1. Introduction
Autonomous vehicles (AVs) represent a transformative leap in transportation, blending advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and sensor integration to enable self-driving capabilities. These vehicles operate with minimal human intervention, relying on an intricate network of hardware and software systems to perceive their environment, make decisions, and navigate complex traffic scenarios. The core functionality of AVs hinges on their ability to process and respond to vast amounts of data in real time, sourced from onboard sensors, vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) communication, and cloud-based services.
However, the reliance on interconnected systems also exposes AVs to a wide array of cybersecurity threats. Potential vulnerabilities range from data breaches and unauthorized access to critical control systems to more sophisticated attacks, such as sensor spoofing and malware infiltration. Such threats not only jeopardize passenger safety but also undermine public trust in the technology. As AVs continue to evolve, the cybersecurity landscape surrounding them grows increasingly complex, necessitating robust defense mechanisms to safeguard these systems.
Big Data Analytics (BDA) emerges as a pivotal solution in addressing these challenges. By leveraging large volumes of data generated by AVs, BDA enables real-time monitoring, predictive insights, and adaptive threat responses. Its ability to detect anomalies, anticipate potential risks, and optimize system resilience positions it as an indispensable tool in the cybersecurity arsenal for AVs.
This article explores the critical role of Big Data Analytics in strengthening cyber defense mechanisms for autonomous vehicles. It examines the unique cybersecurity challenges faced by AV systems, the application of BDA in mitigating these risks, and the potential of data-driven approaches to enhance AV security. The discussion also addresses implementation challenges and future directions, emphasizing the importance of a collaborative approach to ensuring the safe and secure deployment of autonomous vehicles.
2. Understanding Cybersecurity Challenges in Autonomous Vehicles
Autonomous vehicles (AVs) rely on complex interconnected systems to operate safely and efficiently. These systems include advanced software, hardware components, and communication networks, making AVs susceptible to a variety of cybersecurity vulnerabilities. Understanding these challenges is crucial to developing effective defense mechanisms that ensure the safety and trustworthiness of AV technology.
A. Key Vulnerabilities in AV Systems
1. Communication Protocols
Autonomous vehicles rely on vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication, which includes vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) and vehicle-to-infrastructure (V2I) exchanges, to share critical information such as traffic conditions and navigation data. These communication channels can be exploited by attackers to intercept or manipulate data, leading to incorrect decision-making or system failure.
2. Software Bugs
The software systems in AVs comprise millions of lines of code, increasing the likelihood of undetected bugs or vulnerabilities. Cybercriminals can exploit these weaknesses to gain unauthorized access or disrupt vehicle operations.
3. Sensor Spoofing
AVs rely heavily on sensors like LiDAR, radar, and cameras to perceive their environment. Sensor spoofing attacks manipulate or distort sensor inputs, tricking the vehicle into misinterpreting its surroundings. For example, a spoofed signal might cause an AV to misjudge the distance to an obstacle, resulting in accidents.
4. Insecure Updates
Many AV systems receive over-the-air (OTA) software updates, which, if inadequately secured, can be intercepted or modified by attackers, introducing malicious code into the vehicle's system.
B. Types of Cyber Threats
1. Data Breaches
Cybercriminals may target sensitive user data stored in AV systems, including location history, personal preferences, and biometric data. Such breaches compromise user privacy and expose drivers to additional risks, such as identity theft.
2. Ransomware Attacks
Ransomware attacks on AVs or their associated networks can disable critical systems, rendering the vehicle inoperable unless a ransom is paid. These attacks can cause widespread disruption and financial losses.
3. Denial-of-Service (DoS) Attacks
A DoS attack overwhelms the vehicle's computational or communication resources, disrupting its ability to process data and make decisions. This can immobilize the vehicle or impair its functionality, leading to potential safety hazards.
4. Malware and Trojans
Malicious software introduced into AV systems can grant attackers control over critical functions such as braking, steering, or acceleration. These attacks pose severe safety risks to passengers and other road users.
C. Potential Impacts of Cyberattacks on AV Safety and User Trust
The consequences of cyberattacks on autonomous vehicles extend beyond technical disruptions, posing significant risks to safety and eroding public trust.
Safety Risks
Cyberattacks can compromise the decision-making capabilities of AVs, leading to accidents or hazardous scenarios. For example, a manipulated navigation system might guide a vehicle into dangerous conditions or away from its intended route.
Erosion of User Trust
High-profile cybersecurity breaches can damage public confidence in AV technology. Consumers may hesitate to adopt autonomous vehicles if they perceive them as unsafe or vulnerable to cyberattacks.
Economic and Reputational Damage
For manufacturers, cybersecurity failures can result in costly recalls, legal liabilities, and reputational harm. Addressing these challenges is essential to fostering long-term adoption and acceptance of AVs.
By understanding and addressing these cybersecurity challenges, the industry can implement robust defenses that protect the safety and privacy of AV users while promoting trust and confidence in this transformative technology.
3. Overview of Big Data Analytics
Big Data Analytics (BDA) has become a cornerstone of modern technological advancements, particularly in domains that involve complex systems like autonomous vehicles (AVs). Its ability to process vast volumes of data and derive actionable insights makes it indispensable for enhancing the safety, efficiency, and security of AV systems.

A. Definition and Significance of BDA
Big Data Analytics refers to the systematic analysis of large, diverse datasets to uncover patterns, trends, and correlations that can inform decision-making. In the context of AVs, these datasets are derived from sensors, communication systems, and user interactions, generating terabytes of data in real time.
