1. Introduction
The rapid evolution of artificial intelligence (AI) is reshaping both research and practice, demanding constant reflection on emerging methods, scalable infrastructures, and transformative applications. The purpose of this issue of The Cognitive Nexus Magazine is to provide a curated view of current advances that highlight the interplay between theoretical innovation, industrial deployment, and systems engineering. The paper goal is to synthesize these diverse contributions into a cohesive narrative, offering readers not only a collection of articles but also an integrated perspective on the trajectory of the field. By situating diverse contributions within a shared context, the issue aims to serve as both a scholarly reference and a practical guide for researchers, practitioners, and policy-makers.
Three central themes anchor this edition. The first is the rise of
neuro-symbolic reinforcement learning, which integrates symbolic reasoning with statistical learning to produce models that are not only performant but also interpretable [
1,
2]. The second theme is
AI for retail and commerce, where real-time machine learning and natural language processing are enabling demand forecasting, omnichannel synchronization, and customer personalization at unprecedented scale [
3,
4]. The third theme concerns
multi-tenant AI platforms, an area of growing importance as organizations deploy large models in shared infrastructures, raising questions of efficiency, resource isolation, and fairness in allocation [
5,
6].
Taken together, these themes reflect a broader trajectory in AI: from abstract model design toward trustworthy, interpretable, and production-ready systems. They also surface recurring challenges—such as balancing accuracy with transparency, optimizing efficiency without compromising equity, and aligning innovation with responsible governance. This paper introduction positions the articles of this issue within that larger discourse, offering a roadmap through the key contributions while situating them in the wider landscape of AI research and practice.
2. Thematic Overview of Contributions
The six articles featured in this issue are positioned within the broader themes of methodological innovation, applied AI, infrastructure, and governance. Each work highlights a distinct dimension of artificial intelligence research—ranging from advances in neuro-symbolic reinforcement learning to case studies in retail optimization and architectural innovations for multi-tenant platforms. While the contributions differ in scope and technical emphasis, they collectively advance a cohesive narrative centered on the development of trustworthy, scalable, and responsible AI systems. Taken together, these works underscore the interdependence of theory, practice, and systems design in shaping the next generation of intelligent technologies.
