Submitted:
03 September 2025
Posted:
04 September 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
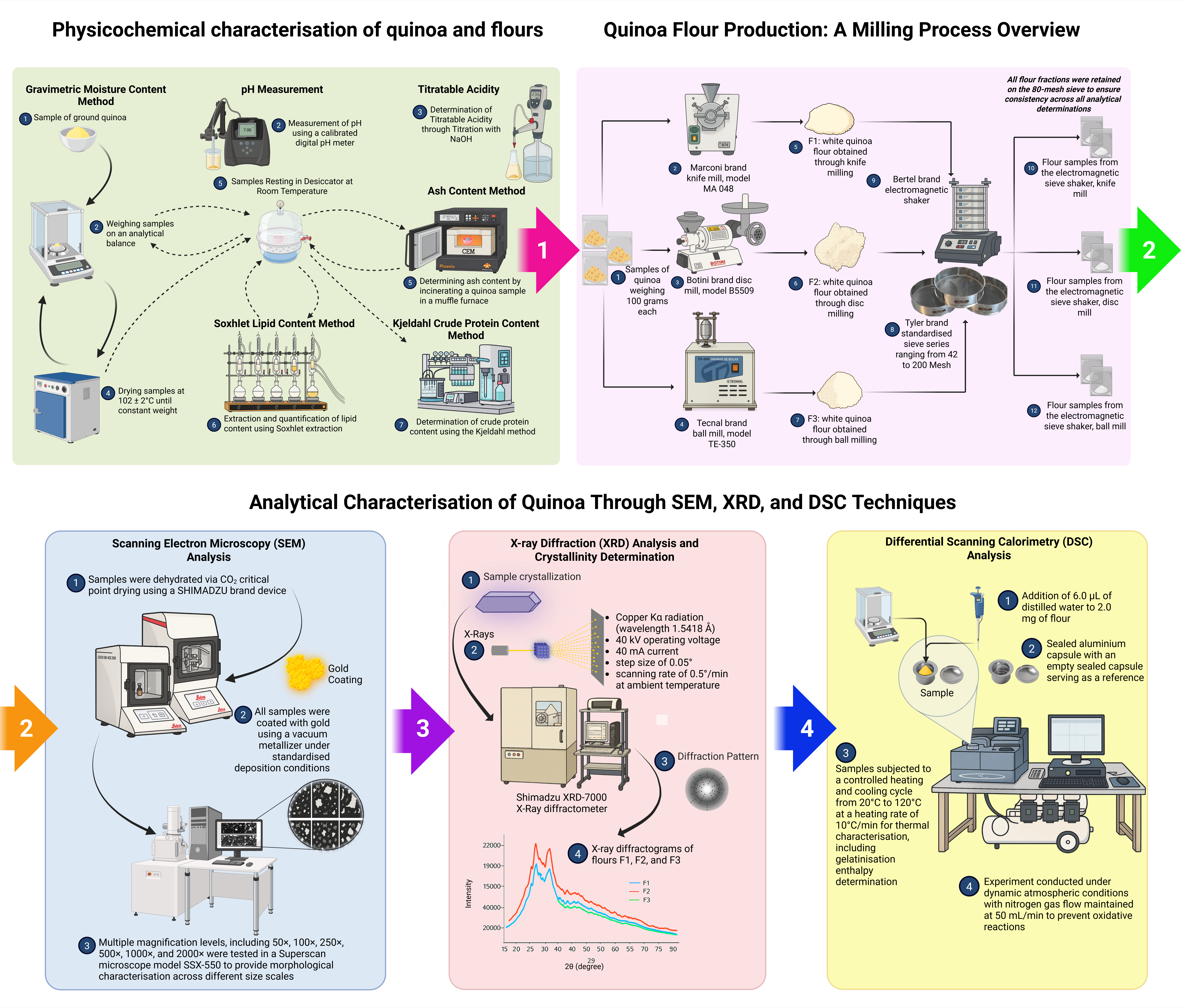
2.1. Experimental Location and Facilities
2.2. Raw Materials
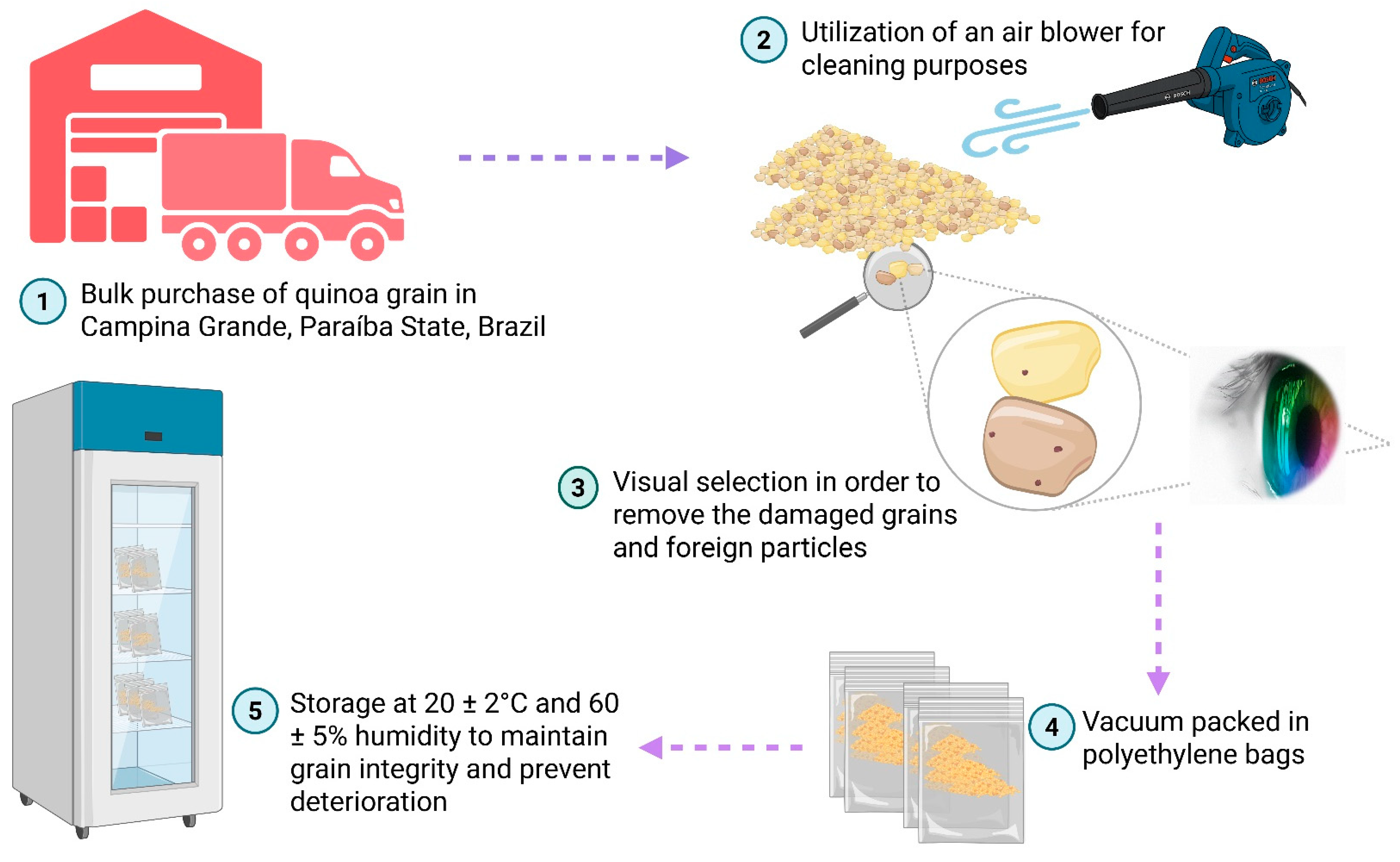
2.2.1. Quinoa Grain Procurement and Preparation
2.2.2. Chemicals and Reagents
2.3. Equipment and Instrumentation
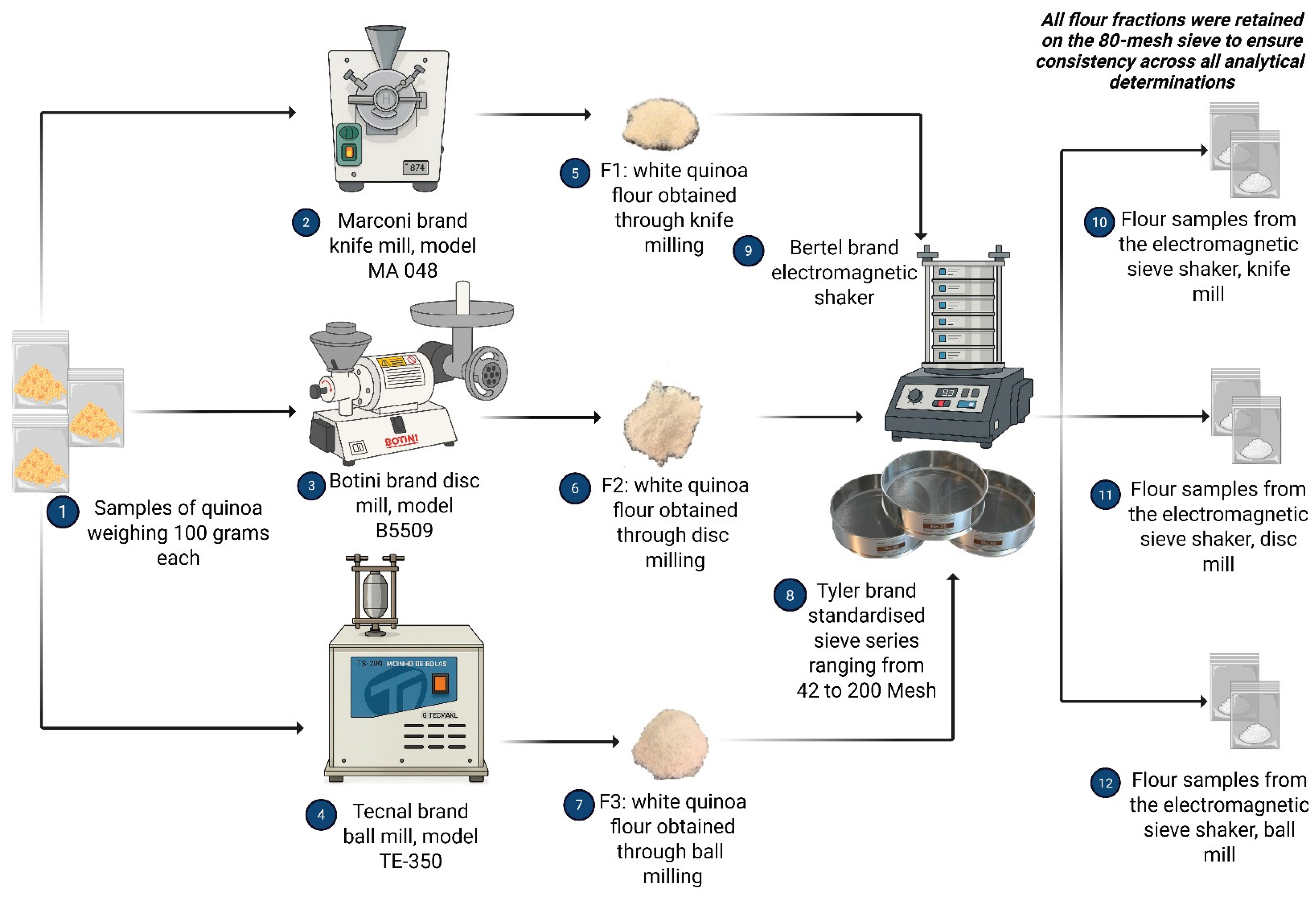
2.4. Flour Production and Sample Designation
2.4.1. Milling Process Design and Equipment Specifications
2.4.2. Equipment Technical Specifications
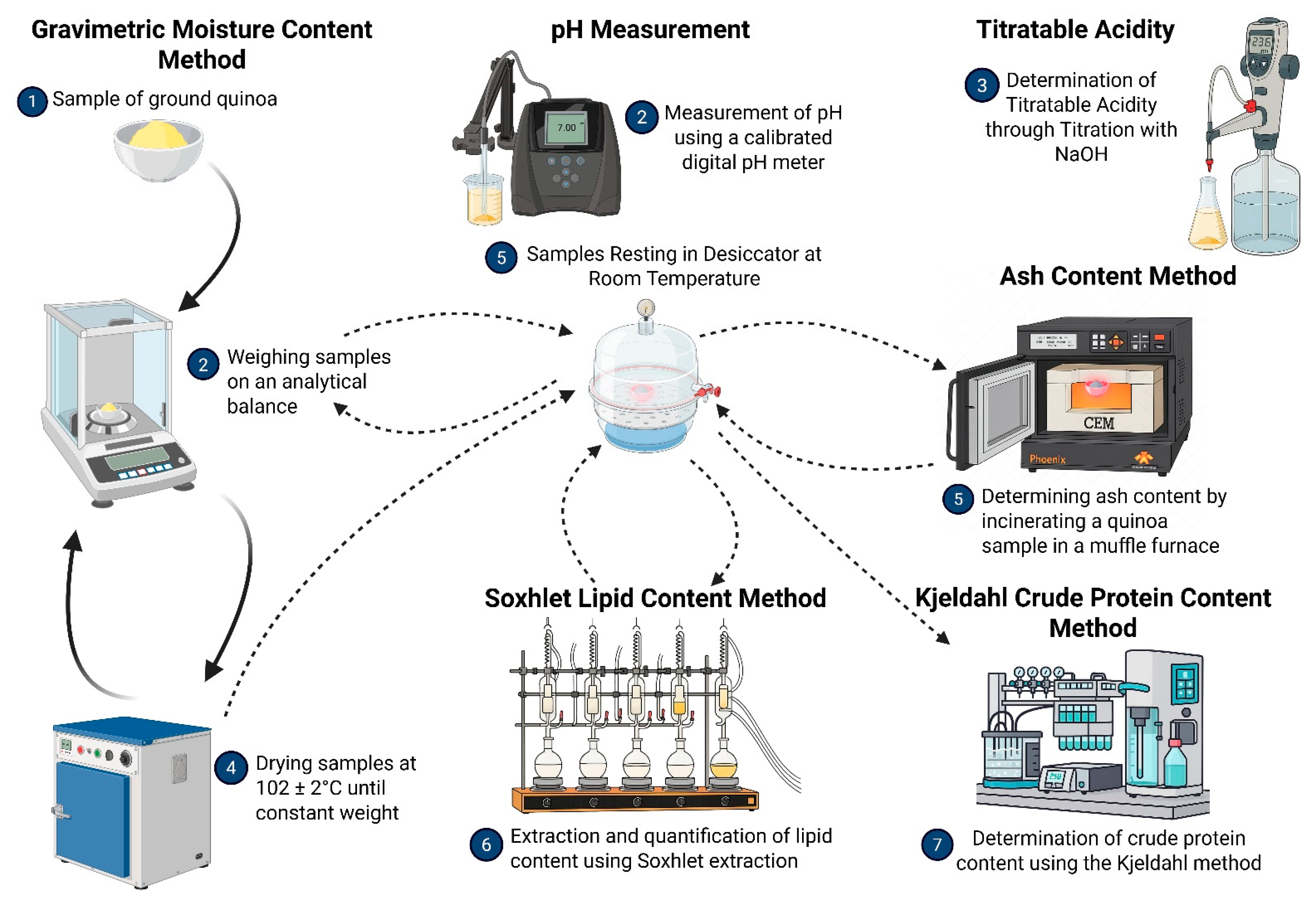
2.5. Physicochemical Characterisation
2.5.1. Proximate Analysis Methodology
2.6. Particle Size Distribution Analysis
2.6.1. Sieve Analysis Procedure
2.6.2. Mathematical Modelling of Particle Size Distribution
2.6.3. Particle Size Standardisation Protocol VG
2.7. Technological Properties Characterisation
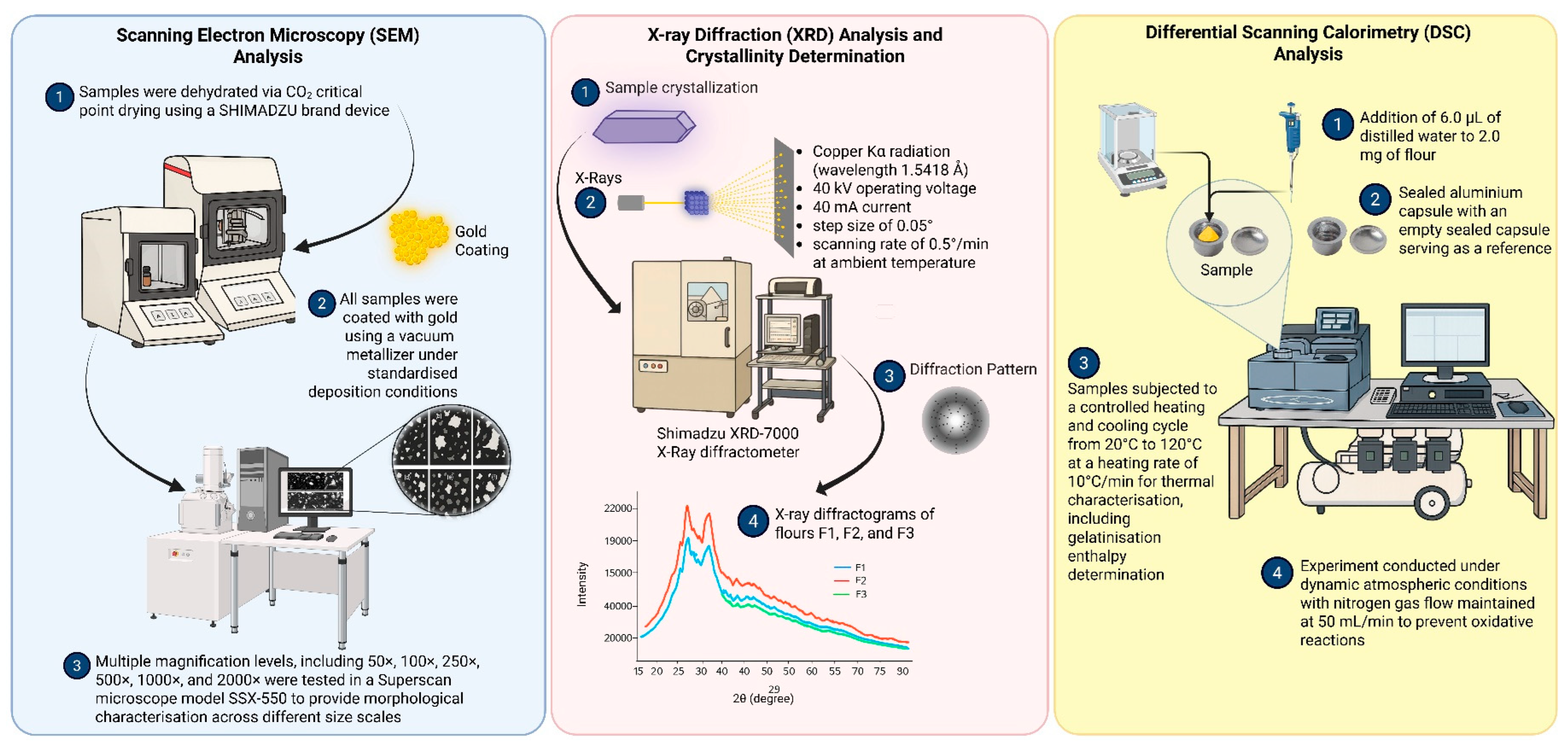
2.7.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) Analysis
2.7.2. X-Ray Diffraction (XRD) Analysis and Crystallinity Determination
2.7.3. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) Analysis
2.7.4. Statistical Analysis.
3. Results and Discussion
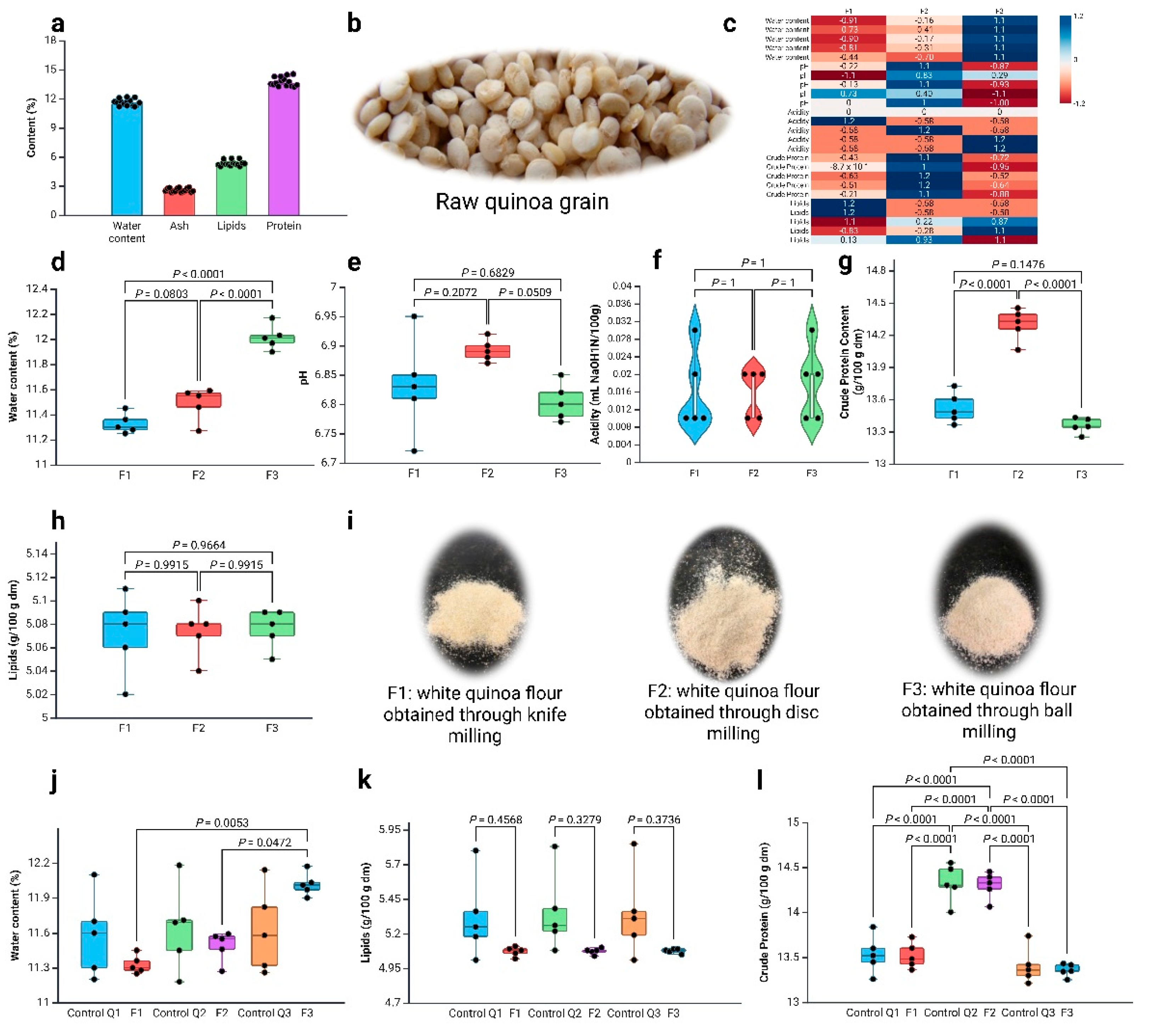
3.1. Grain Characterisation
3.2. Characterisation of White Quinoa Flour
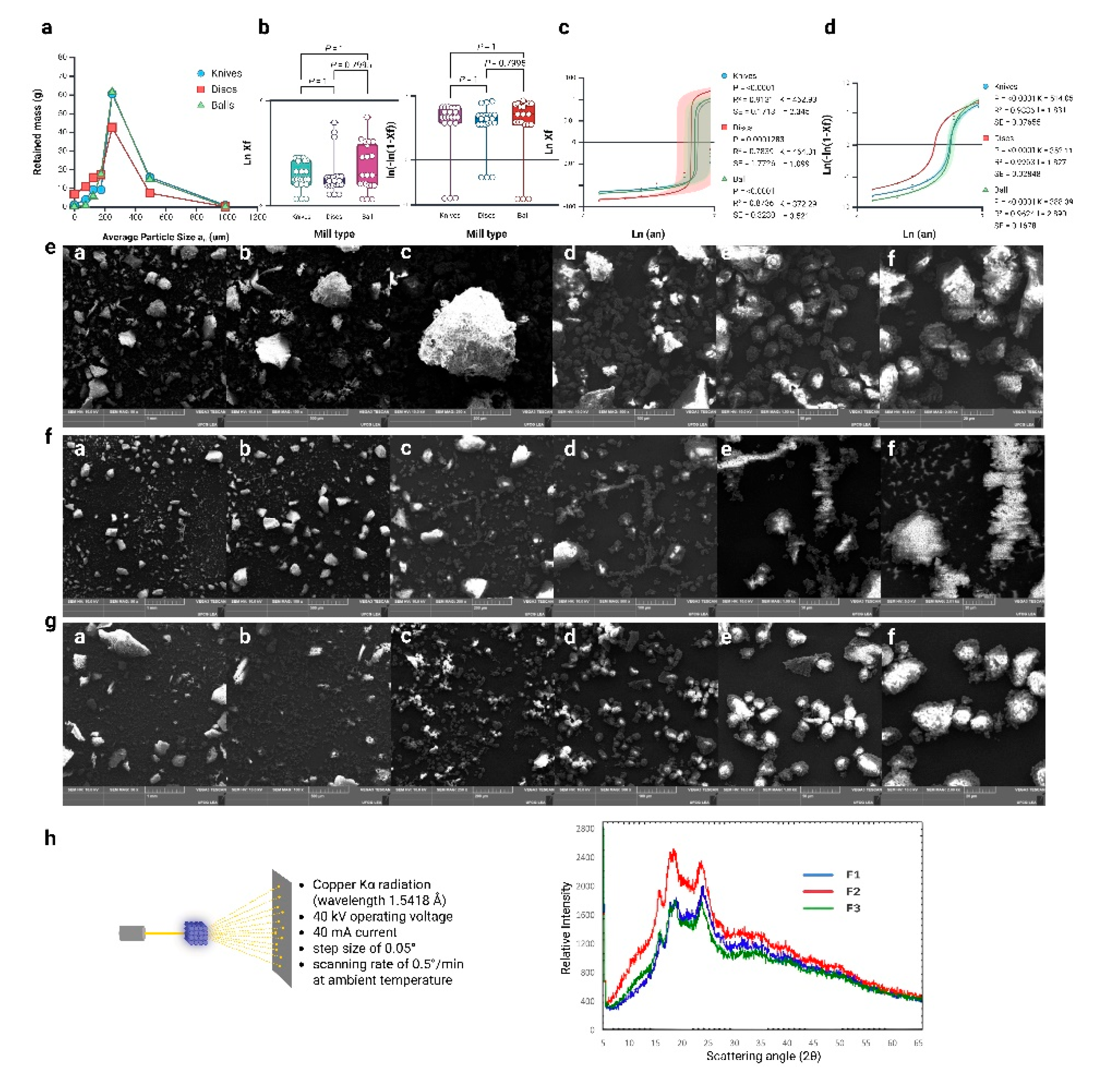
