Submitted:
28 April 2025
Posted:
29 April 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Design and Data Sources
2.2. Data Mining Algorithm
3. Results
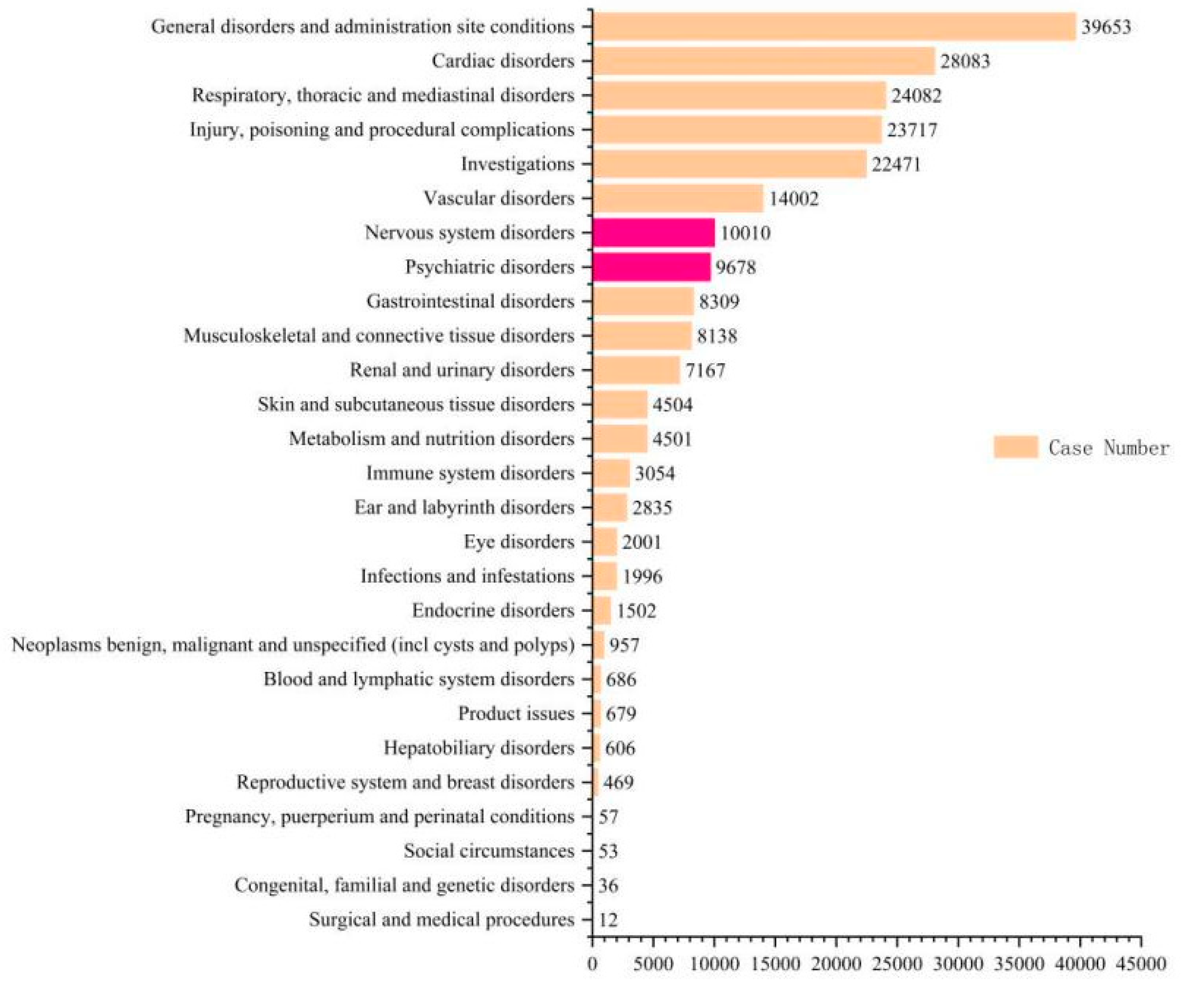
3.1. Descriptive Results
3.2. Signal Values Associated with Sacubitril/Valsartan
3.3. Analysis of Nervous System and Psychiatric Disorders Associated with Sacubitril/Valsartan
3.4. Distribution of Preferred Terms (PTs) for Neuropsychiatric Adverse Events
3.5. Analysis of PT deaths in neuropsychiatric symptoms ADEs
4. Discussion
References
- Lavie, C. J. Progress in Cardiovascular Diseases Statistics 2022. Prog Cardiovasc Dis., 2022,73:94-95. [CrossRef]
- Huang, E.; Bernard, M.L.; Elise Hiltbold, A.; Khatib, S.; Polin, G.M.; Rogers, P.A.; Dominic, P.; Morin, D.P. Sacubitril/valsartan: An antiarrhythmic drug? J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol., 2022,33(11):2375-2381. [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Yang, H. Comparison of sacubitril/valsartan with olmesartan for hypertension: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Medicine., 2024,103(14), e37501. [CrossRef]
- Mann, D.L.; Givertz, M.M.; Vader, J.M.; Starling, R.C.; Shah, P.; McNulty; S.E.; Anstrom, K.J.; Margulies, K.B.; Kiernan, M.S.; Mahr, C.; et al. Effect of Treatment With Sacubitril/Valsartan in Patients With Advanced Heart Failure and Reduced Ejection Fraction: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA cardiology., 2022,7(1), 17–25. [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Li, C.; Zhang, X. Sacubitril/valsartan improves the prognosis of acute myocardial infarction: a meta-analysis. Coronary artery disease., 2024,35(3), 231–238. [CrossRef]
- Kuang, H.; Huang, X.; Zhou, Z.; Cheng, X.; Xu, G. Sacubitril/valsartan in chronic kidney disease: From pharmacological mechanism to clinical application. European journal of pharmacology., 2021,907, 174288. [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, S.; McMurray, J.J.V.; Nasu, T.; Ishii, S.; Kagiyama, N.; Kida, K.; Fujimoto, W.; Kikuchi, A.; Ijichi, T.; Shibata, T.; et al. Relevant adverse events and drug discontinuation of sacubitril/valsartan in a real-world Japanese cohort: REVIEW-HF registry. Journal of cardiology., 2024,84(2), 133–140. [CrossRef]
- Galo, J.; Celli, D.; Colombo, R. Effect of Sacubitril/Valsartan on Neurocognitive Function: Current Status and Future Directions. American journal of cardiovascular drugs : drugs, devices, and other interventions., 2021,21(3), 267–270. [CrossRef]