2.1. Neuro-Symbolic Reinforcement Learning
The first contribution, Causal Neuro-Symbolic Reinforcement Learning with Temporal Logic and Structural Causal Models (SCMs), advances the methodological frontier of AI by fusing symbolic reasoning with reinforcement learning. The authors propose a framework where structural causal models guide decision-making, and temporal logic provides a formal means of capturing long-horizon constraints. This hybrid design yields systems that are both statistically powerful and logically interpretable. Key outcomes include improved robustness when operating under uncertainty and enhanced transparency in how policies are learned and executed. Within the paper themes, this work directly addresses the challenge of building trustworthy AI by ensuring that learned agents are not only performant but also explainable and aligned with human-understandable principles.
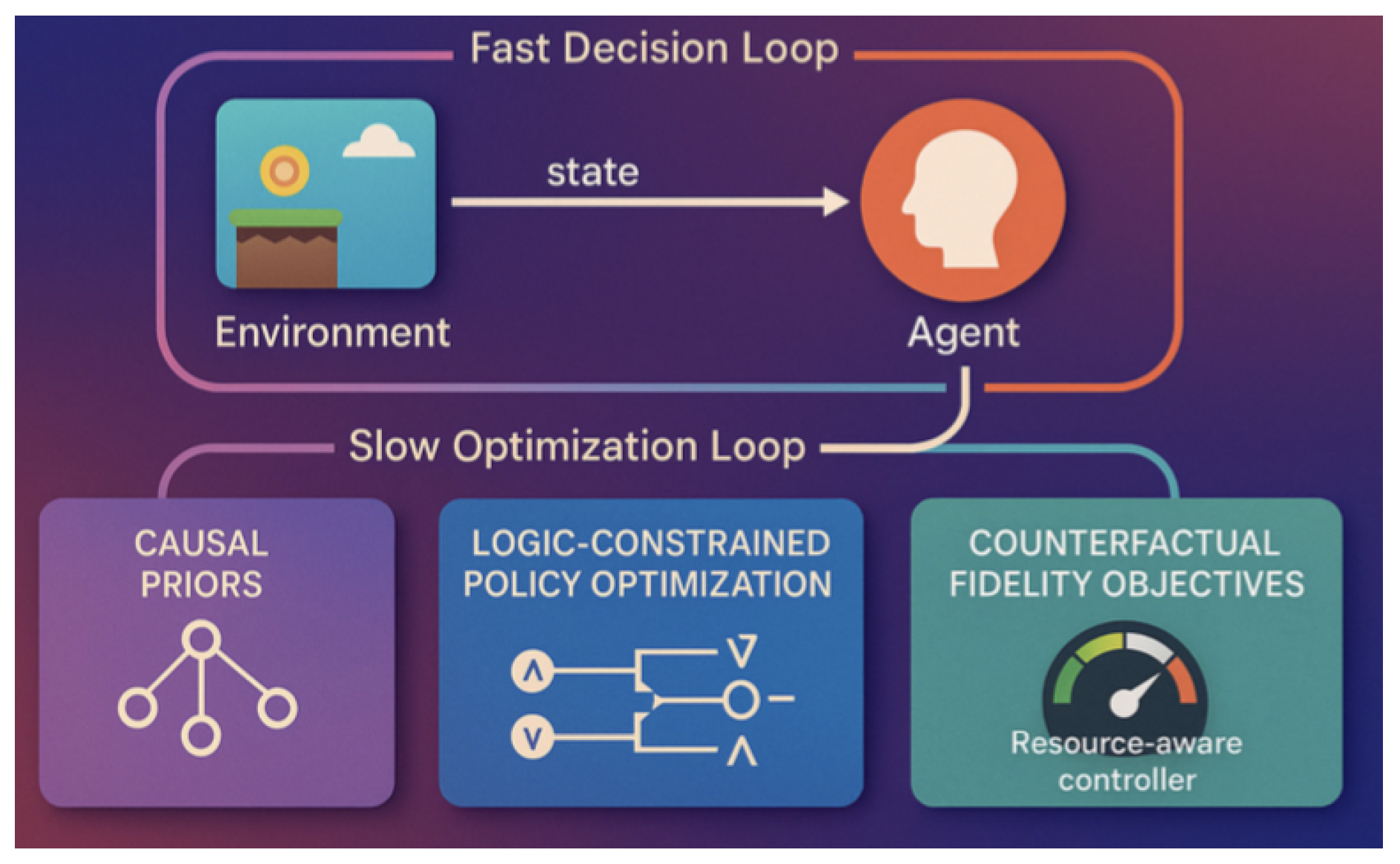
Figure 1.
CNS-RL architecture with causal prior, logic constraints, and resource manager, from the paper Causal Neuro-Symbolic Model for Robust Decision-Making in Uncertain Game Environments
Figure 1.
CNS-RL architecture with causal prior, logic constraints, and resource manager, from the paper Causal Neuro-Symbolic Model for Robust Decision-Making in Uncertain Game Environments
2.2. AI for Retail and Commerce
The second article, AI-Driven Framework for Real-Time Retail eCommerce and Point-of-Sale Optimization, demonstrates the applied potential of artificial intelligence in large-scale commercial environments. The proposed framework integrates demand forecasting, dynamic inventory management, and personalized recommendation engines into a unified real-time decision platform. By leveraging predictive analytics and adaptive optimization, the system achieves measurable improvements in operational efficiency and customer satisfaction. The results highlight significant gains in sales forecasting accuracy, reduced supply chain inefficiencies, and enhanced consumer engagement through personalization. This case study exemplifies applied AI at its most impactful, showing how carefully designed systems can translate advanced algorithms into tangible business and societal benefits.