3.3. Granulometric Analysis of White Quinoa Flour
3.4. Application of Mathematical Models
3.5. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
3.6. Nutritional and Bioactive Enhancements
3.7. X-Ray Diffraction (XRD) Analysis and Crystallinity
3.8. Effects on Cellular Structure, Granule Disruption and Size Reduction
3.9. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MDPI | Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute |
| DOAJ | Directory of open access journals |
| TLA | Three letter acronym |
| LD | Linear dichroism |
References
- Schmidt, D.; Mendes, M.T.; Borges, R.; De Souza Gallo, A.; Forti, V.A.; Verruma-Bernardi, M.R. Purchase and Consumption Habits for Quinoa and Amaranth in Brazil. Food Science and Technology 2024, 44, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, G.; Teng, C.; Fan, X.; Guo, S.; Zhao, G.; Zhang, L.; Liang, Z.; Qin, P. Nutrient Composition, Functional Activity and Industrial Applications of Quinoa (Chenopodium Quinoa Willd.). Food Chem 2023, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pathan, S.; Siddiqui, R.A. Nutritional Composition and Bioactive Components in Quinoa (Chenopodium Quinoa Willd.) Greens: A Review. Nutrients 2022, 14.
- Stikic, R.; Glamoclija, D.; Demin, M.; Vucelic-Radovic, B.; Jovanovic, Z.; Milojkovic-Opsenica, D.; Jacobsen, S.E.; Milovanovic, M. Agronomical and Nutritional Evaluation of Quinoa Seeds (Chenopodium Quinoa Willd.) as an Ingredient in Bread Formulations. J Cereal Sci 2012, 55, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghanian, Z.; Ahmadabadi, M.; Asgari Lajayer, B.; Gougerdchi, V.; Hamedpour-Darabi, M.; Bagheri, N.; Sharma, R.; Vetukuri, R.R.; Astatkie, T.; Dell, B. Quinoa: A Promising Crop for Resolving the Bottleneck of Cultivation in Soils Affected by Multiple Environmental Abiotic Stresses. Plants 2024, Vol. 13, Page 2117 2024, 13, 2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, G.S.; Zillman, R.R.; Eskin, N.A.M. Dough Mixing and Breadmaking Properties of Quinoa-Wheat Flour Blends. Int J Food Sci Technol 1992, 27, 701–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzanilla-Valdez, M.L.; Boesch, C.; Orfila, C.; Montaño, S.; Hernández-Álvarez, A.J. Unveiling the Nutritional Spectrum: A Comprehensive Analysis of Protein Quality and Antinutritional Factors in Three Varieties of Quinoa (Chenopodium Quinoa Wild). Food Chem X 2024, 24, 101814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, J.; Qi, Y.; Gong, K.; Chen, zhizhou; Brennan, M. A.; Ma, Q.; Wang, J.; Brennan, C.S. Effects of Quinoa Flour (Chenopodium Quinoa Willd) Substitution on Wheat Flour Characteristics. Curr Res Food Sci 2023, 7, 