- Watamura, N.; Kakiya, N.; Fujioka, R.; Kamano, N.; Takahashi, M.; Nilsson, P.; Saito, T.; Iwata, N.; Fujisawa, S.; Saido, T.C. The dopaminergic system promotes neprilysin-mediated degradation of amyloid-β in the brain. Science signaling., 2024,17(848), eadk1822. [CrossRef]
- Garnier-Crussard, A. Association between treatment with sacubitril/valsartan and the risk of Alzheimer's disease: a clinical update. Alzheimer's research & therapy., 2024,16(1), 177. [CrossRef]
- Morris, R.; Ali, R.; Cheng, F. Drug Repurposing Using FDA Adverse Event Reporting System (FAERS) Database. Current drug targets., 2024,25(7), 454–464. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Hu, M.; Liang, Y.; Zhong, M.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Luo, Z.; Zeng, W.; Li, J.; et al. Pharmacovigilance analysis of orlistat adverse events based on the FDA adverse event reporting system (FAERS) database. Heliyon., 2024,10(14), e34837. [CrossRef]
- Docherty, K.F.; Vaduganathan, M.; Solomon, S.D.; McMurray, J.J.V. Sacubitril/Valsartan: Neprilysin Inhibition 5 Years After PARADIGM-HF. JACC. Heart failure., 2020,8(10), 800–810. [CrossRef]
- Tian, Q.; Xiong, Z.; Fan, H.; Ning, T.; Zheng, Z. The Efficacy and Safety of Sacubitril-Valsartan for the Treatment of Heart Failure in Adults: A Meta-Analysis. The Annals of pharmacotherapy., 2023,57(4), 441–449. [CrossRef]
- Erdogan, B.R.; Yesilyurt-Dirican, Z.E.; Karaomerlioglu, I.; Muderrisoglu, A.E.; Sevim, K.; Michel, M.C.; Arioglu-Inan, E. Sacubitril/Valsartan Combination Partially Improves Cardiac Systolic, but Not Diastolic, Function through β-AR Responsiveness in a Rat Model of Type 2 Diabetes. Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 2;25(19):10617. PMID: 39408945; PMCID: PMC11476658. [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.; Kim, H.; Jedrychowski, M.P.; Bakiasi, G.; Park, J.; Kruskop, J.; Choi, Y.; Kwak, S.S.; Quinti, L.; Kim, D.Y.; et al. Irisin reduces amyloid-β by inducing the release of neprilysin from astrocytes following downregulation of ERK-STAT3 signaling. Neuron., 2023,111(22), 3619–3633.e8. [CrossRef]
- Ali, N. H.; Al-Kuraishy, H. M. ; Al-Gareeb, A. I.; Alnaaim, S. A.; Alexiou, A.; Papadakis, M.; Khalifa, A.A; Saad, H.M; Batihaet, E.S. Neprilysin inhibitors and risk of Alzheimer's disease: A future perspective. Journal of cellular and molecular medicine., 2024,28(2), e17993. [CrossRef]
- Qian, C.; Yang, C.; Lu, M.; Bao, J.; Shen, H.; Deng, B.; Li, S.; Li, W.; Zhang, M.; Cao, C. Activating AhR alleviates cognitive deficits of Alzheimer's disease model mice by upregulating endogenous Aβ catabolic enzyme Neprilysin. Theranostics., 2021,11(18), 8797–8812. [CrossRef]
