Submitted:
05 January 2024
Posted:
08 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Review of evaluation studies on balanced regional development
3. Research methods and data sources
3.1. Construction of the evaluation index system
3.1.1. Construction of the evaluation index system for the population development subsystem
3.1.2. Construction of an evaluation index system for the economic development subsystem
3.1.3. Construction of an evaluation index system for social development subsystems
3.2. Construction of the coupled and coordinated development evaluation model
3.2.1. Determination of weights using the entropy weight method
3.2.2. Modeling the degree of coordination of coupled demographic-economic-social systems
3.3. Study area and data sources
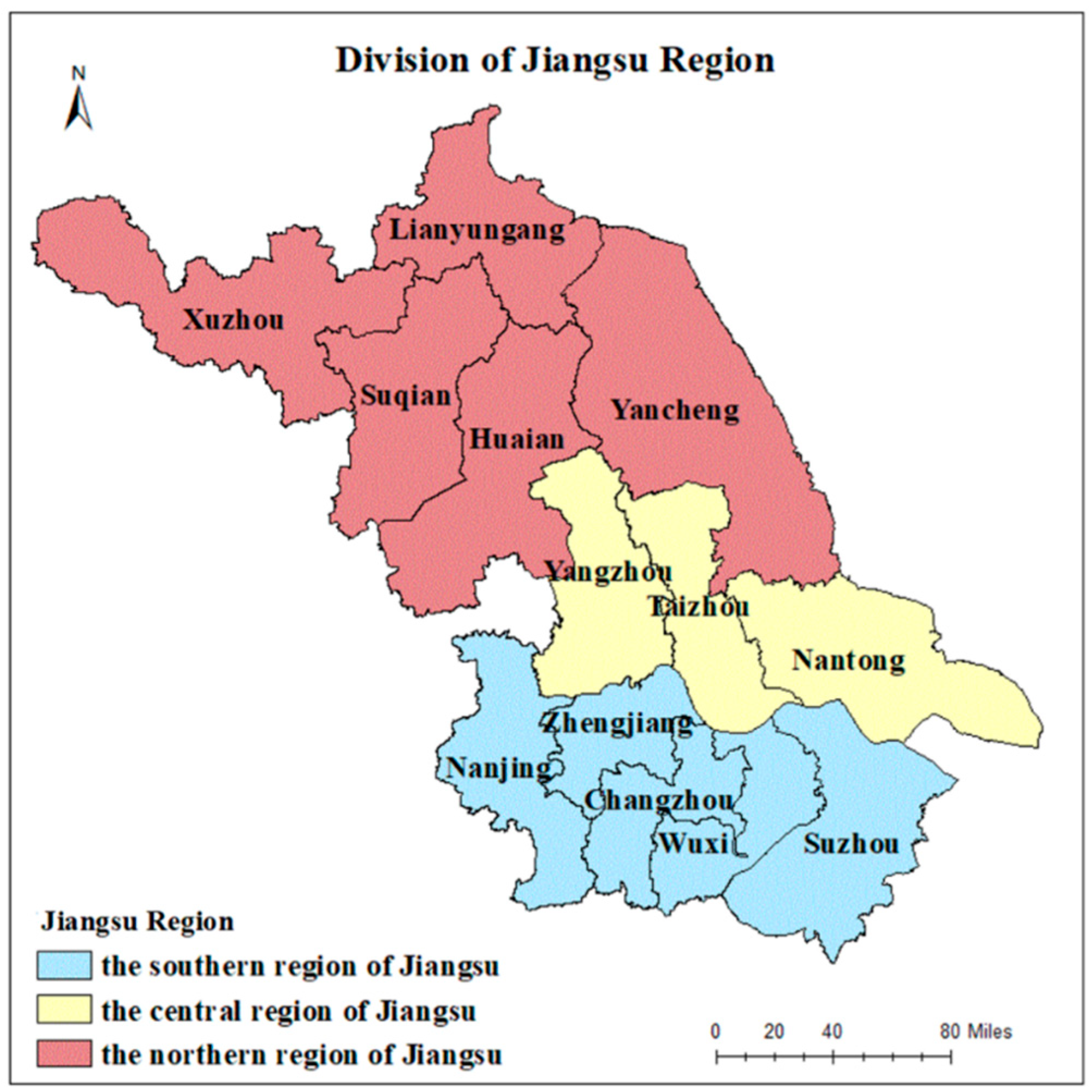
4. Analysis of results
4.1. Index weighting values
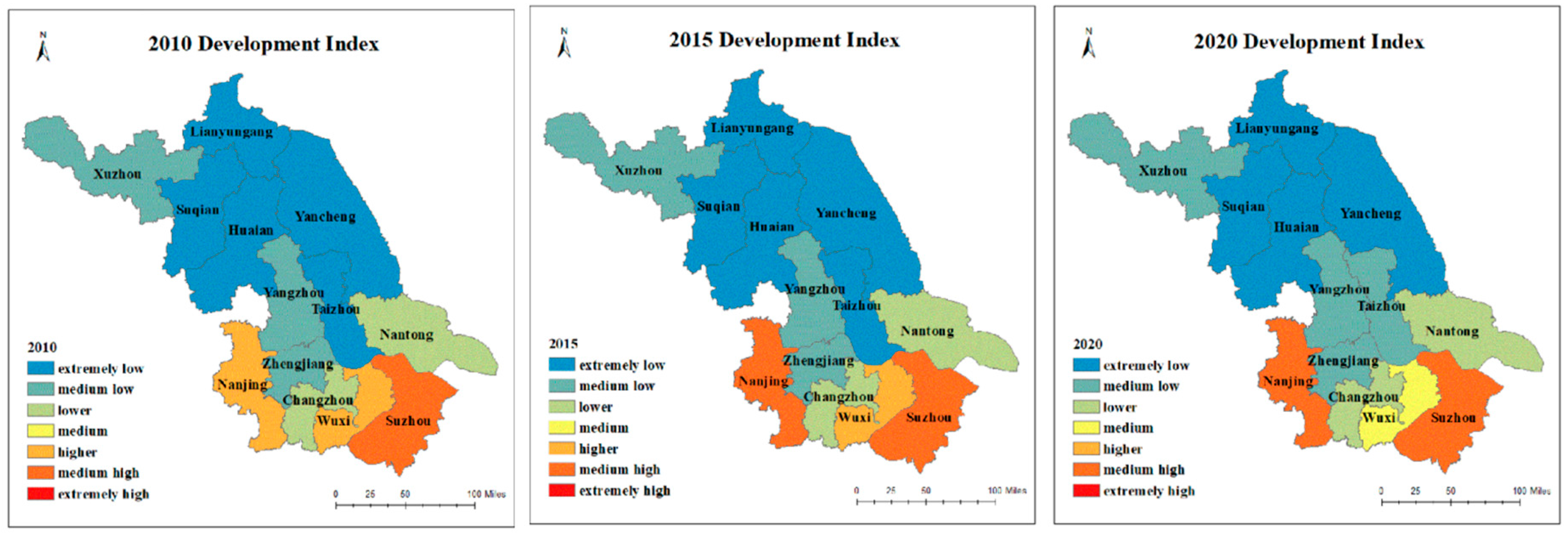
4.2. Development indices
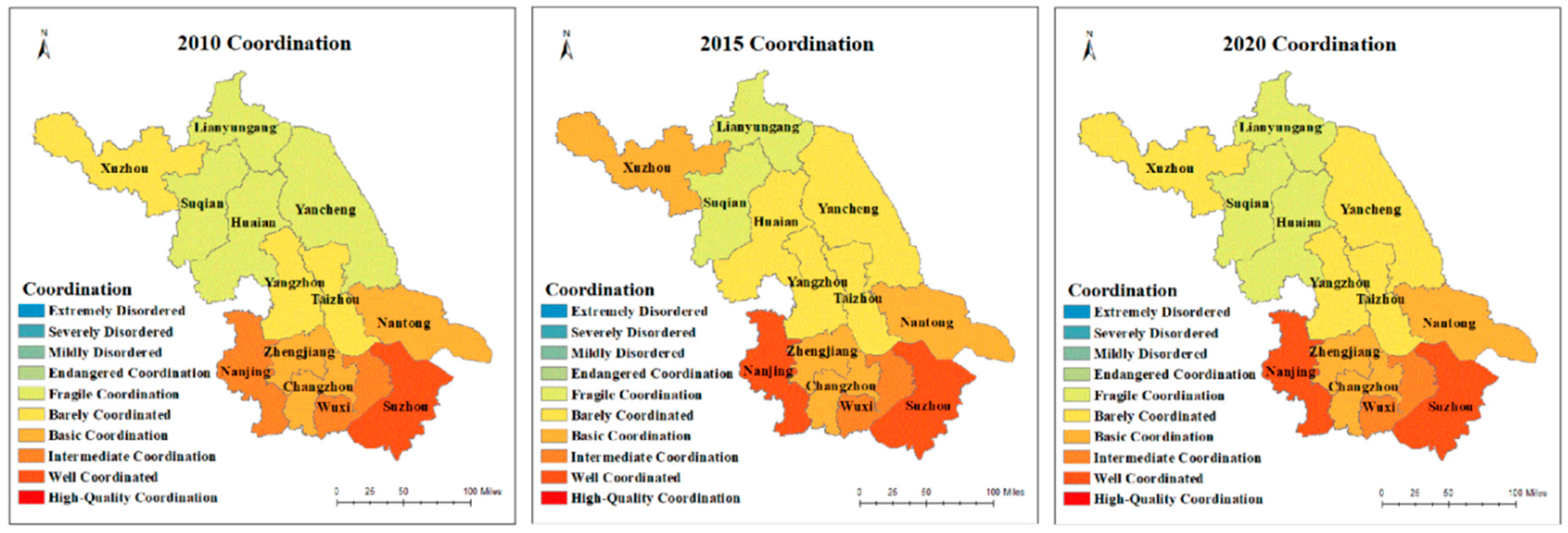
4.3. Coordination indices
5. Discussion
5.1. Geographic differences
5.2. The Matthew Effect
5.3. Game thinking
5.4. Differences in industrial structure
6. Conclusions and Recommendations
6.1. Strengthen cross-regional cooperation
6.2. Promote data sharing and interoperability
6.3. Deepen industrial synergistic development
6.4. Foster innovation capacity
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
| 1 | Regional balanced development in this study refers to the balance between regional coordination and regional development. For the purpose of this study, regional balanced development refers to the balance of inter-regional development, and regional coordinated development refers to the coordination of demographic, economic, and social development factors within cities, and the balance of regional development is measured through the development index of urban development and the degree of coupled coordination. |