100556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghumman, A.; Mudgal, S.; Singh, N.; Ranjan, B.; Kaur, A.; Rana, J.C. Physicochemical, Functional and Structural Characteristics of Grains, Flour and Protein Isolates of Indian Quinoa Lines. Food Research International 2021, 140, 109982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanwar, B.; Goyal, A.; Irshaan, S.; Kumar, V.; Sihag, M.K.; Patel, A.; Kaur, I. Quinoa. Whole Grains and their Bioactives: Composition and Health. [CrossRef]
- Afzal, I.; Haq, M.Z.U.; Ahmed, S.; Hirich, A.; Bazile, D. Challenges and Perspectives for Integrating Quinoa into the Agri-Food System. Plants 2023, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gautheron, O.; Nyhan, L.; Ressa, A.; Torreiro, M.G.; Tlais, A.Z.A.; Cappello, C.; Gobbetti, M.; Hammer, A.K.; Zannini, E.; Arendt, E.K.; et al. Solid-State Fermentation of Quinoa Flour: An In-Depth Analysis of Ingredient Characteristics. Fermentation 2024, Vol. 10, Page 360 2024, 10, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Deng, X.; Ping, C.; Li, X.; Li, D.; Wu, X.; Xiao, X.; Kong, R. Quinoa: Nutritional and Phytochemical Value, Beneficial Effects, and Future Applications. Applied Food Research 2025, 5, 100766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ANVISA Resolução No 91. Agência Nacional de Vigilância Sanitária (ANVISA). Ministério da Saúde 2008.