- Dargad, R.R.; Prajapati, M.R.; Dargad, R.R.; Parekh, J.D. Sacubitril/valsartan: A novel angiotensin receptor-neprilysin inhibitor. Indian heart journal., 2018,70 Suppl 1(Suppl 1), S102–S110. [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Jin, Y.; Xue, H.; Liu, R.; Zhang, M.; Liao, R.; Chen, M.; Zhou, X.; He, X.; Qin, M.; et al. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of sacubitril/valsartan in peritoneal dialysis patients. Nephrology, dialysis, transplantation : official publication of the European Dialysis and Transplant Association - European Renal Association., 2023,38(8), 1880–1889. [CrossRef]
- Langenickel, T.H.; Tsubouchi, C.; Ayalasomayajula, S.; Pal, P.; Valentin, M.A.; Hinder, M.; Jhee, S.; Gevorkyan, H.; Rajman, I. The effect of LCZ696 (sacubitril/valsartan) on amyloid-β concentrations in cerebrospinal fluid in healthy subjects. British journal of clinical pharmacology., 2016,81(5), 878–890. [CrossRef]
- Schoenfeld, H.A.; West, T.; Verghese, P.B.; Holubasch, M.; Shenoy, N.; Kagan, D.; Buono, C.; Zhou, W.; DeCristofaro, M.; Douville, J.; et al. The effect of angiotensin receptor neprilysin inhibitor, sacubitril/valsartan, on central nervous system amyloid-β concentrations and clearance in the cynomolgus monkey. Toxicology and applied pharmacology., 2017,323, 53–65. [CrossRef]
- Pena, O.Y.; Kyung, K. Drug-Induced Delirium Associated With Sacubitril/Valsartan in a Patient With Chronic Kidney Disease: A Case Report. Cureus., 2024,16(10), e72524. [CrossRef]
- Martins E Pereira, G. et al., Safety and tolerability of sacubitril-valsartan: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Expert opinion on drug safety., 2021,20(5), 577–588. [CrossRef]
- Dewan, P.; Shen, L.; Pedro Ferreira, J.; Jhund, P.S.; Anand, I.S.; Chandra, A.; Chiang, L.M.; Claggett, B.; Desai, A.S.; Gong, J.; et al. Effect of Sacubitril/Valsartan on Cognitive Function in Patients With Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction: A Prespecified Analysis of PARAGON-HF. Circulation., 2024,150(4), 272–282. [CrossRef]
- Hammadi, S.H.; Hassan, M.A.; Allam, E.A.; Elsharkawy, A.M.; Shams, S.S. Effect of sacubitril/valsartan on cognitive impairment in colchicine-induced Alzheimer's model in rats. Fundamental & clinical pharmacology., 2023,37(2), 275–286. [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Roselló, V.; Batalla-Monedero, M.; Sánchez-Lázaro, I.; López-Vilella, R.; Sierra-San Miguel, P.; Almenar-Bonet, L. Three cases of psychosis after use of sacubitril/valsartan. Revista espanola de cardiologia (English ed.)., 2021,74(1), 103–105. [CrossRef]