| 2 | There are various studies on the connotation of social development. In this paper, social development refers to the ecological environment, infrastructure, social security system, scientific and educational development of the whole society, excluding population development and economic development. Essentially, social development is the social attributes of the environment and resources. The study of population-economic-social development system in this paper belongs to the research subfield of population economics. |
References
- Jiang Changliu, X.Y., Jiang Chengtao, Analysis of the Promoting Effect of New Urbanization Innovation with Inclusive Connotation. Finance and Accounting Monthly, 2020. 2020, (23): p. 124-133.
- Xiang Yuqiong, J.Y., From Technological Transformation to Value Co creation: The Development and Evolutionary Logic of Smart Communities: A Diachronic Study Based on the "Palm Cloud Community" in Qixia District, Nanjing. Administrative Forum, 2023. 30 (06): p. 142-149.
- Wen, G., Digital Retina, Evolving Smart Cities from "Clear" to "Understanding" Science China, 2020. (12): p. 30-31.
- Wang Bo, L.P., Zhen Feng, Urban Geography Research in a Smart Society from the Perspective of Resident Activities Geography Research, 2018. 37 (10): p. 2075-2086.
- Del Bo, C., Smart Cities: Is It Just a Fad? [electronic resource]. Scienze regionali : Italian Journal of regional Science, 2018. 19(1).
- Wu Zhiqiang, P.Y., Ye Qiming, Kong Lingyu, Intelligent City Evaluation Index System: Development Process and Application. Engineering geology, 2016. 2 (02): p. 105-137.
- Dongqi, B., Empowering High Quality Development of Commercial and Logistics Enterprises with Smart Cities: Analysis of Effects and Mechanisms. Price Theory and Practice, 2023. (05): p. 188-191.