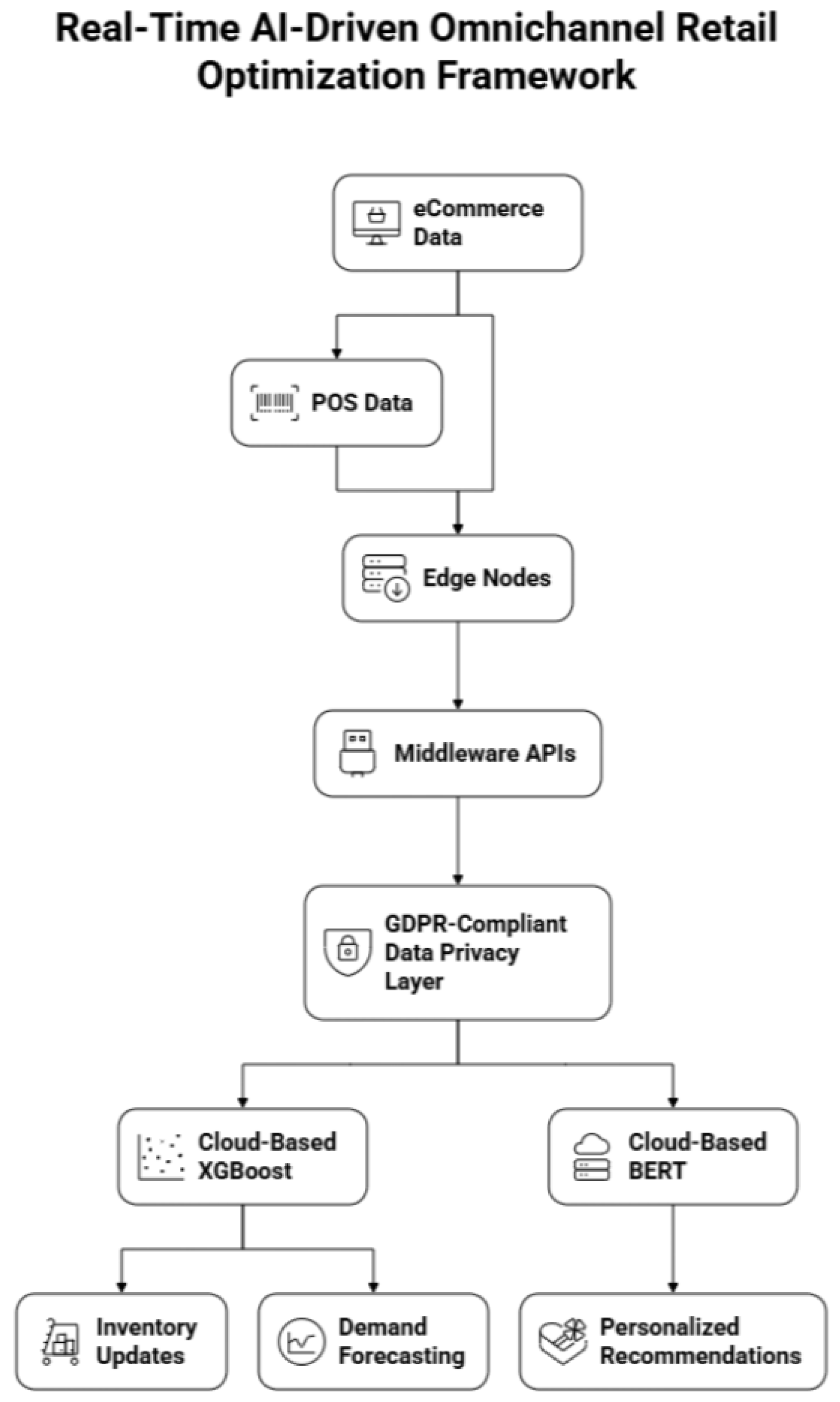
Figure 2.
Real-Time AI-Driven Omnichannel Retail Opti- mization Framework between data flows from POS terminals to edge nodes for real-time processing, from the paper Real-Time AI-Driven Retail eCommerce and POS Optimization: A Scalable Framework for Growth and Monetization
Figure 2.
Real-Time AI-Driven Omnichannel Retail Opti- mization Framework between data flows from POS terminals to edge nodes for real-time processing, from the paper Real-Time AI-Driven Retail eCommerce and POS Optimization: A Scalable Framework for Growth and Monetization
2.3. Multi-Tenant AI Platforms
The third contribution, Multi-Tenant AI Platforms: Architecture for Performance and Efficiency, addresses the growing infrastructure demands posed by enterprise-scale AI adoption. The article proposes a comprehensive architectural framework for multi-tenant AI platforms that balances resource efficiency with robust performance isolation. Key components include dynamic resource management, observability systems, and tenant isolation mechanisms, all designed to enable high concurrency while preventing cross-tenant interference. Drawing from both empirical research and production deployments, the work demonstrates that well-implemented multi-tenant architectures can significantly reduce infrastructure costs while maintaining predictable performance across diverse AI workloads. Within the paper themes, this contribution exemplifies the challenges of infrastructure design, showing how scalable systems engineering underpins the trustworthy and efficient deployment of advanced AI solutions.