- Wooster, J.; Cook, E.A.; Shipman, D. Psychiatric Manifestations With Sacubitril/Valsartan: A Case Report. Journal of pharmacy practice., 2020,33(4), 553–557. [CrossRef]
| Algorithms | Equation | Criteria |
| ROR | ROR =(a / c)/(b / d) 95%CI = eln.ROR±1.96(1/a+1/b+1/c+1/d)^0.5 |
a ≥ 3, lower limit of 95% CI > 1 |
| PRR | PRR = a(c + d)/c(a + b) χ2 = [(ad - bc)2](a + b + c + d)/[(a + b)(c + d)(a + c)(b + d)] |
a ≥ 3, PRR ≥ 2, χ2 ≥ 4 |
| Variables | Characteristics | Case number, n | Case proportion, % |
| Gender | Female | 29311 | 33.05 |
| Male | 53018 | 59.79 | |
| Unknown | 6346 | 7.16 | |
| Age (year) | <18 | 42 | 0.05 |
| 18-44 | 1270 | 1.43 | |
| 45-64 | 8071 | 9.1 | |
| ≥65 | 12907 | 14.56 | |
| Unknown | 66385 | 74.86 | |
| Outcome of ADEs | Unknown | 48229 | 54.39 |
| Other | 16534 | 18.65 | |
| Death | 12747 | 14.37 | |
| Hospitalization - Initial or Prolonged | 9742 | 10.99 | |
| Life-Threatening | 1051 | 1.19 | |
| Disability | 363 | 0.41 | |
| Required Intervention to Prevent Permanent Impairment | 7 | 0.01 | |
| Congenital Anomaly | 2 | 0 | |
| Reported Countries | United States | 46045 | 51.93 |
| Japan | 1640 | 1.85 | |
| India | 1468 | 1.66 | |
| Philippines | 981 | 1.11 | |
| Germany | 802 | 0.9 | |
| France | 579 | 0.65 | |
| China | 531 | 0.6 | |
| Brazil | 517 | 0.58 | |
| Other | 4840 | 5.46 | |
| Country Not Specified | 31272 | 35.27 | |
| Reported years | 2023 | 12043 | 13.58 |
| 2022 | 19189 | 21.64 | |
| 2021 | 14268 | 16.09 | |
| 2020 | 8678 | 9.79 | |
| 2019 | 11979 | 13.51 | |
| 2018 | 10842 | 12.23 | |
| 2017 | 6465 | 7.29 | |
| 2016 | 4574 | 5.16 | |
| 2015 | 637 | 0.72 |
| PT | N | ROR(95%CI) | PRR(X2) |
| Hypotension | 8609 | 15.94(16.32-15.56) | 14.49(4173449.39) |
| Death | 8377 | 2.26(2.31-2.20) | 2.14(30080690.27) |
| Wrong technique in product usage process | 6577 | 5.79(5.94-5.65) | 5.44(9243891.4) |
| Dizziness | 6349 | 3.94(4.05-3.84) | 3.73(13168883.04) |
| Dyspnoea | 6277 | 3.60(3.70-3.51) | 3.42(14234157.38) |
| Cough | 6223 | 7.21(7.41-7.02) | 6.78(6943847.31) |
| Fatigue | 6139 | 2.23(2.28-2.17) | 2.14(22277132.74) |
| Weight decreased | 3861 | 4.56(4.72-4.42) | 4.41(6789523.83) |
| Malaise | 3485 | 2.08(2.15-2.01) | 2.04(13487983.1) |
| Cardiac failure | 2865 | 11.66(12.12-11.21) | 11.31(1840646.56) |
| Asthenia | 2587 | 2.25(2.34-2.16) | 2.21(9259604.37) |