- Repo-Carrasco-Valencia, R.; Tomos, M.C. Native Crops in Latin America Biochemical, Processing, and Nutraceutical Aspects. Native Crops in Latin America: Biochemical, Processing, and Nutraceutical Aspects 2022, 1–382. [CrossRef]
- Rao, M.A.; Rizvi, S.S.H.; Datta, A.K. Engineering Properties of Foods: Third Edition. Engineering Properties of Foods: Third Edition 2014, 1–739. [CrossRef]
- Barbosa-Cánovas, G. V.; Ortega-Rivas, E.; Juliano, P.; Yan, H. Food Powders - Physical Properties, Processing, and Functionality; Springer Nature US, 2005;
- Scholz, M.B.S.; Bordignon, J.R.; Miranda, M.Z. de; Silva, V.C. da; Tatsch, P.O. Granulometria e Amido Danificado de Farinhas de Trigo Obtidas Em Diferentes Moinhos Experimentais. Available online: https://www.alice.cnptia.embrapa.br/alice/handle/doc/1020729 (accessed on 25 July 2025).
- Coțovanu, I.; Batariuc, A.; Mironeasa, S. Characterization of Quinoa Seeds Milling Fractions and Their Effect on the Rheological Properties of Wheat Flour Dough. Applied Sciences (Switzerland) 2020, 10, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, J.; Thomas, L.; Arfat, Y.A. Functional, Rheological, Microstructural and Antioxidant Properties of Quinoa Flour in Dispersions as Influenced by Particle Size. Food Research International 2019, 116, 302–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burbano, J.J.; Di Pierro, J.P.; Camacho, C.; Vidaurre-Ruiz, J.; Repo-Carrasco-Valencia, R.; Iglesias, F.A.; Sánchez, M.; Ospina, Y.A.M.; Igartúa, D.E.; Correa, M.J.; et al. Extruded Quinoa Flour Applied for the Development of Gluten-Free Breads: A Technological, Sensory and Microstructural Approach. Plant Foods for Human Nutrition 2025, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, D.; Gao, F.; Cao, H.; Song, H.; Huang, K.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Tan, Z.; Lu, J.; Guan, X.; et al. Moderate Milling Improved Storage Stability of Quinoa Based on the Evaluation of Lipid Oxidation and Physicochemical Characteristics. J Food Sci 2025, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saroja, P.E.; Muthugounder, P.; Shanmugam, S.; Dhairiyasamy, R. Enhancing Flour Quality and Milling Efficiency: Experimental Study on Bullet Plate Type Flour Grinding Machine. Matéria (Rio de Janeiro) 2024, 29, e20240331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Cao, H.; Wang, P.; Dai, Z.; Guan, X.; Huang, K.; Zhang, Y.; Song, H. Changes of Components and Organizational Structure Induced by Different Milling Degrees on the Physicochemical Properties and Cooking Characteristics of Quinoa. Food Structure 2023, 36, 100316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casalvara, R.F.A.; Ferreira, B.M.R.; Gonçalves, J.E.; Yamaguchi, N.U.; Bracht, A.; Bracht, L.; Comar, J.F.; de Sá-Nakanishi, A.B.; de Souza, C.G.M.; Castoldi, R.; et al. Biotechnological, Nutritional, and Therapeutic Applications of Quinoa (Chenopodium Quinoa Willd.) and Its By-Products: A Review of the Past Five-Year Findings. Nutrients 2024, 16, 840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshpande, R.H.; Kumar, A.; Katare, M.; Sakhare, S.D.; Inamdar, A.A. Effect of Grinding Techniques and Supplementation of Quinoa on the Carbohydrate Profile of Tortillas. J Food Sci Technol 2022, 59, 3600–3608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abugoch James, L.E. Quinoa (Chenopodium Quinoa Willd.): Composition, Chemistry, Nutritional, and Functional Properties. Adv Food Nutr Res 2009, 58, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, R.L.J.; Santos, N.C.; Pereira, T. dos S.; Silva, V.M. de alcântara; Silva, L.N.; Santiago, Â.M.; Moreira, F.I.N.; Silva, L.R.I. da; Borges, E.M.E.S.; Queiroga, A.P.R. de Análise Morfológica Em Flocos de Arroz. Research, Society and Development 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camalan, M. Investigating the Effects of Random Sieving Losses on Particle Size Distributions. Particulate Science and Technology 2021, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camalan, M. Simulating Probabilistic Sampling on Particle Populations to Assess the Threshold Sample Sizes for Particle Size Distributions. Particulate Science and Technology 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camalan, M. Estimating the Number-Weighted Equivalents of the Mass-Weighted Size Distribution Functions. Powder Technol 2020, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colorado-Arango, L.; Menéndez-Aguado, J.M.; Osorio-Correa, A. Particle Size Distribution Models for Metallurgical Coke Grinding Products. Metals (Basel) 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, D.; Li, K.; Yan, X.; Lin, J. Rock Fragmentation Size Distribution Prediction and Blasting Parameter Optimization Based on the Muck-Pile Model. Min Metall Explor 2021, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Instituto Adolfo Lutz Métodos Físicos-Quimicos Para Análise de Alimentos; 2008;
- de Gusmão, R.P.; Cavalcanti-Mata, M.E.R.M.; Duarte, M.E.M.; Gusmão, T.A.S. Particle Size, Morphological, Rheological, Physicochemical Characterization and Designation of Minerals in Mesquite Flour (Proposis Julifrora). J Cereal Sci 2016, 69, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmisaoui, S.; Latifi, A.M.; Khamar, L. Analysis of the Dissolution of Phosphate Ore Particles in Phosphoric Acid: Influence of Particle Size Distribution. Hydrometallurgy 2024, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoyan, D.; Zhang, Z.X. A Stochastic Model Leading to Various Particle Mass Distributions Including the RRSB Distribution. Granul Matter 2023, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.; Xu, Z.; Li, Z.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, S.; Liu, Y. Study on the Relationship between the Particle Size Distribution Characteristics of Ground Granulated Blast Furnace Slag and Its Mortar Properties. Front Mater 2022, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.; Li, Z.; Zhao, S.; Zhao, X.; Qu, X. Study on the Particle Morphology, Powder Characteristics and Hydration Activity of Blast Furnace Slag Prepared by Different Grinding Methods. Constr Build Mater 2021, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrakis, E.; Komnitsas, K. Modeling of Bauxite Ore Wet Milling for the Improvement of Process and Energy Efficiency. Circular Economy and Sustainability 2022, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atrous, H.; Benbettaieb, N.; Chouaibi, M.; Attia, H.; Ghorbel, D. Changes in Wheat and Potato Starches Induced by Gamma Irradiation: A Comparative Macro and Microscopic Study. Int J Food Prop 2017, 20, 1532–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, C.; Jin, Y. ik; Kim, M.; Lee, Y.; Chang, Y.H. Structural and Rheological Properties of Potato Starch Affected by Degree of Substitution by Octenyl Succinic Anhydride. Int J Food Prop 2017, 20, 3076–3089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bock, P.; Cnops, G.; Muylle, H.; Quataert, P.; Eeckhout, M.; Van Bockstaele, F. Physicochemical Characterization of Thirteen Quinoa (Chenopodium Quinoa Willd.) Varieties Grown in North-West Europe—Part II. Plants 2022, 11, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, V.; Du, J.; Charrondière, U.R. Assessment of the Nutritional Composition of Quinoa (Chenopodium Quinoa Willd.). Food Chem 2016, 193, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhargava, A.; Shukla, S.; Ohri, D. Chenopodium Quinoa—An Indian Perspective. Ind Crops Prod 2006, 23, 73–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saffeir, J.B. Eating