- Deng Xiangzheng, L.L., Wu Feng, Wang Zhenbo, He Shujin, Regional Balanced Development in China from the Perspective of Development Geography. Journal of Geography, 2021. 76 (02): p. 261-276.
- Zeng Mingxing, C.L., Ding Jinhong, Regional Equilibrium Issues and Solutions in Population Development in China. Ningxia Social Sciences, 2019. No.214 (02): p. 101-108.
- Zhou Lei, S.N., Miao Yefeng, Polarization and Diffusion: The Role of the Yangtze River Delta in Regional Balanced Development: Evidence from the Yangtze River Delta and Urban Agglomeration in the Middle Reaches of the Yangtze River Resources and Environment of the Yangtze River Basin, 2021. 30 (04): p. 782-795.
- Hickel, J., The sustainable development index: Measuring the ecological efficiency of human development in the anthropocene. Ecological economics, 2020. 167: p. 106331. [CrossRef]
- Shi, T., et al., Coupling coordination degree measurement and spatiotemporal heterogeneity between economic development and ecological environment----Empirical evidence from tropical and subtropical regions of China. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2020. 244: p. 118739. [CrossRef]
- Mingguang, H., Differences in Regional Models of Vocational Education from the Perspective of Economic Development Imbalance: A Case Study of Jiangsu's "North South Cooperation" Vocational Education Model Social Scientist, 2008. No.135 (07): p. 127-129.
- Meng Yuenan, X.C., Theory and Practice of Regional Coordinated Balanced Development in China. Gansu Social Sciences, 2020. (04): p. 188-195.
- Xia Wanjun, Y.G., Research on the Imbalance of Regional Economic Development in China. Journal of Anhui Normal University (Humanities and Social Sciences Edition), 2018. 46 (04): p. 111-121.
