Submitted:
26 November 2024
Posted:
26 November 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. System-Field Interactions Model
3. Gravitional Decoherence Near the Black Hole Horizon
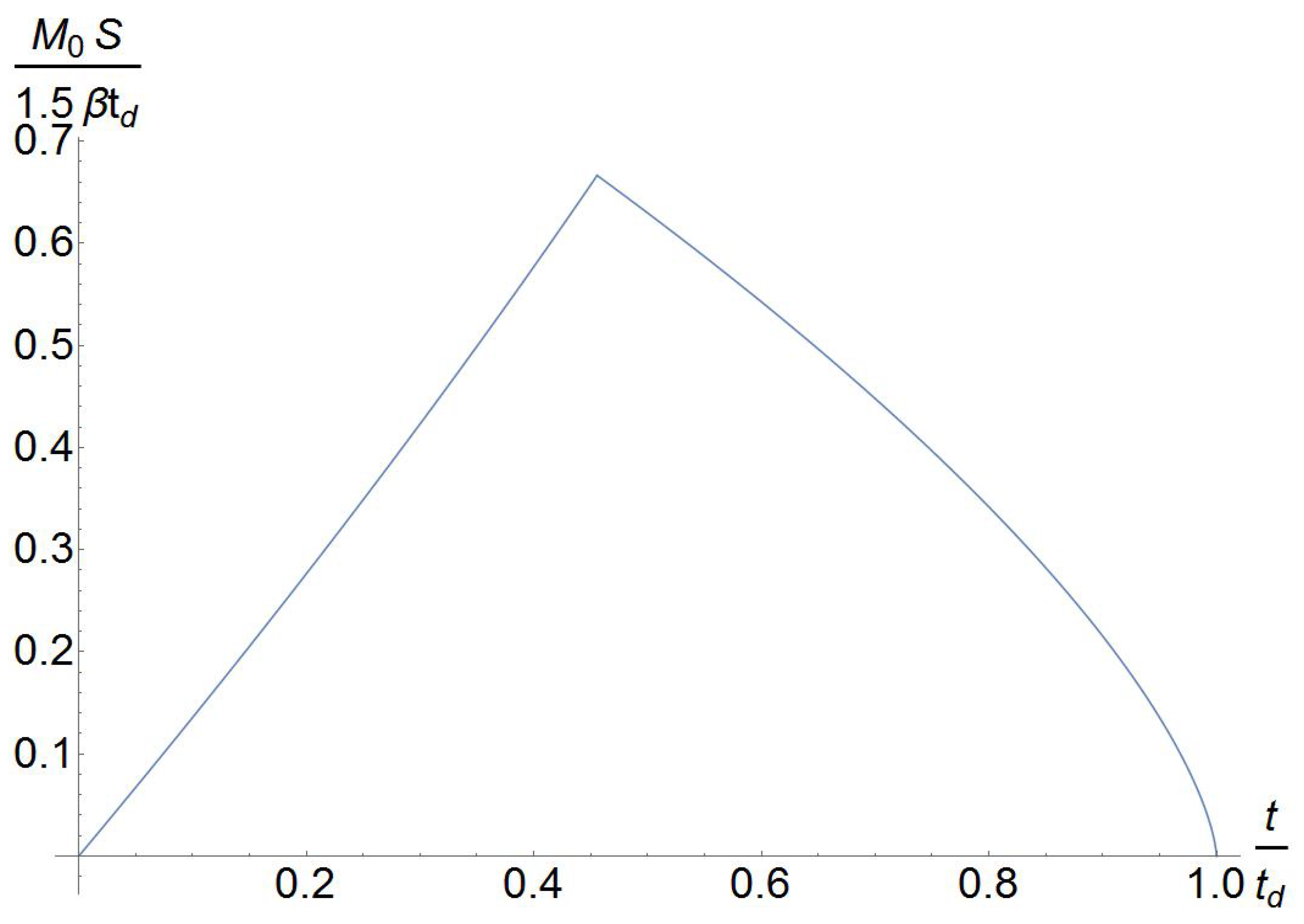
4. Non-Markovianity and Information Backflow
5. Discussion
References
- Zeh, H.D. On the interpretation of measurement in quantum theory. Foundations of Physics 1970, 1, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlosshauer, M. Quantum decoherence. Physics Reports 2019, 831, 1–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zurek, W.H. Decoherence, einselection, and the quantum origins of the classical. Reviews of modern physics 2003, 75, 715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlosshauer, M. Decoherence, the measurement problem, and interpretations of quantum mechanics. Reviews of Modern physics 2004, 76, 1267–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghirardi, G.C.; Rimini, A.; Weber, T. Unified dynamics for microscopic and macroscopic systems. Physical review D 1986, 34, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearle, P. Combining stochastic dynamical state-vector reduction with spontaneous localization. Physical Review A 1989, 39, 2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diósi, L. Models for universal reduction of macroscopic quantum fluctuations. Physical Review A 1989, 40, 1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penrose, R. On gravity’s role in quantum state reduction. General relativity and gravitation 1996, 28, 581–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penrose, R. Wavefunction collapse as a real gravitational effect. In Mathematical physics 2000; World Scientific, 2000; pp. 266–282. [Google Scholar]
- Penrose, R. On the gravitization of quantum mechanics 1: Quantum state reduction. Foundations of Physics 2014, 44, 557–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donadi, S.; Piscicchia, K.; Curceanu, C.; Diósi, L.; Laubenstein, M.; Bassi, A. Underground test of gravity-related wave function collapse. Nature Physics 2021, 17, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oppenheim, J. A postquantum theory of classical gravity? Physical Review X 2023, 13, 041040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambini, R.; Porto, R.A.; Pullin, J. Realistic clocks, universal decoherence, and the black hole information paradox. Physical review letters 2004, 93, 240401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milburn, G. Lorentz invariant intrinsic decoherence. New Journal of Physics 2006, 8, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonifacio, R. Time as a statistical variable and intrinsic decoherence. AIP Conference Proceedings. American Institute of Physics; 1999; 461, pp. 122–134. [Google Scholar]