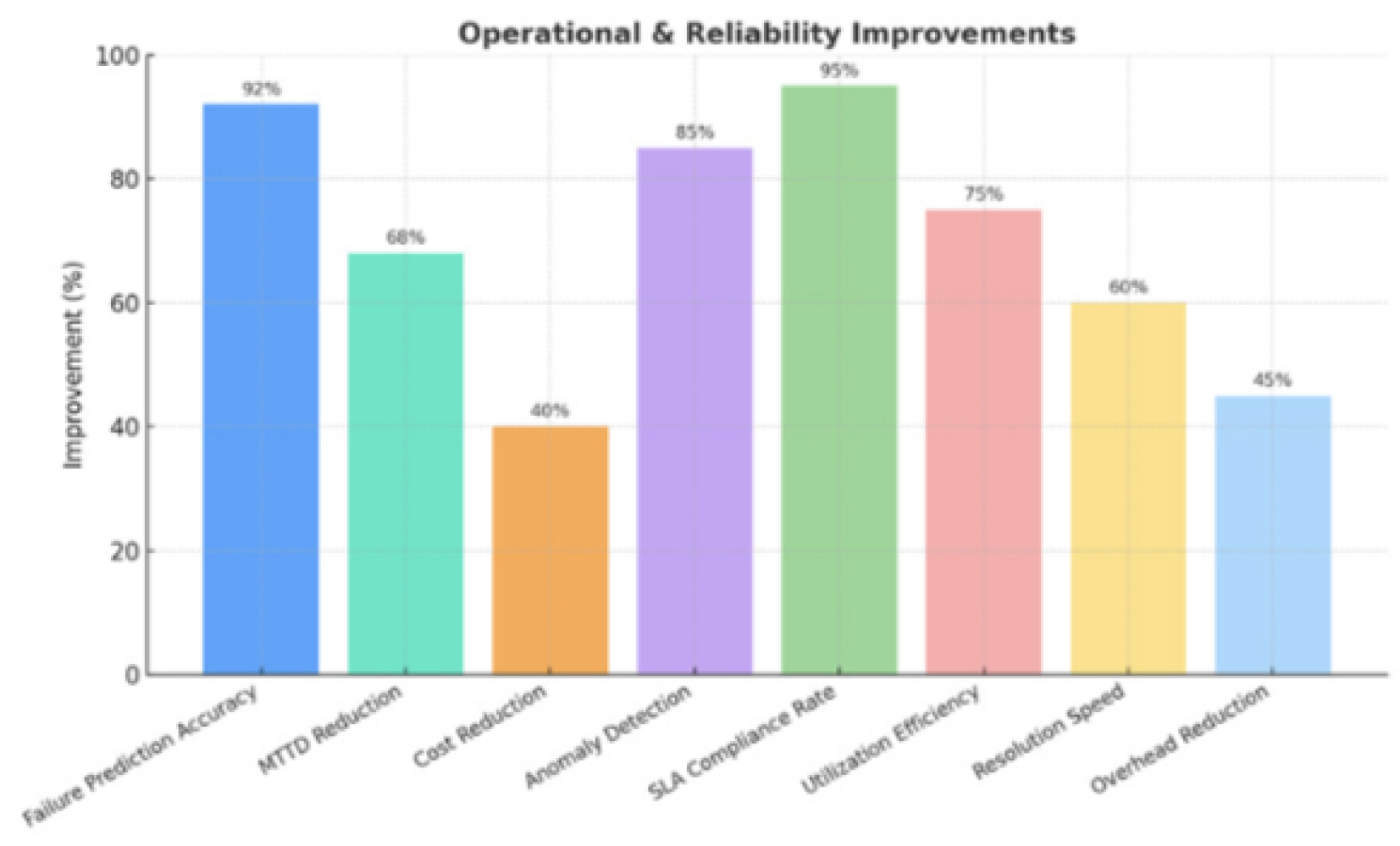
Figure 3.
AI Platform Optimization Improvements, from the paper Multi-Tenant AI Platforms: Architecture for Performance and Efficiency
Figure 3.
AI Platform Optimization Improvements, from the paper Multi-Tenant AI Platforms: Architecture for Performance and Efficiency
2.4. Datasets and Benchmarking: Multilingual Multi-Turn Dialogue
Synthetic Conversation Dataset using Large Language Models introduces the Multi-Lingual Dialogue Dataset (MLDD), a large-scale resource of 200,000 multi-turn conversations designed to reflect real-world, multilingual, emotionally nuanced dialogue. The dataset is generated by prompting a frontier LLM with titles and summaries from a structured New York Times corpus to produce 4–8 turn conversations, while explicitly configuring emotion, pitch, and speaking rate and injecting realistic background noise via text-to-speech to better approximate naturalistic audio conditions. A two-stage filtering pipeline first prunes topics and then uses cosine similarity between prompts and generated dialogue to retain on-topic samples; the final split comprises 140k training and 60k test conversations.