| Weight increased | 2575 | 3.59(3.74-3.45) | 3.52(5737334.15) |
| Myocardial infarction | 2466 | 7.21(7.51-6.91) | 7.03(2658752.04) |
| Blood pressure decreased | 2256 | 12.62(13.19-12.07) | 12.32(1318323.16) |
| Inappropriate schedule of product administration | 2248 | 3.03(3.16-2.90) | 2.98(5953164.97) |
| Hypoacusis | 2120 | 9.95(10.41-9.51) | 9.74(1608134.65) |
| Feeling abnormal | 2060 | 2.27(2.37-2.17) | 2.24(7297335.07) |
| Cardiac disorder | 1924 | 6.31(6.62-6.03) | 6.2(2375626.01) |
| Memory impairment | 1807 | 3.39(3.56-3.24) | 3.34(4253697.31) |
| Hypertension | 1795 | 2.76(2.89-2.63) | 2.72(5218151.4) |
| Ejection fraction decreased | 1730 | 45.46(48.17-42.9) | 44.59(211321.34) |
| Fluid retention | 1673 | 10.00(10.53-9.51) | 9.83(1256056.74) |
| Peripheral swelling | 1562 | 2.42(2.55-2.30) | 2.39(5181575.16) |
| Prescribed underdose | 1516 | 17.21(18.19-16.29) | 16.94(616643.97) |
| Cerebrovascular accident | 1473 | 3.04(3.20-2.89) | 3.01(3872691.21) |
| Chest pain | 1367 | 2.69(2.84-2.55) | 2.66(4072939.37) |
| Nasopharyngitis | 1363 | 2.21(2.34-2.10) | 2.19(4947533.12) |
| Throat clearing | 1328 | 146.52(159.82-134.34) | 144.35(28130.31) |
| Atrial fibrillation | 1272 | 4.11(4.35-3.89) | 4.07(2448626.26) |
| Illness | 1099 | 2.54(2.70-2.39) | 2.52(3465002.82) |
| Blood potassium increased | 1021 | 25.62(27.47-23.89) | 25.34(257076.92) |
| Cardiac failure congestive | 980 | 6.73(7.18-6.31) | 6.67(1121437.23) |
| Diabetes mellitus | 947 | 3.98(4.24-3.72) | 3.94(1883814.82) |
| Renal impairment | 935 | 2.86(3.05-2.68) | 2.84(2610776.82) |
| Weight fluctuation | 890 | 31.18(33.65-28.89) | 30.88(175269.93) |
| Cardiac arrest | 868 | 3.88(4.16-3.63) | 3.86(1768420.9) |
| Heart rate increased | 844 | 2.81(3.01-2.62) | 2.79(2398489.81) |
| Renal disorder | 821 | 4.60(4.93-4.29) | 4.56(1402732.06) |
| Underdose | 792 | 2.34(2.51-2.18) | 2.33(2715268.83) |
| Product prescribing error | 790 | 6.56(7.06-6.11) | 6.51(926968.3) |
| Heart rate decreased | 769 | 6.81(7.33-6.33) | 6.76(866916.76) |
| Blood creatinine increased | 753 | 3.95(4.25-3.67) | 3.93(1505041.68) |
| Swelling | 743 | 2.23(2.40-2.07) | 2.22(2676216.69) |
| Dehydration | 724 | 2.03(2.19-1.89) | 2.02(2864971.08) |
| Syncope | 670 | 2.08(2.24-1.92) | 2.07(2588998.16) |
| Stress | 630 | 2.68(2.90-2.47) | 2.67(1880648.6) |
| Rhinorrhoea | 621 | 2.69(2.92-2.49) | 2.68(1843046.36) |
| Pollakiuria | 594 | 4.42(4.80-4.07) | 4.4(1055264.21) |
| Pulmonary oedema | 562 | 4.37(4.76-4.01) | 4.35(1011052.68) |