- Anastopoulos, C.; Hu, B. Intrinsic and fundamental decoherence: issues and problems. Classical and Quantum Gravity 2008, 25, 154003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastopoulos, C.; Hu, B. A master equation for gravitational decoherence: probing the textures of spacetime. Classical and Quantum Gravity 2013, 30, 165007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiang, J.T.; Cho, H.T.; Hu, B.L. Graviton physics: Quantum field theory of gravitons, graviton noise and gravitational decoherence–a concise tutorial. arXiv preprint 2024, arXiv:2405.11790 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blencowe, M. Effective field theory approach to gravitationally induced decoherence. Physical review letters 2013, 111, 021302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.L.; Paz, J.P.; Zhang, Y. Quantum Brownian motion in a general environment: Exact master equation with nonlocal dissipation and colored noise. Physical Review D 1992, 45, 2843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Matacz, A. Quantum Brownian motion in a bath of parametric oscillators: A model for system-field interactions. Physical Review D 1994, 49, 6612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galve, F.; Zambrini, R.; Maniscalco, S. Non-markovianity hinders quantum darwinism. Scientific reports 2016, 6, 19607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pleasance, G.; Garraway, B.M. Application of quantum Darwinism to a structured environment. Physical Review A 2017, 96, 062105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciampini, M.A.; Pinna, G.; Mataloni, P.; Paternostro, M. Experimental signature of quantum Darwinism in photonic cluster states. Physical Review A 2018, 98, 020101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldeira, A.O.; Leggett, A.J. Path integral approach to quantum Brownian motion. Physica A: Statistical mechanics and its Applications 1983, 121, 587–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrasmith, A.; Albrecht, A.; Zurek, W.H. Decoherence of black hole superpositions by Hawking radiation. Nature communications 2019, 10, 1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landau, L.; Lifshitz, E.; Reichl, L. Statistical Physics, Part 1; Butterworth, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Page, D.N. Time dependence of Hawking radiation entropy. Journal of Cosmology and Astroparticle Physics 2013, 2013, 028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, D.N. Comment on" Entropy Evaporated by a Black Hole". Physical Review Letters 1983, 50, 1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, L.; Svaiter, N. Cosmological and black hole horizon fluctuations. Physical Review D 1997, 56, 2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruban, V. Spherically symmetric T-models in the general theory of relativity. General Relativity and Gravitation 2001, 33, 375–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glatthard, J. Page-curve-like entanglement dynamics in open quantum systems. Physical Review D 2024, 109, L081901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).