Some Invasive Species Could Help to Mitigate the Impacts of Climate Change-Related Invasions, and May Increase Future Food Security. Independent Study Project (ISP) Collection. School for International Training, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Q.; Wang, X.; Zou, X.; Zhang, X.; Zou, L.; Hu, X. Preparation of Multi-Grain Flour with High Content of Resistant Starch and the Mechanism Underlying the Improved Digestion Resistance. Starch/Staerke 2024, 76, 2300301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Song, S.; Wang, Y.; Sun, B.; Wang, X.; Ma, S. Structural Modification of Starch and Protein: From the Perspective of Gelatinization Degree of Oat Flour. Int J Biol Macromol 2024, 260, 129406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortiz-Gómez, V.; Nieto-Calvache, J.E.; Roa-Acosta, D.F.; Solanilla-Duque, J.F.; Bravo-Gómez, J.E. Preliminary Characterization of Structural and Rheological Behavior of the Quinoa Hyperprotein-Defatted Flour. Front Sustain Food Syst 2022, 6, 852332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ba, Y.B.; Li, R.; Zhang, J.Y.; Zou, L.; Wu, D.T.; Hu, Y.C. Evaluation of Lipidomics Profile of Quinoa Flour and Changes during Storage Based on Ultra Performance Liquid Chromatography Coupled with Quadrupole Exactive Orbitrap Mass Spectrometry. Foods 2023, 12, 4434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, O.L.; Lema, M.; Galeano, Y. V. Effect of Using Quinoa Flour (Chenopodium Quinoa Willd.) on the Physicochemical Characteristics of an Extruded Pasta. Int J Food Sci 2021, 2021, 8813354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covarrubias, N.; Sandoval, S.; Vera, J.; Núñez, C.; Alfaro, C.; Lutz, M.; Covarrubias, N.; Sandoval, S.; Vera, J.; Núñez, C.; et al. Contenido de Humedad, Proteínas y Minerales En Diez Variedades de Quínoa Chilena Cultivadas En Distintas Zonas Geográficas. Revista chilena de nutrición 2020, 47, 730–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laqui-Vilca, C.; Limaylla Guerrero, K.M.; Laqui, W. Características Del Grano y Almidón Obtenido de Ecotipos de Quinua (Chenopodium Quinoa Willd.) de Color Producido En El Altiplano Peruano. 2022. [CrossRef]
- Núñez-Santiago, M.C.; Bello-Pérez, L.A.; Tecante, A. Swelling-Solubility Characteristics, Granule Size Distribution and Rheological Behavior of Banana (Musa Paradisiaca) Starch. Carbohydr Polym 2004, 56, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, J.; Alazemi, A.; Ponnumani, P.; B. , B.T.; Soliman, M.; Emmanuval, L.; Thomas, N.M. Transformation of Quinoa Seeds to Nanoscale Flour by Ball Milling: Influence of Ball Diameter and Milling Time on the Particle Sizing, Microstructure, and Rheology. J Food Eng 2024, 379, 112127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Wu, D.; Guo, L.; Yao, Y.; Yao, X.; Wang, Z.; Wu, K.; Cao, X.; Gao, X. Effects of Quinoa Flour on Wheat Dough Quality, Baking Quality, and in Vitro Starch Digestibility of the Crispy Biscuits. Front Nutr 2022, 9, 846808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, H.; Xue, S.; Sun, Q.; Shi, J.; Zhang, D.; Wang, D.; Wei, J. Research Progress of Quinoa Seeds (Chenopodium Quinoa Wild.): Nutritional Components, Technological Treatment, and Application. Foods 2023, 12.
- Vilcacundo, R.; Hernández-Ledesma, B. Nutritional and Biological Value of Quinoa (Chenopodium Quinoa Willd.). Curr Opin Food Sci 2017, 14, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angeli, V.; Silva, P.M.; Massuela, D.C.; Khan, M.W.; Hamar, A.; Khajehei, F.; Graeff-Hönninger, S.; Piatti, C. Quinoa (Chenopodium Quinoa Willd.): An Overview of the Potentials of the “Golden Grain” and Socio-Economic and Environmental Aspects of Its Cultivation and Marketization. Foods 2020, Vol. 9, Page 216 2020, 9, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervilla, N.S.; Mufari, J.R.; Calandri, E.L.; Guzman, C.A. Determinación Del Contenido de Aminoácidos En Harina de Quinoa de Origen Argentino. Evaluación de Su Calidad Proteica. 2023.
- Craine, E.B.; Murphy, K.M. Seed Composition and Amino Acid Profiles for Quinoa Grown in Washington State. Front Nutr 2020, 7, 545066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos-Rodriguez, J.; Acosta-Coral, K.; Paucar-Menacho, L.M.; Campos-Rodriguez, J.; Acosta-Coral, K.; Paucar-Menacho, L.M. Quinua (Chenopodium Quinoa): Composición Nutricional y Componentes Bioactivos Del Grano y La Hoja, e Impacto Del Tratamiento Térmico y de La Germinación. Scientia Agropecuaria 2022, 13, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navruz-Varli, S.; Sanlier, N. Nutritional and Health Benefits of Quinoa (Chenopodium Quinoa Willd.). J Cereal Sci 2016, 69, 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filho, A.M.M.; Pirozi, M.R.; Borges, J.T.D.S.; Pinheiro Sant’Ana, H.M.; Chaves, J.B.P.; Coimbra, J.S.D.R. Quinoa: Nutritional, Functional, and Antinutritional Aspects. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 2017, 57, 1618–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, M.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, R.; Chen, H.; Wu, J.; Xu, J.; Tu, K.; Shi, J.; Sun, X. Basic Nutrients and UPLC- ZenoTOF-MS/MS Based Lipomics Analysis of Chenopodium Quinoa Willd. Varieties. Food Production, Processing and Nutrition 2024, 6, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özer, C.O.; Seçen, S.M. Effects of Quinoa Flour on Lipid and Protein Oxidation in Raw and Cooked Beef Burger during Long Term Frozen Storage. Food Science and Technology 2018, 38, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajbli, N.; Zine-eddine, Y.; Laaraj, S.; Ait El Alia, O.; Elfazazi, K.; Bouhrim, M.; Herqash, R.N.; Shahat, A.A.; Benbati, M.; Kzaiber, F.; et al. Effect of Quinoa Flour on Fermentation, Physicochemical and Sensory Properties of Goat Milk Yogurt. Front Sustain Food Syst 2025, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mufari, J.R.; Miranda-Villa, P.P.; Calandri, E.L. Quinoa Germ and Starch Separation by Wet Milling, Performance and Characterization of the Fractions. LWT 2018, 96, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Li, J.; Ji, J.; Wen, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, J.; Sun, B. Endogenous Protein and Lipid Facilitate the Digestion Process of Starch in Cooked Quinoa Flours. Food Hydrocoll 2023, 134, 108099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, P.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Xiao, X. The Effect of Protein–Starch Interaction on the Structure and Properties of Starch, and Its Application in Flour Products. Foods 2025, Vol. 14, Page 778 2025, 14, 778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jebalia, I.; Maigret, J.E.; Réguerre, A.L.; Novales, B.; Guessasma, S.; Lourdin, D.; Della Valle, G.; Kristiawan, M. Morphology and Mechanical Behaviour of Pea-Based Starch-Protein Composites Obtained by Extrusion. Carbohydr Polym 2019, 223, 115086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerkovic, A.; Kriegel, A.M.; Bradner, J.R.; Atwell, B.J.; Roberts, T.H.; Willows, R.D. Strategic Distribution of Protective Proteins within Bran Layers of Wheat Protects the Nutrient-Rich Endosperm. Plant Physiol 2010, 152, 1459–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelgrom, P.J.M.; Boom, R.M.; Schutyser, M.A.I. Method Development to Increase Protein Enrichment During Dry Fractionation of Starch-Rich Legumes. Food Bioproc Tech 2015, 8, 1495–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simsek, S.; Baasandorj, T.; Dykes, L.; Ohm, J.B. Study of Hard Red Spring Wheat Millstreams on the Correlation between Protein Molecular Weight Parameters and Bread-Making Quality. Cereal Chem 2023, 100, 1357–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamothe, L.M.; Srichuwong, S.; Reuhs, B.L.; Hamaker, B.R. Quinoa (Chenopodium Quinoa W.) and Amaranth (Amaranthus Caudatus L.) Provide Dietary Fibres High in Pectic Substances and Xyloglucans. Food Chem 2015, 167, 490–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bravi, E.; Sileoni, V.; Marconi, O. Quinoa (Chenopodium Quinoa Willd.) as Functional Ingredient for the Formulation of Gluten-Free Shortbreads. Foods 2024, 13, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsuhaibani, A.M.; Alkuraieef, A.N.; Aljobair, M.O.; Alshawi, A.H. Technological, Sensory, and Hypoglycemic Effects of Quinoa Flour Incorporation into Biscuits. J Food Qual 2022, 2022, 6484953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haros, C.M.; Reguera, M.; Sammán, N.; Paredes-López, O. Latin-American Seeds: Agronomic, Processing and Health Aspects. Latin-American Seeds: Agronomic, Processing and Health Aspects. [CrossRef]