Methodologically, the contribution is twofold: (i) a reusable, prompting-based data-generation pipeline for multilingual, multi-turn dialogue with controllable paralinguistics; and (ii) an evaluation showing that audio–language models (e.g., Audio-Flamingo, LTU, Qwen-Audio) improve on CIDEr and BLEU-4 after fine-tuning on MLDD versus zero-shot use, indicating practical value for dialogue-rich ASR and audio-understanding tasks. The work helps close a recognized gap—lack of diverse, multilingual conversational speech data—and advances benchmarking practices by coupling synthetic dialogue with audio augmentation and systematic filtration for topic fidelity.
2.5. Reliability and Security Evaluation for RAG Systems
Building a Security and Reliability Evaluation Suite for Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) Systems presents Secure-RAG, a modular, security-first evaluation framework that instruments the full RAG pipeline—query, retrieval, and generation—with lightweight monitors and standardized metrics. Beyond correctness, Secure-RAG treats security and calibration/abstention as first-class dimensions alongside faithfulness, context precision/recall, hallucination detection, bias/fairness, and toxicity. The suite integrates provenance-aware checks (mapping claims to sources), adversarial stress testing (prompt injection, jailbreaks, context poisoning), and selective QA analyses to relate confidence to empirical accuracy.
Architecturally, Secure-RAG operates in both offline (batch) and online (continuous) modes, producing structured reports that surface failure modes and trade-offs (e.g., reliability versus utility) that siloed tools often miss. By unifying disparate evaluators into a single methodology and tying acceptance criteria to policy and risk, it offers a practical blueprint for deploying trustworthy RAG applications in high-stakes domains without sacrificing coverage of real-world threats.
2.6. Governance and Security of Agentic AI (MCP)
Securing Agentic AI: A Comprehensive Threat Analysis of Model Context Protocol Systems with Layered Defense Strategies analyzes agentic AI through a five-layer model—Prompt & Reasoning, Tool & Supply Chain, Execution & Configuration, Protocol & Network, and Data & Telemetry—and enumerates more than twenty attack vectors spanning direct/indirect prompt injection, tool poisoning and shadowing, composability chaining, sandbox escape via tool composition, protocol rebinding, and telemetry inference attacks. The paper grounds the analysis in recent incidents (e.g., CVE-2025-32711 “EchoLeak”; CVE-2025-6514) and shows how classic threats evolve when LLMs gain tool-use via MCP, turning semantic manipulation into concrete risks like unauthorized tool execution and data exfiltration.
