech., 2024, 19(1). [CrossRef]
- Gaurav Singh, V.; Singh, S. K. Analysis of geo-morphometric and topo-hydrological indices using COP-DEM: a case study of Betwa River Basin, Central India. Geology, Geol. ecol. landsc, 2024, 8(2): 101-128. [CrossRef]
- Kluger, M. O.; Jorat, M. E.; Moon, V. G.; Kreiter, S.; De Lange, W. P.; Mörz, T.; Robertson, T.; Lowe, D. J. Rainfall threshold for initiating effective stress decrease and failure in weathered tephra slopes. Landslides, 2020, 17(2): 267-281. [CrossRef]
- Firoozi, A. A.; Firoozi, A. A. Water Erosion Processes: Mechanisms, Impact, and Management Strategies. Result Eng., 2024: 103237. [CrossRef]
- Jabbarzadeh, M.; Sadeghi, H.; Tourchi, S.; Darzi, A. G. Thermo-hydraulic analysis of desiccation cracked soil strata considering ground temperature and moisture dynamics under the influence of soil-atmosphere interactions. Geomech. Energy Environ, 2024, 38: 100558. [CrossRef]
- Richardson, C. M.; Davis, K. L.; Ruiz-González, C.; Guimond, J. A.; Michael, H. A.; Paldor, A.; Moosdorf, N.; Paytan, A. The impacts of climate change on coastal groundwater. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ., 2024, 5(2): 100-119. [CrossRef]
| Type | Website | Start Data | End Data |
| Sentinel-1A | https://search.asf.alaska.edu/ | 2021.07.10 | 2022.03.07 |
| Satellite POD | https://step.esa.int/auxdata | 2021.07.30 | 2022.03.27 |
| SRTM DEM | https://srtm.csi.cgiar.org/ | ||
| Geological Drilling Data | https://ndcp.cgsi.cn/ | ||
| Dry Bulb Temperture | https://www.theweatheronline.net/ | 2021.07.10 | 2022.03.07 |
| Relative Humidity | https://www.theweatheronline.net/ | 2021.07.10 | 2022.03.07 |
| Point Name | P1 | P2 | P3 | P4 | P5 | P6 | |
| Relative Humidity | Correlation | -0.860** | -0.805** | -0.805** | -0.842** | -0.800** | -0.513* |
| P(2-tailed) | 1.16E-06 | 1.9E-05 | 6.4E-06 | 3.22E-06 | 2.29E-05 | 0.02078 | |
| Point Name | P7 | P8 | P9 | P10 | P11 | P12 | |
| Relative Humidity | Correlation | 0.961** | 0.920** | 0.928** | 0.929** | 0.929** | 0.934** |
| P(2-tailed) | 1.76E-11 | 9.2E-09 | 3.88E-09 | 3.23E-09 | 3.23E-09 | 1.81E-09 | |
| **Significant correlation at the 0.01 level (2-tailed) | |||||||
| Point Name | P1 | P2 | P3 | P4 | P5 | P6 | |
| Dry Bulb Temperature | Correlation | -0.911** | -0.911** | -0.863** | -0.866** | -0.893** | -0.693** |
| P(2-tailed) | 2.34E-8 | 2.34E-8 | 9.62E-7 | 7.97E-7 | 1.16E-7 | 7.01E-4 | |
| Point Name | P7 | P8 | P9 | P10 | P11 | P12 | |
| Dry Bulb Temperature | Correlation | 0.908** | 0.869** | 0.827** | 0.866** | 0.881** | 0.866** |
| P(2-tailed) | 3.12E-8 | 6.57E-7 | 6.88E-6 | 7.97E-7 | 2.89E-7 | 7.97E-7 | |
| **Significant correlation at the 0.01 level (2-tailed) | |||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





