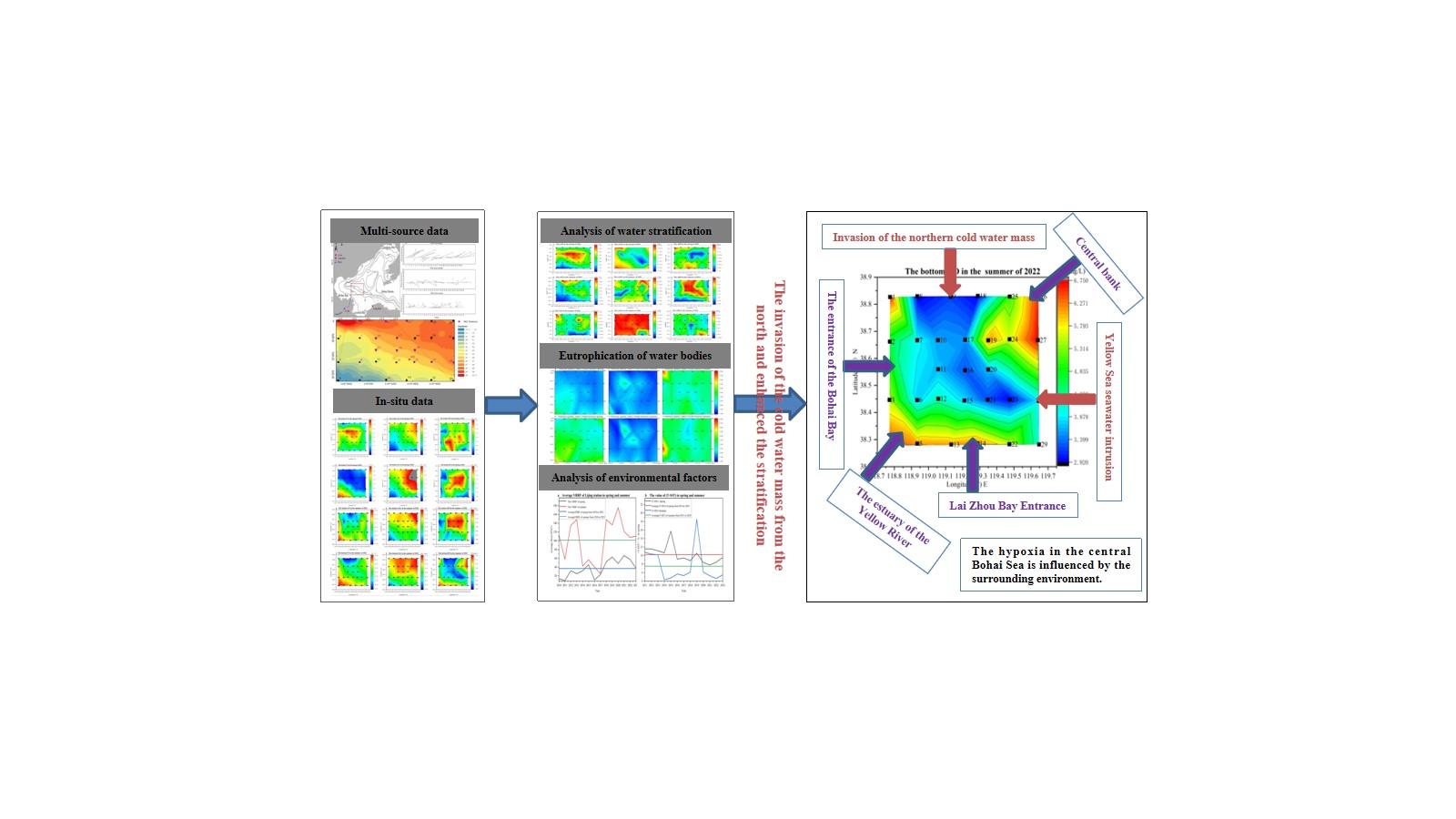
The central Bohai Sea (CBS) serves as a distribution center and wintering ground for the migration of economically important species of fish, shrimp, and crabs from the Yellow Sea and the BS. The frequency of hypoxia has gradually increased, posing a threat to the ecology of the CBS. Data from an on-site investigation of the cold water mass coverage area in the southern part of the BS in the spring, summer, and autumn of 2022 were an-alyzed to determine the relevant factors using stratification data and the nutritional status quality index. The results indicated that stratification was the leading cause of hypoxia. The 'boot-shaped' distribution of hypoxia in summer was primarily the result of the intrusion of cold and highly saline water in the northern part of the study area, as well as the intrusion of high-temperature and low-salinity water from the Yellow River estuary and the high salinity water in the northeast corner of the study area. The study found that the cold water mass in the northern part of the Bohai Sea invades the cold water mass in the southern part. This study provides novel insights into the formation and distribution of hypoxia in the CBS.