- Elbendari, A.M.; Ibrahim, S.S. Optimizing Key Parameters for Grinding Energy Efficiency and Modeling of Particle Size Distribution in a Stirred Ball Mill. Sci Rep 2025, 15, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Liu, P.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, X.; Wang, H.; Gui, X. Design Boundary Layer Structure for Improving the Particle Separation Performance of a Hydrocyclone. Powder Technol 2019, 350, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, S.; Manthey, F.A. Effect of Different Mills on the Physical and Flow Properties of Selected Black Bean Flour Particle Size Fractions. Cereal Chem 2022, 99, 751–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AmanNejad, M.; Barani, K. Effects of Ball Size Distribution and Mill Speed and Their Interactions on Ball Milling Using DEM. Mineral Processing and Extractive Metallurgy Review 2021, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Huang, Q.; Xiao, J.; Wang, Y. Milled Miscellaneous Black Rice Particles Stabilized Pickering Emulsions with Enhanced Antioxidation Activity. Food Chem 2022, 385, 132639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruszelnicka, W.; Opielak, M.; Ambrose, K.; Pukalskas, S.; Tomporowski, A.; Walichnowska, P. Energy-Dependent Particle Size Distribution Models for Multi-Disc Mill. Materials 2022, 15, 6067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barretto, R.; Buenavista, R.M.; Pandiselvam, R.; Siliveru, K. Influence of Milling Methods on the Flow Properties of Ivory Teff Flour. J Texture Stud 2022, 53, 820–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeulin, M.; Cahuc, O.; Darnis, P.; Laheurte, R. A 6-Components Mechanistic Model of Cutting Forces and Moments in Milling. Forces in Mechanics 2022, 9, 100130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mete, E.; Haszard, J.; Perry, T.; Oey, I.; Mann, J.; Morenga, L. Te Effect of Wholegrain Flour Particle Size in Bread on Glycaemic and Insulinaemic Response among People with Risk Factors for Type 2 Diabetes: A Randomised Crossover Trial. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballester-Sánchez, J.; Gil, J. V.; Fernández-Espinar, M.T.; Haros, C.M. Quinoa Wet-Milling: Effect of Steeping Conditions on Starch Recovery and Quality. Food Hydrocoll 2019, 89, 837–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribera-Castelló, A.; Haros, C.M. Obtaining Quinoa Germ via Wet Milling and Extracting Its Oil via Cold Pressing. Biology and Life Sciences Forum 2023, Vol. 25, Page 3 2023, 25, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, A.; Muhammed Muneer, B.M.; Sakhare, S.D. Analysis of Quinoa Roller Millstreams: Physical, Chemical, and Functional Properties. J Cereal Sci 2024, 117, 103890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Han, X.; Chen, D.-L.; Ren, Y.-P.; Yang, S.-Y.; Huang, Y.-X.; Yang, J.; Zhang, L. Dry Ball-Milled Quinoa Starch as a Pickering Emulsifier: Preparation, Microstructures, Hydrophobic Properties and Emulsifying Properties. Foods 2024, 13, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aweya, J.J.; Sharma, D.; Bajwa, R.K.; Earnest, B.; Krache, H.; Moghadasian, M.H. Ancient Grains as Functional Foods: Integrating Traditional Knowledge with Contemporary Nutritional Science. Foods 2025, Vol. 14, Page 2529 2025, 14, 2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar Pathak, M.; Patel, T. Quinoa: A History of Ancient Grains and Modern Diets. Agriculture & Food: E-Newsletter, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Li, L.; Zheng, X. A Review of Milling Damaged Starch: Generation, Measurement, Functionality and Its Effect on Starch-Based Food Systems. Food Chem 2020, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, Y.G.; Loubes, M.A.; González, L.C.; Tolaba, M.P. Energy-Size Relationship and Starch Modification in Planetary Ball Milling of Quinoa. J Cereal Sci 2024, 119, 104004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, B.; Cheng, B.; Song, X.; Ji, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z. Experimental Study on the Influence of Rotational Speed on Grinding Efficiency for the Vertical Stirred Mill. Minerals 2024, Vol. 14, Page 1208 2024, 14, 1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Gao, P.; Tang, Z.; Han, Y.; Meng, X. Effect of Grinding Media Properties and Stirrer Tip Speed on the Grinding Efficiency of a Stirred Mill. Powder Technol 2021, 382, 556–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhumathi, R.; Prashanth, K.V.H.; Inamdar, A.A. Fractionation of Roller-Milled Quinoa: Evaluation of Functional and Nutritional Properties of Different Fractions. Journal of Food Measurement and Characterization 2025, 19, 4191–4202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Jing, L.; Wang, D.; Bao, F.; Lu, W.; Wang, G. Grain and Starch Granule Morphology in Superior and Inferior Kernels of Maize in Response to Nitrogen. Sci Rep 2018, 8, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvador-Reyes, R.; Rebellato, A.P.; Lima Pallone, J.A.; Ferrari, R.A.; Clerici, M.T.P.S. Kernel Characterization and Starch Morphology in Five Varieties of Peruvian Andean Maize. Food Research International 2021, 140, 110044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y. The Fractal Evolution of Particle Fragmentation under Different Fracture Energy. Powder Technol 2018, 323, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alina Marc, R.; Valero Díaz, A.; Posada Izquierdo, G.D. Food Processing. IntechOpen 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Wang, X.; Ma, S.; Sun, B.; Li, L.; Wang, Z. Study of the Ball Milling Condition Effect on Physicochemical and Structural Characteristics of Wheat Flour. J Food Process Preserv 2022, 46, e16203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Pu, D.; Hao, Z.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Y. The Effect of Prickly Ash (Zanthoxylum Bungeanum Maxim) on the Taste Perception of Stewed Sheep Tail Fat by Lc-Qtof-Ms/Ms and a Chemometrics Analysis. Foods 2021, 10, 2709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, Y.; Zhong, W.; Yang, C.; Klahn, E.; Grosshans, H. Modeling the Agglomeration of Electrostatically Charged Particles. J Phys Conf Ser 2019, 1322, 012026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO/WHO Platform of Information on Quinoa. Available online: https://www.fao.org/in-action/quinoa-platform/en/ (accessed on 27 July 2025).