| Hyperkalaemia | 547 | 5.05(5.50-4.63) | 5.02(846078.03) |
| Variables | Characteristics | Number of cases of psychoneurotic symptoms | Case proportion, % |
| Gender | Female | 7533 | 38.26 |
| Male | 11580 | 58.82 | |
| Unknown | 575 | 2.92 | |
| <18 | 0 | 0 | |
| Age (year) | 18-44 | 289 | 1.47 |
| 45-64 | 2323 | 11.8 | |
| ≥65 | 2831 | 14.38 | |
| Unknown | 14245 | 72.35 | |
| Outcome of ADEs | Unknown | 7268 | 36.92 |
| Other | 7891 | 40.08 | |
| Death | 708 | 3.6 | |
| Hospitalization - Initial or Prolonged | 2961 | 15.04 | |
| Life-Threatening | 698 | 3.55 | |
| Disability | 159 | 0.81 | |
| Required Intervention to Prevent Permanent Impairment | 3 | 0.02 | |
| Congenital Anomaly | 0 | 0 | |
| Reported Countries | United States | 12379 | 62.88 |
| Japan | 130 | 0.66 | |
| India | 51 | 0.26 | |
| Philippines | 127 | 0.65 | |
| Germany | 156 | 0.79 | |
| France | 67 | 0.34 | |
| China | 29 | 0.15 | |
| Brazil | 203 | 1.03 | |
| Other | 997 | 5.06 | |
| Country Not Specified | 5549 | 28.18 | |
| Reported years | 2023 | 3735 | 18.97 |
| 2022 | 5329 | 27.07 | |
| 2021 | 3564 | 18.1 | |
| 2020 | 1949 | 9.9 | |
| 2019 | 2282 | 11.59 | |
| 2018 | 1568 | 7.96 | |
| 2017 | 857 | 4.35 | |
| 2016 | 375 | 1.9 | |
| 2015 | 29 | 0.15 |
| SOC | PT | N | ROR(95%CI) | PRR(X2) |
| Psychiatric disorders | Memory impairment | 1807 | 3.39(3.56-3.24) | 2.43(1642487.56) |
| Stress | 630 | 2.68(2.9-2.47) | 2.28(376033.75) | |
| Amnesia | 501 | 2.44(2.67-2.23) | 2.73(11607.78) | |
| Fear | 145 | 2.19(2.58-1.86) | 4.19(26138.87) | |
| Dementia Alzheimer's type | 114 | 3.2(3.86-2.66) | 3.08(23126.67) | |
| Aphonia | 107 | 2.28(2.76-1.88) | 2.87(55401.95) | |
| Frustration tolerance decreased | 91 | 2.14(2.63-1.74) | 3.12(50875.05) | |
| Laziness | 41 | 6.27(8.61-4.57) | 2.36(23662.9) | |
| Reading disorder | 31 | 3.54(5.06-2.47) | 3.01(3872691.21) | |
| Daydreaming | 21 | 3.38(5.22-2.18) | 5.94(5096.26) | |
| Fear of death | 21 | 3.76(5.82-2.43) | 3.21(24579.45) | |
| Claustrophobia | 10 | 3.21(6.04-1.71) | 3.1(10159.23) | |
| Fear of disease | 9 | 2.11(4.09-1.09) | 3.38(49159.47) | |
| Impaired reasoning | 6 | 4.03(9.13-1.78) | 3.14(921322.65) | |
| Grief reaction | 5 | 2.78(6.77-1.14) | 3.2(282309.69) | |
| Boredom | 4 | 2.73(7.37-1.01) | 2.71(196796.7) | |
| Confabulation | 4 | 3.1(8.4-1.14) | 2.98(45249.93) | |
| Fear of surgery | 3 | 54.39(227.61-13) | 2.19(530848.65) | |
| Fear-related avoidance of activities | 3 | 3.24(10.24-1.02) | 3.76(43910.47) | |
