Submitted:
04 December 2025
Posted:
09 December 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
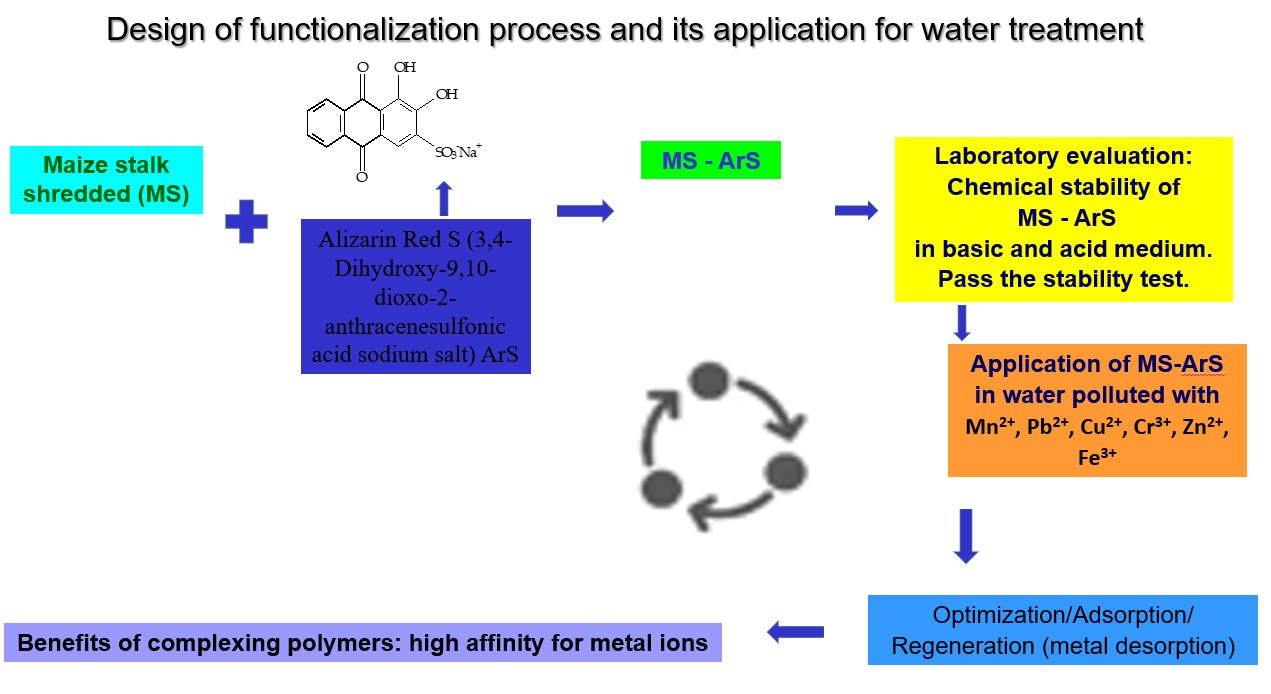
In this study, a novel material obtained from shredded maize stalk (MS) was functionalized using Alizarine Red S (ArS), a complexing agent that contains -OH and -C=O groups in its structure (MS-ArS). The obtained material MS-ArS was employed in adsorption experiments for Mn2+, Pb2+, Cu2+, Cr3+, Zn2+ and Fe3+ (Mn+) removal. Initially, complex formation between (Mn+) and ArS in buffer solution at pH 4 and 10 was investigated using UV-Vis spectrometric method. The functionalization process of MS was done at pH = 2, 4, 6, 8, and 10. The results showed that the best functionalization was obtained at pH=2. After functionalization study, Mn+ adsorption onto MS-ArS at pH 4 and 10 was tested. Mn+ adsorption proved to be pH dependent. It was observed that pH=10 was the optimum medium for Mn+ adsorption. MS-ArS has affinity for Mn+ in the following order Fe3+>Cu2+>Zn2+>Mn2+>Pb2+>Cr3+. The results demonstrate also remarkable desorption rates (D(%)) when 0.5 M HCl is used as regeneration solvent: 94% for Cu²⁺, 92.4% for Fe³⁺, 91.7% for Cr³⁺, 90.8% for Zn²⁺, 90.3% for Pb²⁺, and 86.1% for Mn²⁺. These findings highlight the potential of this sustainable material for effective adsorption and recovery of the complexing material in order to respect the principle of circular economy approach.