- Contreras-Jiménez, B.; Torres-Vargas, O.L.; Rodríguez-García, M.E. Physicochemical Characterization of Quinoa (Chenopodium Quinoa) Flour and Isolated Starch. Food Chem 2019, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bangar, S.P.; Singh, A.; Ashogbon, A.O.; Bobade, H. Ball-Milling: A Sustainable and Green Approach for Starch Modification. Int J Biol Macromol 2023, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Pérez, J.E.; Romo-Hernández, A.; Ramírez-Corona, N.; López-Malo, A. Modeling Mass Transfer during Osmodehydration of Apple Cubes with Sucrose or Apple Juice Concentrate Solutions: Equilibrium Estimation, Diffusion Model, and State Observer-Based Approach. J Food Process Eng 2022, 45, e14125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junejo, S.A.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Jia, R.; Zhou, Y.; Li, S. Multi-Scale Structures and Functional Properties of Quinoa Starch Extracted by Alkali, Wet-Milling, and Enzymatic Methods. Foods 2022, Vol. 11, Page 2625 2022, 11, 2625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.; Kataria, A.; Singh, B. Effect of Thermal Processing on the Bioactive Compounds, Antioxidative, Antinutritional and Functional Characteristics of Quinoa (Chenopodium Quinoa). LWT 2022, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira-de-Almeida, C.A.; Ribas Filho, D. Positioning on the Use of Polyols as Table Sweeteners. International Journal of Nutrology 2021, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Kashyap, S.; Singh, S. Exploring the Advances in Quinoa Processing: A Comprehensive Review Enhancing Nutritional Quality and Health Benefits along with Industrial Feasibility of Quinoa. Food Research International 2025, 206, 116093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, E.; Encina-Zelada, C.; Barros, L.; Gonzales-Barron, U.; Cadavez, V.; C. F.R. Ferreira, I. Chemical and Nutritional Characterization of Chenopodium Quinoa Willd (Quinoa) Grains: A Good Alternative to Nutritious Food. Food Chem 2019, 280, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, N.; Ureta, M.M.; Guerrero-Sánchez, M.; Gómez-Zavaglia, A. Nutritional and Technological Properties of a Quinoa (Chenopodium Quinoa Willd.) Spray-Dried Powdered Extract. Food Research International 2020, 129, 108884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Du, C.; Guo, Y.; Fu, J.; Jiang, W.; Du, S. kui Physicochemical and Structural Properties of Starches Isolated from Quinoa Varieties. Food Hydrocoll 2020, 101, 105515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Londoño-Restrepo, S.M.; Rincón-Londoño, N.; Contreras-Padilla, M.; Millan-Malo, B.M.; Rodriguez-Garcia, M.E. Morphological, Structural, Thermal, Compositional, Vibrational, and Pasting Characterization of White, Yellow, and Purple Arracacha Lego-like Starches and Flours (Arracacia Xanthorrhiza). Int J Biol Macromol 2018, 113, 1188–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salman, H.; Blazek, J.; Lopez-Rubio, A.; Gilbert, E.P.; Hanley, T.; Copeland, L. Structure–Function Relationships in A and B Granules from Wheat Starches of Similar Amylose Content. Carbohydr Polym 2009, 75, 420–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Hu, J.; Sha, X.; Meng, D.; Yang, R. Phycobiliproteins, the Pigment-Protein Complex Form of Natural Food Colorants and Bioactive Ingredients. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 2022.
- Li, G.; Zhu, F. Quinoa Starch: Structure, Properties, and Applications. Carbohydr Polym 2018, 181, 851–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, L.C.; Loubes, M.A.; Tolaba, M.P. Incidence of Milling Energy on Dry-Milling Attributes of Rice Starch Modified by Planetary Ball Milling. Food Hydrocoll 2018, 82, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bala, S.; Garg, D.; Thirumalesh, B.V.; Sharma, M.; Sridhar, K.; Inbaraj, B.S.; Tripathi, M. Recent Strategies for Bioremediation of Emerging Pollutants: A Review for a Green and Sustainable Environment. Toxics 2022, Vol. 10, Page 484 2022, 10, 484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Sun, R.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Guan, X.; Huang, K.; Zhang, Y. Appropriate Microwave Improved the Texture Properties of Quinoa Due to Starch Gelatinization from the Destructed Cyptomere Structure. Food Chem X 2022, 14, 100347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Mill Type | Sieve (mesh) | Average Size (µm) | Retained Mass (g) | |||
| Knife | 16 | 991 | 0.780±0.017a‡ | 6.90 | -0.0078±1.71E-04a | 1.5801±0.0040a |
| 32 | 495 | 15.82±0.001b | 6.20 | -0.1719±1.19E-05a | 0.6128±3.42E-05a | |
| 60 | 248 | 60.39±0.231c | 5.51 | -0.9235±0.006a | -0.6811±0.0080a | |
| 80 | 175 | 9.100±0.079d | 5.16 | -0.0952±0.001a | 0.8749±0.0040a | |
| 115 | 124 | 9.160±0.058d | 4.82 | -0.0959±0.001a | 0.8721±0.0030a | |
| 200 | 74 | 3.830±0.011e | 4.30 | -0.0390±1.14E-04a | 1.1830±0.0010a | |
| Tray | - | 1.090±0.027ae | - | - | - | |
| Disc | 16 | 991 | 0.040±0.028a | 6.900 | -0.0004±2.80E-04a | 2.0574±0.1090a |
| 32 | 495 | 7.300±0.011b | 6.200 | -0.0757±1.18E-04a | 0.9628±0.0010a | |
| 60 | 248 | 42.53±0.024b | 5.510 | -0.5527±4.16E-04a | -0.1548±0.0010a | |
| 80 | 175 | 17.14±0.032c | 5.160 | -0.1877±3.85E-04a | 0.5684±0.0010a | |
| 115 | 124 | 15.67±0.090c | 4.822 | -0.1701±0.0010a | 0.6179±0.0030a | |
| 200 | 74 | 10.76±0.010bc | 4.300 | -0.1136±1.12E-04a | 0.8024±4.17E-04a | |
| Tray | - | 6.720±0.012b | - | - | - | |
| Ball | 16 | 991 | 0.090±0.084a | 6.900 | -0.0009±0.0010a | 1.9479±0.2230a |
| 32 | 495 | 14.74±0.002b | 6.200 | -0.1594±2.34E-05a | 0.6498±7.08E-05a | |
| 60 | 248 | 61.29±0.017c | 5.510 | -0.9481±4.38E-04a | -0.7130±0.0010a | |
| 80 | 175 | 17.47±0.046b | 5.160 | -0.1919±0.0010a | 0.5569±0.0020a | |
| 115 | 124 | 5.660±0.008b | 4.820 | -0.0582±8.47E-05a | 1.0551±4.92E-04a | |
| 200 | 74 | 0.690±0.051a | 4.300 | -0.0069±0.0010a | 1.6048±0.0150a | |
| Tray | - | 0.120±0.002a | - | - | - |
| Types of crystallinity | Intensity peaks at the diffraction angle 2θ |
|---|---|
| A | 15.3°| 17.1° | 18.2° | 23.5° |
| B | 5.6°| 14.4°| 17.2°| 22.2°| 24° |
| C | 5.6°| 15.3°| 17.3°| 23.5° |
| Flours | |||
| Parameters | F1 | F2 | F3 |
| TO (°C) (gelatinisation) | 50.19±0.01ª⁑ | 50.04±0.02b | 50.08±0.02ab |
| TP (°C) | 79.35±0.03ª | 71.68±0.09ab | 70.47±0.02b |
| TP – TO (°C) | 29.16±0.03ª | 21.64±0.09ab | 20.39±0.04b |
| ΔH (J/g) (enthalpy of gelatinisation) | 1791±0.71ª | 1211±0.71b | 1221±1.10c |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