- Li Yuwen, C.H., Xu Zhongmin, Research on Integrated Water Resource Management Theory and Quantitative Evaluation Application: A Case Study of the Heihe River Basin. China Industrial Economy,, 2010. No.264 (03): p. 139-148.
- Li Jin, C.Y., Sun Changqing, Research on Regional Economic Differences and Coordinated Development in Henan Province. Economic Journal, 2018. 35 (02): p. 20-26.
- Xiong Ying, W.K., Guo Xian, Comprehensive Evaluation and Zoning of Economic Differences in Hunan Province Regional Research and Development, 2004. (03): p. 37-40.
- Wu Yuming, Z.Y., Research on the Coupling and Coordinated Development of Regional Economic Growth and Environment in China. Resource Science, 2008. (01): p. 25-30.
- Xiaolin, L., Quantitative evaluation of coordinated development of regional population, resources, environment, and economic systems. Statistics and Decision Making, 2007. No.229 (01): p. 64-65.
- Wang Siwei, L.Y., Measurement of Regional Coordinated Development Level from the Perspective of High Quality Development Statistics and Decision Making, 2023. 39 (02): p. 99-104.
- Chenghong, X., Research on Regional Differences and Coordinated Development Based on Regional Economic Competitiveness. Ecological Economy, 2008. No.192 (01): p. 46-51+157.
- Liu Qiang, L.Z., Industrial Structure Upgrading and Regional Economic Coordinated Development: Empirical Evidence from Provinces and Urban Agglomerations. Economist, 2022. (08): p. 53-64.
- Wang Zhonghui, F.Y., Zhang Fei, Comprehensive evaluation of the high-quality economic development capacity of coastal provinces in China. Statistics and Decision Making, 2022. 38 (09): p. 114-118.
- Xu Yingzhi, W.H., Empirical Study on the Comprehensive Efficiency of Regional Coordinated Development under Environmental Constraints. China Industrial Economy,, 2010. (8): p. 34-44.
- Zhang Chao, Z.C., Jiang Tianying, Li Xingyuan, Spatial and temporal differentiation of regional coordinated development in China and its influencing factors. Economic Geography, 2020. 40 (09): p. 15-26.
- Shengnan, S., Performance Evaluation of Regional Coordinated Development under Urban Circle Integration. Jianghuai Forum, 2021. (03): p. 61-68.
- Deng Zhongliang, Z.C., Population mobility and regional coordinated development under the background of domestic circulation Economic Review, 2022. No. 443 (10): p. 54-64.
- Liu Bingsickle, F.X., Theoretical Logic and Path Selection of Regional Coordination Centered on Economic Construction Beijing Social Sciences, 2023. No.239 (03): p. 24-34.
- Yu, X. and P. Wang, Economic effects analysis of environmental regulation policy in the process of industrial structure upgrading: Evidence from Chinese provincial panel data. Science of the Total Environment, 2021. 753: p. 142004. [CrossRef]
- Lewis., A., Theory of Dual Economy. 1989: Beijing Institute of Economics Press.
- Zhongsheng, L., Population Economics. 2013, Beijing: Tsinghua University Press.
- A, L.W., Economic development with unlimited supplies of labo. The manchester school of economic and social studies, 1954. 22(2): p. 139-191.
- E, N.B., The spatial variation of urban population densities. Geographical review, 1969. 59(2): p. 242-252.
- S, L.E., A theory of migration. Demographic Research, 1966. 3(1): p. 47-57.
- Jiansong, P., The Formation and Development of Contemporary Western Demographic Economics. Population and Economy, 1987. (5): p. 55-60.
- Liu, J., et al., A new framework of land use efficiency for the coordination among food, economy and ecology in regional development. Science of the Total Environment, 2020. 710: p. 135670. [CrossRef]
- Grennfelt, P., et al., Acid rain and air pollution: 50 years of progress in environmental science and policy. Ambio, 2020. 49: p. 849-864. [CrossRef]
- Cai, J., et al., Coupling and coordinated development of new urbanization and agro-ecological environment in China. Science of The Total Environment, 2021. 776: p. 145837. [CrossRef]
- Li, W. and P. Yi, Assessment of city sustainability—Coupling coordinated development among economy, society and environment. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2020. 256: p. 120453.
- Qiu, M., et al., Evaluation on the relevance of regional urbanization and ecological security in the nine provinces along the Yellow River, China. Ecological Indicators, 2021. 132: p. 108346. [CrossRef]
- Kvint, V., Theoretical basis and methodology of strategizing of the private and public sectors of the Kuzbass region as a medial subsystem of the national economy. Russian Journal of Industrial Economics, 2020. 13(3). [CrossRef]
- Malizia, E., et al., Understanding local economic development. 2020: Routledge.