| Nervous system disorders | Cerebrovascular accident | 1473 | 3.04(3.2-2.89) | 2.11(34085.16) |
| Speech disorder | 385 | 2.27(2.52-2.06) | 54.39(225.54) | |
| Dementia | 365 | 3.15(3.5-2.84) | 3.24(7258.02) | |
| Orthostatic hypotension | 188 | 3.25(3.76-2.81) | 2.14(341513.26) | |
| Hypokinesia | 161 | 3.03(3.55-2.59) | 7.55(2922.91) | |
| Near death experience | 96 | 5.97(7.34-4.85) | 2.78(14237.54) | |
| Dysgraphia | 67 | 2.71(3.46-2.13) | 3.03(422255.64) | |
| Carotid artery occlusion | 20 | 2.87(4.48-1.84) | 4.03(11617.85) | |
| Carotid artery stenosis | 20 | 3.12(4.87-1.99) | 3.36(6986.54) | |
| Dyslexia | 17 | 2.98(4.83-1.84) | 6.27(50113.71) | |
| Brain hypoxia | 14 | 4.19(7.16-2.45) | 3.34(4253697.31) | |
| Carotid artery disease | 9 | 3.08(5.98-1.58) | 5.96(123897.14) | |
| Cerebral palsy | 7 | 2.36(5-1.11) | 2.63(21126.97) | |
| Orthostatic hypertension | 7 | 2.63(5.58-1.24) | 3.24(458990.28) | |
| Cerebrovascular insufficiency | 4 | 5.94(16.35-2.16) | 3.53(69208.04) | |
| Visual brightness | 4 | 3.49(9.47-1.28) | 2.27(1356844.21) | |
| Fumbling | 3 | 7.55(24.53-2.33) | 2.67(1880648.6) | |
| Irregular sleep phase | 3 | 3.36(10.63-1.06) | 3.49(8982.67) |
| PT | ROR(95%CI) | PRR(X2) | total number of deaths | Total number of reports | % |
| Irregular sleep phase | 3.36(10.63-1.06) | 3.49(8982.67) | 1 | 3 | 33.33 |
| Cerebrovascular insufficiency | 5.94(16.35-2.16) | 3.53(69208.04) | 1 | 4 | 25.00 |
| Impaired reasoning | 4.03(9.13-1.78) | 3.14(921322.65) | 1 | 6 | 16.67 |
| Carotid artery stenosis | 3.12(4.87-1.99) | 3.36(6986.54) | 3 | 20 | 15.00 |
| Orthostatic hypertension | 2.63(5.58-1.24) | 3.24(458990.28) | 1 | 7 | 14.29 |
| Cerebrovascular accident | 3.04(3.20-2.89) | 2.11(34085.16) | 123 | 1473 | 8.35 |
| Dementia Alzheimer's type | 3.20(3.86-2.66) | 3.08(23126.67) | 7 | 114 | 6.14 |
| Dementia | 3.15(3.50-2.84) | 3.24(7258.02) | 22 | 365 | 6.03 |
| Hypokinesia | 3.03(3.55-2.59) | 7.55(2922.91) | 9 | 161 | 5.59 |
| Orthostatic hypotension | 3.25(3.76-2.81) | 2.14(341513.26) | 8 | 188 | 4.26 |
| Speech disorder | 2.27(2.52-2.06) | 54.39(225.54) | 14 | 385 | 3.64 |
| Stress | 2.68(2.90-2.47) | 2.28(376033.75) | 18 | 630 | 2.86 |
| Aphonia | 2.28(2.76-1.88) | 2.87(55401.95) | 3 | 107 | 2.80 |
| Dysgraphia | 2.71(3.46-2.13) | 3.03(422255.64) | 1 | 67 | 1.49 |
| Fear | 2.19(2.58-1.86) | 4.19(26138.87) | 1 | 145 | 0.69 |
| Amnesia | 2.44(2.67-2.23) | 2.73(11607.78) | 3 | 501 | 0.60 |
| Memory impairment | 3.39(3.56-3.24) | 2.43(1642487.56) | 10 | 1807 | 0.55 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




