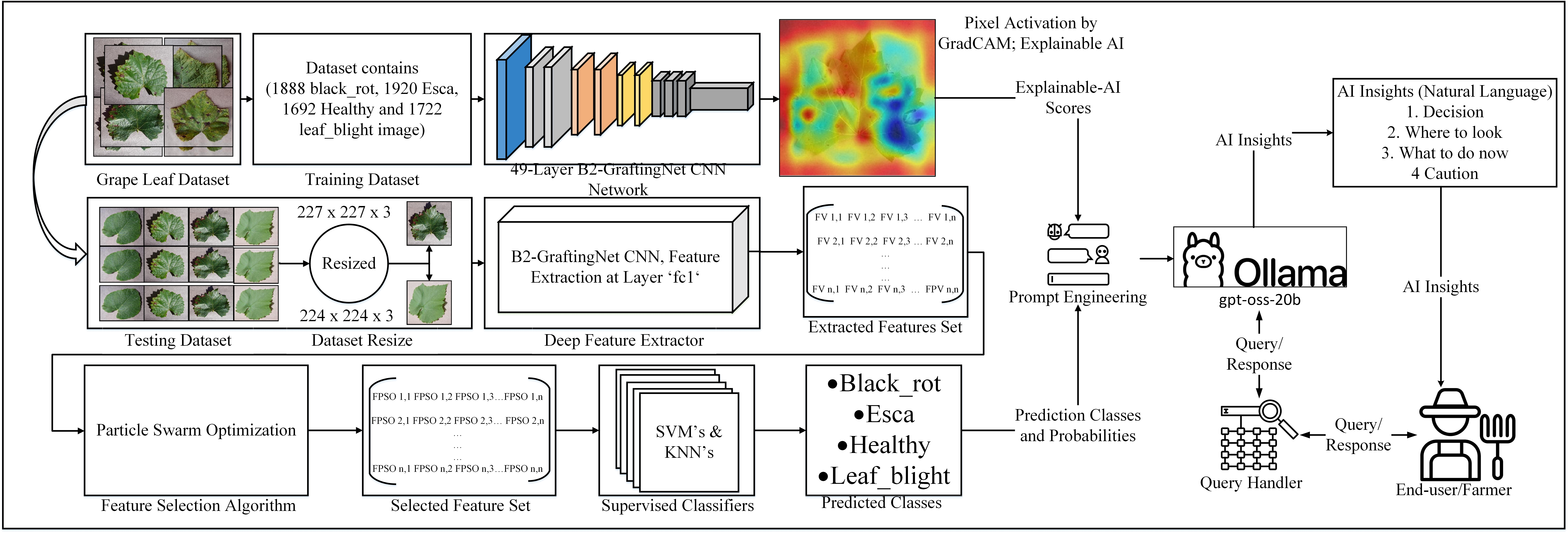
Owing to changing climatic and environmental conditions, plant diseases are becoming increasingly prevalent, posing a serious threat to global agriculture. Timely and accurate diagnosis remains challenging, especially where scouting still relies on manual inspection. We propose B2-GraftingNet, a deep learning framework for automated detection of grape leaf diseases. B2-GraftingNet is a streamlined variant of our earlier B4-GraftingNet, retaining its strengths while simplifying blocks for faster inference and deployment. The architecture combines a VGG16 backbone with Inception-style blocks inside a custom CNN to extract robust, multi-scale features based on color, size, and shape. To reduce redundancy and improve generalization, Binary Particle Swarm Optimization (BPSO) selects informative features prior to classification. We evaluate Support Vector Machines (SVM) and k-Nearest Neighbors (KNN); a cubic SVM attains 99.56% peak accuracy on the public Kaggle grape-leaf dataset. For context, we also benchmarked standard pretrained CNNs on the same data, observing validation accuracies of 34.04% (VGG16), 34.04% (VGG19), 97.95% (Xception), 94.91% (Darknet), and 98.44% (ResNet-50); B2-GraftingNet matches or exceeds these while remaining lighter and faster to train and deploy. To enhance transparency and actionability, we pair Grad-CAM, LIME, and occlusion-sensitivity visualizations with a local gpt-oss:20b assistant (served via Ollama) that converts evidence into plain, grower-focused guidance and supports interactive chat validated by horticulturists. Results are further checked against expert-annotated ground-truth labels, confirming high accuracy and computational efficiency. Overall, B2-GraftingNet offers a reliable, interpretable, and scalable solution for early grape-leaf disease detection. The complete setup (code, model, web platform, configuration, and assets) is available on Zenodo: https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.17353656.