- Wezel, A., et al., Agroecological principles and elements and their implications for transitioning to sustainable food systems. A review. Agronomy for Sustainable Development, 2020. 40: p. 1-13. [CrossRef]
- Duong, V.C. and B. Sung, Examining the role of luxury elements on social media engagement. Journal of Global Fashion Marketing, 2021. 12(2): p. 103-119. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y., D. Tian, and F. Yan, Effectiveness of entropy weight method in decision-making. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2020. 2020: p. 1-5. [CrossRef]
- Li, J., et al., Coupling coordination degree of production, living and ecological spaces and its influencing factors in the Yellow River Basin. Journal of cleaner production, 2021. 298: p. 126803. [CrossRef]
- Feng Chaolin, H.Y., Luo Yuyan, A Study on the Coupling and Coordination of EEET Systems in Western Resource Based Cities: A Case Study of Three Cities in Guangxi. Ecological Economy, 2020. 36 (02): p. 104-110.
- Zhao Tao, Y.C., Pan Hui, Research on the Coupling Coordination Degree of Low Carbon City 3E1S System. Statistics and Decision Making, 2019. 35 (22): p. 131-135.
- Li Jiufeng, Y.H., Fu Yingchun, Zhao Yaolong, The spatiotemporal changes and clustering model of "population economy land society ecology" urbanization co scheduling in Guangdong Province. Progress in Geographic Science, 2018. 37 (02): p. 287-298.
- Yao Shujie, Z.F., Balanced and high-quality development of regional economy and the new development pattern of "dual circulation". Macro Quality Research, 2021. 9 (06): p. 1-16.
- Cai Anning, Z.L., Liang Jinshe, Measurement and Analysis of Regional Economic Differences in Jiangsu Province: Based on Gini Coefficient Decomposition Economic Geography, 2011. 31 (12): p. 1995-2000.
- Xu, X., et al., Eco-efficiency evaluation model: a case study of the Yangtze River Economic Belt. Environmental monitoring and assessment, 2021. 193(7): p. 457. [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Pose, A. and M. Storper, Housing, urban growth and inequalities: The limits to deregulation and upzoning in reducing economic and spatial inequality. Urban Studies, 2020. 57(2): p. 223-248. [CrossRef]
- Zhang Heping, T.F., Xiong Yu, Measurement of Matthew Effect: A New Method and Application. Statistics and Decision Making, 2021. 37 (03): p. 36-40.
- Kümpel, A.S., The Matthew Effect in social media news use: Assessing inequalities in news exposure and news engagement on social network sites (SNS). Journalism, 2020. 21(8): p. 1083-1098.
- Pavolini, E. and W. Van Lancker, The Matthew effect in childcare use: a matter of policies or preferences?, in The Future of the Social Investment State. 2020, Routledge. p. 78-93.
- Linde, L., et al., Dynamic capabilities for ecosystem orchestration A capability-based framework for smart city innovation initiatives. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 2021. 166: p. 120614. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y., et al., Human capital quality and the regional economic growth: Evidence from China. Journal of Asian Economics, 2023. 86: p. 101593. [CrossRef]
- Song, Y., X. Zhang, and M. Zhang, The influence of environmental regulation on industrial structure upgrading: Based on the strategic interaction behavior of environmental regulation among local governments. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 2021. 170: p. 120930. [CrossRef]
- Woodall, L.C., et al., Co-development, co-production and co-dissemination of scientific research: a case study to demonstrate mutual benefits. Biology Letters, 2021. 17(4): p. 20200699. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y., et al., Impact of unconventional natural gas development on regional water resources and market supply in China from the perspective of game analysis. Energy Policy, 2020. 145: p. 111750. [CrossRef]
- Zhou Xuan, T.C., Horizontal Knowledge Spillover, Technology Embedded Innovation, and Industrial Structure Coordination: Taking China's Manufacturing Industry as an Example. Scientific Research Management, 2021. 42 (07): p. 126-136.
- Hao, Y., et al., Reexamining the relationships among urbanization, industrial structure, and environmental pollution in China—New evidence using the dynamic threshold panel model. Energy Reports, 2020. 6: p. 28-39.
- Ding Renzhong, W.H., Economic Differences in Urban Agglomeration, Industrial Structure, and North South Economic Differentiation. Finance and Trade Economics, 2022. 43 (12): p. 128-143.
- Li Erling, C.Z., Coupling and Coordination Analysis of Regional Innovation Capability and Economic Development Level in China. Geographic Science, 2018. 38 (09): p. 1412-1421.
- Deng Juanjuan, S.Q., The Impact of Industrial Agglomeration on the Efficiency of Green Development of Logistics Industry: An Empirical Analysis Based on the Yangtze River Economic Belt. Business Economics Research, 2023. (23): p. 176-180.