Defensively, it advocates layered controls: provenance-aware input handling and semantic firewalls for reasoning integrity; cryptographic signing, runtime behavioral analysis, and SBOMs for tools; capability-based execution, configuration immutability, and drift detection for runtime security; mTLS, DNSSEC, version pinning, and state validation for protocol hardening; and privacy-preserving telemetry with leakage detection at the data layer. The discussion highlights emerging frameworks (e.g., identity and zero-trust tool execution with rich observability) as essential scaffolding for building secure, resilient agentic systems in production.
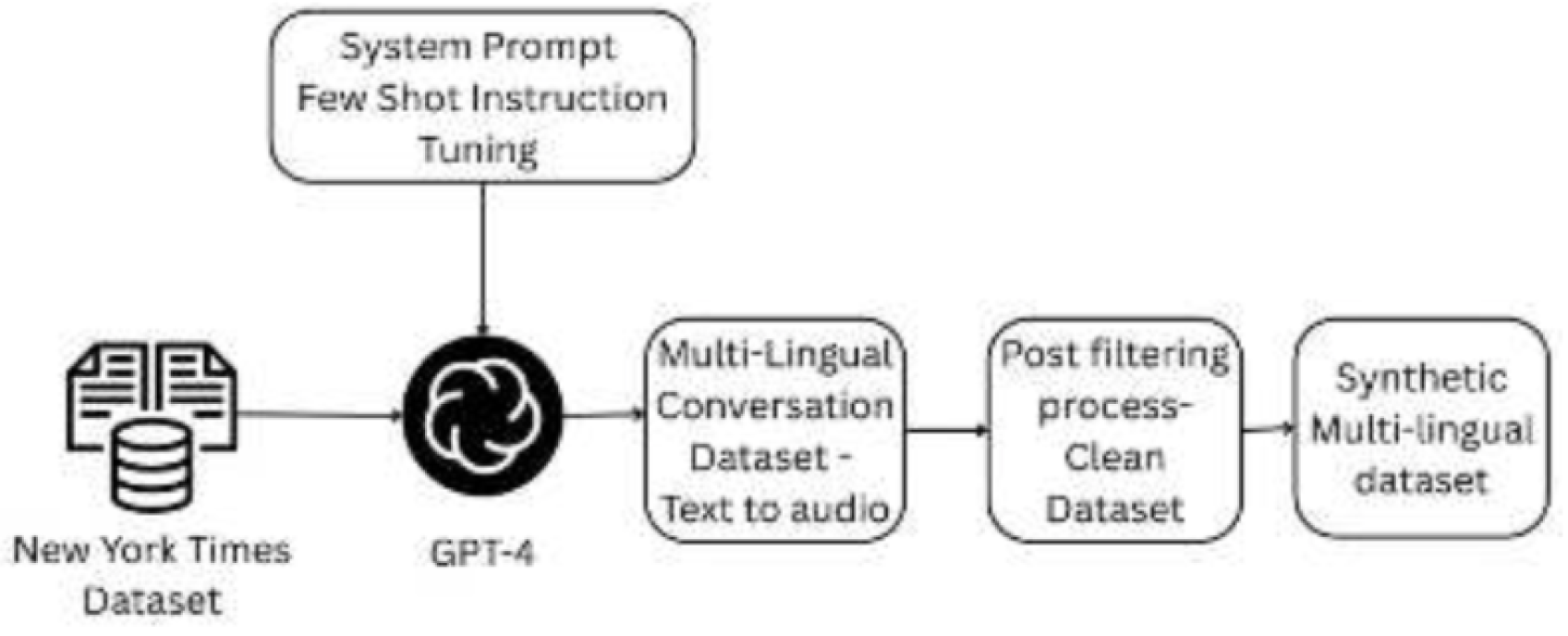
Figure 4.
Illustration of Multi-Lingual Dialogue Dataset Gen- eration Pipeline, from the paper Synthetic Conversation Dataset using Large Language Models
Figure 4.
Illustration of Multi-Lingual Dialogue Dataset Gen- eration Pipeline, from the paper Synthetic Conversation Dataset using Large Language Models
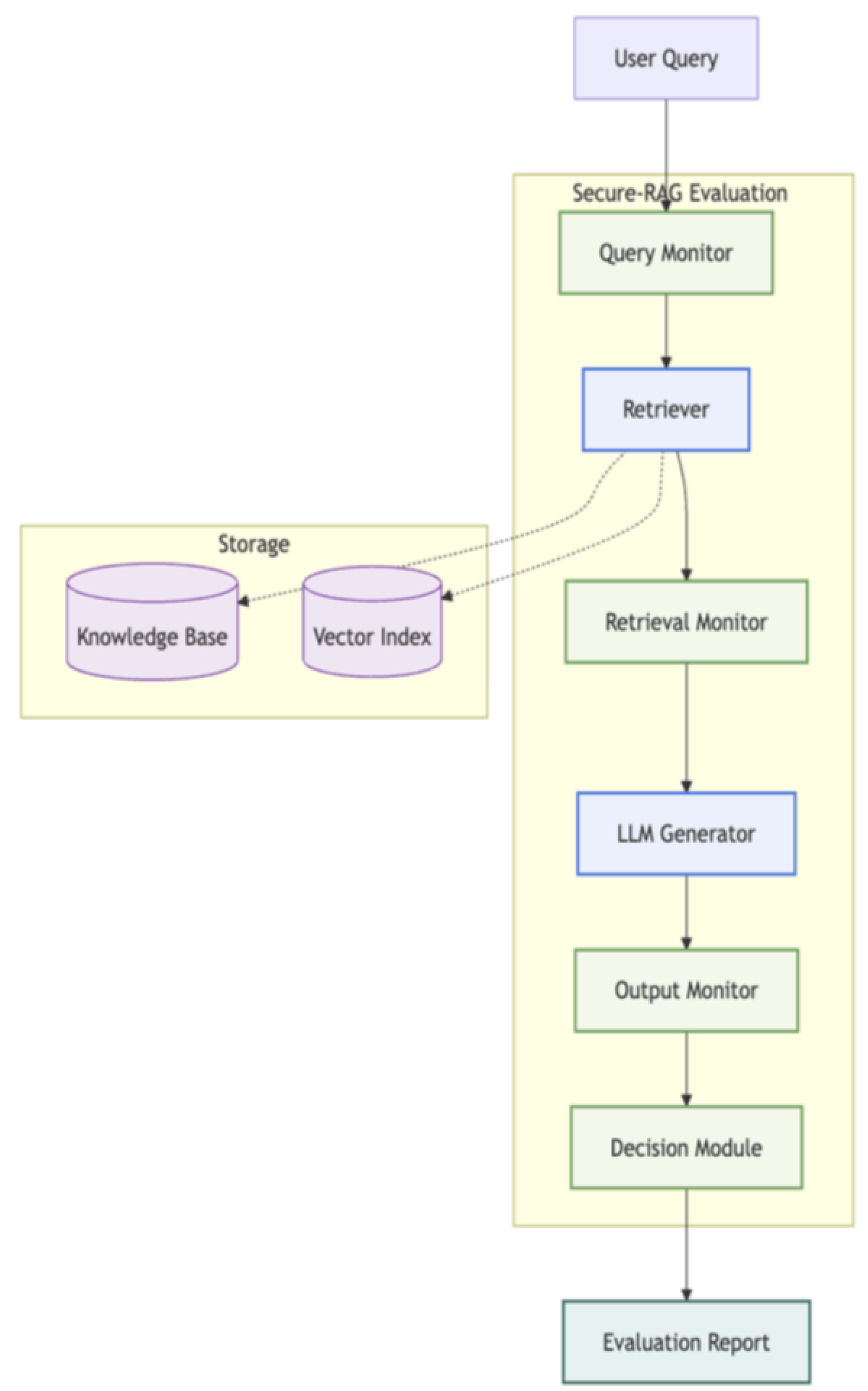
Figure 5.
Secure-RAG Architecture, from the paper Building a Security and Reliability Evaluation Suite for Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) Systems
Figure 5.
Secure-RAG Architecture, from the paper Building a Security and Reliability Evaluation Suite for Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) Systems
Taken together, the six contributions in this issue provide a multi-faceted view of the evolving AI landscape. From advances in neuro-symbolic reinforcement learning that push methodological boundaries, to applied frameworks for retail optimization, to the system-level demands of multi-tenant platforms and scheduling, and finally to new datasets and security frameworks for dialogue, RAG, and agentic AI, the articles highlight the interdependence of innovation, deployment, and governance. By synthesizing these diverse perspectives into a coherent whole, this issue underscores the central aim: to demonstrate how trustworthy, scalable, and secure AI can only be achieved through an integrated conversation across methods, applications, infrastructure, and policy.
3. Broader Insights