- Hengshan, F., Several Thoughts on Deepening Regional Cooperation. Comparison of Economic and Social Systems, 2013. No.168 (04)(1-10).
- Southern, S.Y., Han Bingyang, Analysis of the Funding Performance, Situation, and Inspiration Suggestions of the China Europe Joint Funding Program. Science and Technology Management Research, 2023. 43 (10): p. 43-49.
- Hengshan, F., Deepening the opening-up and regional cooperation of the central region in all aspects. Macroeconomic Management, 2013. No.353 (05): p. 26-29.
- Xiang, Z., How Creative Execution by Local Governments Is Possible - A Case Analysis Based on the Implementation Process of the "Smart T City" Project China Administrative Management, 2023. 39 (09): p. 124-131.
- Moorthy, V., et al., Data sharing for novel coronavirus (COVID-19). Bulletin of the World Health Organization, 2020. 98(3): p. 150. [CrossRef]
- Yu, L., Ethical issues and regulations of scientific research data in the era of big data. Library, 2023. (07): p. 75-81.
- Yuan Jun, Z.Y., Huang Xujia, Research on the Coupled and Coordinated Development of Sports Industry and Tourism Industry in Urban Agglomeration of Guangdong Hong Kong Macao Greater Bay Area. Resource Development and Market, 2023: p. 1-12.
- Ke, Z., Has the construction of smart cities promoted energy conservation and emission reduction—— Based on the Experience Analysis of 141 Districts and Counties in the Yangtze River Delta Urban Agglomeration. Financial Research, 2023. (07): p. 134-153.
- Tang Jun, G.Y., Li Penglin, Can smart cities promote the achievement of the "dual carbon" goal through smart energy construction—— Experimental evidence based on synthetic control method. Soft Science,, 2023. 37 (07): p. 90-96+133.
- Li Xinru, Z.M., Mi Yidong, The Application of Smart Environmental Protection Systems in Environmental Governance. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology, 2021. 11 (05): p. 992-1003.
- Fan, F., H. Lian, and S. Wang, Can regional collaborative innovation improve innovation efficiency? An empirical study of Chinese cities. Growth and Change, 2020. 51(1): p. 440-463. [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Montoya, M.S., et al., Complex thinking in the framework of Education 4.0 and Open Innovation—A systematic literature review. Journal of Open Innovation: Technology, Market, and Complexity, 2022. 8(1): p. 4.
- Zhu Yanjun, S.K., Exploring the influencing factors of enterprise participation in school enterprise patent cooperation: An empirical analysis based on structural equation. Chinese University Science and Technology, 2023. (11): p. 90-96.
| Target Level | Standardized Layer | Serial Number | Index Layer | Index Properties |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Population development subsystem indices | Size of population | A1 | Number of births (persons) | ﹢ |
| A2 | Number of deaths (persons) | - | ||
| A3 | Household population at the end of the year (10,000) | ﹢ | ||
| A4 | Year-end resident population (10,000) | ﹢ | ||
| Quality of population | A5 | Illiteracy and semi-illiteracy (%) | - | |
| A6 | Percentage of people with bachelor's degree or above (%) | ﹢ | ||
| A7 | Percentage of people with high school education or less (%) | - | ||
| Population structure | A8 | Sex ratio at birth | - | |
| A9 | Percentage of 0-14 year olds (%) | ﹢ | ||
| A10 | Percentage of 15-64 year olds (%) | ﹢ | ||
| A11 | Percentage of persons aged 65 and over (%) | ﹢ | ||
| A12 | Population density (persons/km2) | ﹢ | ||
| A13 | Percentage of urban population (%) | ﹢ |
| Target Level | Standardized Layer | Serial Number | Index Layer | Index Properties |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Economic development subsystem indices | Size of economy | B1 | Year-end gross domestic product GDP (billions of yuan) | ﹢ |
| B2 | General public budget revenue (billions of yuan) | ﹢ | ||
| B3 | Gross industrial output (billions of yuan) | + | ||
| Quality of the economy | B4 | GDP per capita ($) | + | |
| B5 | GDP growth rate (%) | + | ||
| B6 | Per capita local fiscal revenue (million yuan) | + | ||
| B7 | Per capita gross industry output (yuan) | + | ||
| Economic structure | B8 | Share of primary production value (%) | + | |
| B9 | Share of secondary production value (%) | + | ||
| B10 | Share of output value of the third sector (%) | + |
| Target Level | Standardized Layer | Serial Number | Index Layer | Index Properties |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Social development subsystem indices | Infrastructure | C1 | Road area per capita (square meters) | + |
| C2 | Public transportation vehicles for 10,000 people (standard units) | + | ||
| C3 | Supply of liquefied petroleum gas per 10,000 people (tons) | + | ||
| C4 | Water supply per capita (tons) | + | ||
| Cultural Education | C5 | Per capita financial expenditure on education (yuan) | + | |
| C6 | Total number of students enrolled in school at all levels (10,000) | + | ||
| C7 | Total number of teachers at all levels (10,000) | + | ||
| C8 | Public library holdings per capita (volumes) | + | ||
| Medical System | C9 | Total number of hospitals, health centers | + | |
| C10 | Number of hospital beds per 10,000 persons (sheets) | + | ||
| C11 | Percentage of persons covered by basic health insurance (%) | + | ||
| C12 | Percentage of employees insured against work-related injuries (%) | + | ||
| C13 | Unemployment insurance participation (%) | + | ||
| Ecological Environment | C14 | Sewage treatment rate (%) | + | |
| C15 | Volume of domestic waste removed (tons) | + | ||
| C16 | Green space per capita in parks (square meters) | + |
| Development Index | [0-0.3) | [0.3-0.4) | [0.4-0.5) | [0.5-0.6) | [0.6-0.7) | [0.7-0.8) | [0.8-1] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Level of development | Extremely low | Medium low | Lower | Medium | Higher | Medium high | Extremely high |
| Low | Medium | High | |||||
| Coordination index | Coordination phase | Degree of coordinated development |
|---|---|---|
| [0-0.1) | Disordered type | Extremely disordered |
| [0.1-0.2) | Severely disordered | |
| [0.2-03) | Mildly disordered | |
| [0.3-0.4) | Transition type | Endangered coordination |
| [0.4-0.5) | Fragile coordination | |
| [0.5-0.6) | Barely coordinated | |
| [0.6-0.7) | Basic coordination | |
| [0.7-0.8) | Coordinated development | Intermediate coordination |
| [0.8-0.9) | Well-coordinated | |
| [0.9-1.0] | High-quality coordination |
| Level 1 indices | Secondary indices | Tertiary indices | W2010 | W2015 | W2020 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Population development subsystem indices | Size of population | Number of births (persons) | 0.09 | 0.08 | 0.07 |
| Number of deaths (persons) | 0.05 | 0.06 | 0.05 | ||
| Household population at the end of the year (10,000) | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.06 | ||
| Year-end resident population (10,000) | 0.08 | 0.07 | 0.09 | ||
| Quality of population | Illiteracy and semi-illiteracy (%) | 0.07 | 0.10 | 0.06 | |
| Undergraduate education and above (%) | 0.07 | 0.10 | 0.06 | ||
| High school education and below (%) | 0.08 | 0.06 | 0.07 | ||
| Population Structure | sex ratio at birth | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.05 | |
| Percentage of 0-14-year-olds (%) | 0.08 | 0.07 | 0.07 | ||
| Percentage of 15-64-year-olds (%) | 0.12 | 0.10 | 0.12 | ||
| Percentage of persons aged 65 and over (%) | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.07 | ||
| Population density (persons/km2) | 0.07 | 0.09 | 0.11 | ||
| Percentage of urban population (%) | 0.10 | 0.09 | 0.11 | ||
| Economic development subsystem indices | Size of economy | Year-end GDP (billions of yuan) | 0.11 | 0.13 | 0.12 |
| Public budget revenue (billions of yuan) | 0.12 | 0.14 | 0.15 | ||
| Gross industrial output (billions of yuan) | 0.11 | 0.12 | 0.12 | ||
| Quality of the economy | GDP per capita ($) | 0.09 | 0.10 | 0.08 | |
| GDP growth rate (%) | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.07 | ||
| Per capita local fiscal revenue (ten thousand yuan) | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.11 | ||
| Gross industrial output per capita (million yuan) | 0.10 | 0.12 | 0.10 | ||
| Economic Structure | Share of primary production value (%) | 0.11 | 0.12 | 0.11 | |