A recurring theme across the six contributions is the increasing interdependence of methodology, application, infrastructure, and governance in the development of artificial intelligence. Advances in neuro-symbolic reinforcement learning show how efforts to enhance reasoning ability are tightly coupled with the need for interpretability and robustness. Applied AI systems in domains such as retail highlight the potential of data-driven optimization, but they also reveal tensions between personalization, fairness, and long-term trust.
Infrastructure-oriented works on multi-tenant platforms and scheduling emphasize that the scalability and efficiency of AI cannot be decoupled from the underlying systems that host these models. Equally important are cross-cutting concerns such as observability, security, and evaluation, which ensure that AI systems remain transparent, reliable, and accountable.
Taken together, these contributions suggest that progress in AI is no longer defined by isolated advances in models or algorithms, but rather by the integration of technical innovation with system-level design and governance principles. This shift points toward a more holistic view of AI, where performance, scalability, and trustworthiness must evolve in tandem.
Figure 6.
Multi-vector EchoLeak attack combining metadata and visual deception, from the paper Securing Agentic AI: A Comprehensive Threat Analysis of Model Context Protocol Systems with Layered Defense Strategies
Figure 6.
Multi-vector EchoLeak attack combining metadata and visual deception, from the paper Securing Agentic AI: A Comprehensive Threat Analysis of Model Context Protocol Systems with Layered Defense Strategies
4. Future Directions
Looking ahead, several promising directions emerge from the themes of this issue. At the methodological level, there is growing urgency to design hybrid models that combine the interpretability of symbolic systems with the adaptability of deep reinforcement learning. Future work should aim not only to enhance robustness under uncertainty but also to provide mechanisms for causal reasoning that are transparent and verifiable.
On the application front, the expansion of AI-driven optimization into retail and other consumer-facing sectors highlights the importance of domain-specific evaluation. Researchers and practitioners will need to balance personalization with fairness, privacy, and long-term trust, especially as data sources become increasingly multimodal and context-rich. Extending such frameworks into global markets with diverse cultural and regulatory requirements remains an open challenge.