| Share of secondary production value (%) | 0.10 | 0.05 | 0.04 | ||
| Share of output value of the third sector (%) | 0.12 | 0.06 | 0.10 | ||
| Social development subsystem indices | Infrastructure | Road area per capita (square meters) | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.08 |
| Public transportation vehicles for 10,000 people (standard units) | 0.06 | 0.04 | 0.07 | ||
| Oil and gas supply for 10,000 people (tons) | 0.05 | 0.06 | 0.04 | ||
| Water supply per capita (tons) | 0.07 | 0.08 | 0.07 | ||
| Cultural Education | Per capita financial expenditure on education (yuan) | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.06 | |
| Total number of students in school (10,000) | 0.04 | 0.06 | 0.07 | ||
| Total number of teachers at all stages (10,000) | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.06 | ||
| Public library holdings per capita (volumes) | 0.06 | 0.07 | 0.06 | ||
| Medical Protection | Total number of hospitals, health centers (number) | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.04 | |
| Number of beds per 10,000 people (beds) | 0.07 | 0.06 | 0.03 | ||
| Number of people enrolled in basic health insurance (%) | 0.06 | 0.07 | 0.06 | ||
| Number of persons insured against work-related injuries (%) | 0.08 | 0.09 | 0.09 | ||
| Number of participants in unemployment insurance (%) | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.08 | ||
| Ecological Environment | Sewage treatment rate (%) | 0.08 | 0.03 | 0.07 | |
| Volume of domestic waste removed (tons) | 0.11 | 0.12 | 0.09 | ||
| Per capita green space in parks (square meters) | 0.05 | 0.03 | 0.04 |
| Regions | 2010 | 2015 | 2020 | |||||||
| Index | Rankings | Leve | Index | Rankings | Leve | Index | Rankings | Leve | ||
| Southern Jiangsu | Suzhou | 0.71 | 1 | Medium High | 0.77 | 1 | Medium High | 0.76 | 1 | Medium High |
| Nanjing | 0.65 | 2 | Higher | 0.70 | 2 | Medium High | 0.72 | 2 | Medium High | |
| Wuxi | 0.63 | 3 | Higher | 0.60 | 3 | Higher | 0.59 | 3 | Higher | |
| Changzhou | 0.45 | 4 | Lower | 0.45 | 4 | Lower | 0.46 | 4 | Lower | |
| Zhenjiang | 0.36 | 6 | Medium Low | 0.39 | 6 | Medium Low | 0.37 | 6 | Medium Low | |
| Central Jiangsu | Nantong | 0.40 | 5 | Lower | 0.42 | 5 | Lower | 0.40 | 5 | Lower |
| Yangzhou | 0.35 | 7 | Medium Low | 0.34 | 8 | Medium Low | 0.33 | 8 | Medium Low | |
| Taizhou | 0.29 | 9 | Extremely Low | 0.28 | 10 | Extremely Low | 0.30 | 9 | Medium Low | |
| Northern Jiangsu | Xuzhou | 0.33 | 8 | Medium Low | 0.36 | 7 | Medium Low | 0.32 | 7 | Medium Low |
| Yancheng | 0.26 | 10 | Extremely Low | 0.29 | 9 | Extremely Low | 0.27 | 10 | Extremely Low | |
| Huai'an | 0.24 | 11 | Extremely Low | 0.28 | 11 | Extremely Low | 0.25 | 11 | Extremely Low | |
| Lianyungang | 0.22 | 12 | Extremely Low | 0.24 | 12 | Extremely Low | 0.23 | 12 | Extremely Low | |
| Suqian | 0.21 | 13 | Extremely Low | 0.23 | 13 | Extremely Low | 0.22 | 13 | Extremely Low | |
| Regions | 2010 | 2015 | 2020 | |||||||
| Value | Level | Rankings | Value | Level | Rankings | Value | Level | Rankings | ||
| Southern Jiangsu | Suzhou | 0.84 | Well | 1 | 0.87 | Well | 1 | 0.87 | Well | 1 |
| Nanjing | 0.79 | Intermediate | 2 | 0.83 | Well | 2 | 0.85 | Well | 2 | |
| Wuxi | 0.79 | Intermediate | 3 | 0.77 | Intermediate | 3 | 0.77 | Intermediate | 3 | |
| Changzhou | 0.67 | Basic | 4 | 0.67 | Basic | 4 | 0.67 | Basic | 4 | |
| Zhenjiang | 0.60 | Basic | 6 | 0.62 | Basic | 6 | 0.60 | Basic | 6 | |
| Central Jiangsu | Nantong | 0.63 | Basic | 5 | 0.65 | Basic | 5 | 0.63 | Basic | 5 |
| Yangzhou | 0.59 | Barely | 7 | 0.58 | Barely | 8 | 0.57 | Barely | 7 | |
| Taizhou | 0.53 | Barely | 9 | 0.53 | Barely | 10 | 0.55 | Barely | 8 | |
| Northern Jiangsu | Xuzhou | 0.57 | Barely | 8 | 0.60 | Basic | 7 | 0.55 | Barely | 9 |
| Yancheng | 0.49 | Fragile | 10 | 0.54 | Barely | 9 | 0.51 | Barely | 10 | |
| Huai’an | 0.48 | Fragile | 11 | 0.52 | Barely | 11 | 0.49 | Fragile | 11 | |
| Lianyungang | 0.45 | Fragile | 12 | 0.48 | Fragile | 12 | 0.47 | Fragile | 12 | |
| Suqian | 0.45 | Fragile | 13 | 0.48 | Fragile | 13 | 0.46 | Fragile | 13 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