From an infrastructure perspective, the maturation of multi-tenant AI platforms and advanced scheduling mechanisms calls for further exploration of scalability under heterogeneous workloads. Future systems must provide seamless observability, efficient resource allocation, and strong guarantees of performance isolation, while remaining cost-effective in cloud and edge environments. This requires closer collaboration between systems engineers and AI model developers to bridge gaps between algorithmic efficiency and deployment constraints.
Finally, the growing prominence of evaluation suites, security protocols, and governance frameworks underscores the necessity of treating trustworthiness as a first-class objective. Retrieval-augmented generation systems, synthetic dataset pipelines, and agentic AI frameworks all demand systematic approaches to robustness, reliability, and layered defense. Progress in this space will depend not only on technical advances but also on interdisciplinary collaboration with legal, policy, and ethics communities.
In sum, the future trajectory of AI will be defined by the interplay between innovation, deployment, and governance. By pursuing methodological advances hand in hand with scalable infrastructure and principled safeguards, the research community can chart a path toward systems that are not only powerful but also reliable, secure, and socially responsible.
5. Conclusions
This issue brings together six diverse contributions that collectively capture the current trajectory of artificial intelligence research and practice. The works span methodological advances in neuro-symbolic reinforcement learning, applied systems for retail optimization, infrastructural solutions for multi-tenant platforms and scheduling, and cross-cutting perspectives on observability, security, and governance. Together, they highlight the need to treat AI development as an integrated enterprise that bridges algorithms, applications, and deployment infrastructures with principles of trustworthiness and responsibility.
A central message that emerges is that progress in AI cannot be measured by technical innovation alone. Robust deployment requires infrastructures that ensure scalability, fairness, and efficiency, while governance mechanisms safeguard against risks and misuses. At the same time, advances in methods and datasets continue to push the boundaries of what is possible, laying the foundation for more transparent and adaptive AI systems.
By synthesizing these threads, this issue underscores that the future of AI will be defined not by isolated breakthroughs but by the coherence with which methodological, applied, infrastructural, and governance dimensions are brought together. Such integration will be essential for realizing AI systems that are not only powerful, but also reliable, equitable, and aligned with broader societal values.
References
- A. S. d’Avila Garcez, L. C. Lamb, and D. M. Gabbay, “Neural-symbolic computing: An effective methodology for principled integration of machine learning and reasoning,” FLAP (Foundations of Logical and Philosophical Logic), vol. 6, no. 1, pp. 1–30, 2019.
- R. Evans and E. Grefenstette, “Neuro-symbolic AI: The state of the art,” in Proc. AAAI Conf. Artif. Intell., vol. 35, no. 17, pp. 15303–15307, 2021.
- T. H. Davenport and R. Mittal, “Artificial intelligence in retail: The coming revolution,” Harvard Business Review, vol. 98, no. 5, pp. 112–121, 2020.
- J. Sun, W. Zhang, and Y. Li, “AI-powered retail: Applications, challenges, and opportunities,” Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services, vol. 67, p. 102960, 2022.
- M. Zaharia, R. S. Xin, P. Wendell, T. Das, M. Armbrust, A. Dave, X. Meng, J. Rosen, S. Venkataraman, M. J. Franklin, et al., “Apache Spark: A unified engine for big data processing,” in Proc. 22nd ACM SIGKDD Int. Conf. Knowl. Discov. Data Min., pp. 1350–1358, 2016.
- J. Dean, G. Corrado, R. Monga, K. Chen, M. Devin, Q. V. Le, M. Z. Mao, M. A. Ranzato, A. Senior, P. Tucker, et al., “Large scale distributed deep networks,” Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst., vol. 25, 2012.
- V. Pendyala, R. Raja, A. Vats, N. Krishnan, A. Kar, L. Yerra, N. Kalu-Mba, M. Venkatram, and S. R. Bolla, “The Cognitive Nexus Magazine (IEEE Silicon Valley CIS Chapter) – Volume 1, Issue 1,” Sep. 2025. [Online]. Available: . [CrossRef]
- Vishnu Pendyala et al., “The Cognitive Nexus Magazine (IEEE Silicon Valley CIS Chapter) – Volume 1, Issue 1,” ResearchGate, Sept. 2025. Available: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/395172379_The_Cognitive_Nexus_MagazineIEEE_Silicon_Valley_CIS_Chapter_-_Volume_1_Issue_1.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).