The significance of BDA lies in its ability to:
- ➢
Process high-velocity data: AVs generate data at unprecedented speeds, necessitating tools that can handle real-time analytics.
- ➢
Improve decision-making: By extracting actionable insights, BDA enhances the vehicle's ability to make accurate and timely decisions.
- ➢
Predict and prevent issues: Proactive threat detection and system maintenance rely on BDA's predictive capabilities.
B. Role of Data Collection, Storage, and Processing in AV Systems
1. Data Collection
AVs are equipped with numerous sensors, including cameras, LiDAR, radar, and GPS, which continuously collect data on the vehicle’s surroundings and operational status. Additionally, vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication gathers external data such as traffic patterns and weather conditions.
2. Data Storage
Given the massive volume of data generated, efficient storage systems are critical. Cloud-based platforms often complement onboard storage, enabling centralized data management and accessibility for analytics.
3. Data Processing
Real-time data processing is essential for AV operations, ensuring that data is quickly analyzed and acted upon. Advanced computational models filter and prioritize critical information, facilitating immediate responses to dynamic situations.
C. How BDA Enables Real-Time and Predictive Insights
1. Real-Time Analytics
BDA allows AV systems to monitor live data streams, detecting anomalies and adapting to changes instantaneously. For example, real-time analysis of traffic data enables dynamic route adjustments, improving safety and efficiency.
2. Predictive Insights
BDA employs machine learning algorithms and predictive modeling to anticipate future events or potential issues. For instance:
- ❖
Predictive Maintenance: By analyzing patterns in sensor data, BDA can forecast component failures and schedule maintenance proactively, minimizing downtime.
- ❖
Threat Detection: Predictive models identify potential cybersecurity threats based on historical attack patterns and behavioral anomalies.
4. Application of Big Data Analytics in Cyber Defense for AVs
The complexity and interconnectivity of autonomous vehicle (AV) systems make them inherently vulnerable to cyber threats. Big Data Analytics (BDA) serves as a critical tool for strengthening AV cybersecurity by enabling proactive threat detection, efficient incident response, and enhanced system resilience. Below are key applications of BDA in cyber defense mechanisms for AVs.
A. Threat Detection and Prevention
1. Real-Time Monitoring of AV Systems for Anomalies
AV systems generate vast amounts of data in real time, including inputs from sensors, communications, and onboard software. BDA analyzes these data streams continuously to identify unusual patterns or behaviors that may indicate a potential cyberattack. For instance, a sudden spike in data transmission rates or unexpected system commands can be flagged as anomalies requiring immediate attention.
2. Use of Machine Learning to Predict and Mitigate Threats
Machine learning models, trained on historical data and known attack patterns, empower AV systems to predict potential threats before they occur. By analyzing large datasets for subtle warning signs, such as deviations in network traffic or irregular sensor inputs, these models can anticipate attacks and take preemptive measures.
B. Incident Response and Recovery
1. Data-Driven Approaches to Identify Attack Patterns
In the aftermath of a cyber incident, BDA plays a crucial role in identifying the nature and source of the attack. By analyzing logs and system behavior during the breach, it can uncover patterns that help organizations understand the attackers’ methods. This intelligence is invaluable for improving future defenses and closing security gaps.
2. Faster Recovery Through Automated Diagnostics and Updates
BDA enables automated diagnostic tools that rapidly assess the impact of an attack and determine the best course of action. Automated software updates and patches can then be deployed to affected systems without delay, ensuring that AVs can resume normal operations quickly and safely. This minimizes downtime and restores user confidence in the technology.
C. Enhancing System Resilience
Predictive Maintenance Using BDA to Identify Potential Weak Points
Cyber resilience begins with ensuring that AV systems are robust and well-maintained. BDA analyzes operational data to predict when critical components, such as sensors or communication modules, may become vulnerable due to wear or software degradation. By addressing these vulnerabilities proactively, the risk of exploitation by attackers is significantly reduced.
5. Case Studies and Examples
The practical application of Big Data Analytics (BDA) in cybersecurity for autonomous vehicles (AVs) has proven its potential to mitigate risks, enhance safety, and improve system resilience. Examining real-world examples and success stories highlights the transformative impact of BDA in this domain and provides valuable lessons for future implementations.
A. Examples of BDA-Powered Cyber Defense Implementations in AVs
1. Tesla’s Data-Driven Threat Monitoring System
Tesla’s autonomous vehicles rely heavily on data analytics to ensure secure operations. By collecting data from its vast fleet of vehicles, Tesla monitors system behavior for anomalies indicative of potential cyber threats. For example, during a 2020 ransomware attack attempt on a Tesla supplier, proactive monitoring enabled early detection and prevention, safeguarding both data and operations.
2. Waymo’s Predictive Cybersecurity Framework
Waymo, Google’s self-driving car initiative, uses predictive analytics to safeguard its AV fleet. The company employs BDA to simulate attack scenarios and identify potential vulnerabilities in its systems. This approach enables Waymo to implement preemptive measures, reducing the risk of exploitation.
B. Success Stories and Lessons Learned
1. Incident Recovery and Lessons from the Jeep Cherokee Hack
Although not an autonomous vehicle, the infamous 2015 Jeep Cherokee hack serves as a critical lesson for the AV industry. Researchers demonstrated how vulnerabilities in the vehicle’s infotainment system could be exploited to gain control of critical functions. This incident underscored the importance of continuous data monitoring and secure software updates. Manufacturers have since incorporated BDA into their cybersecurity frameworks to prevent similar exploits, emphasizing the value of real-time threat detection.
2. BMW’s Enhanced System Resilience
BMW implemented a BDA-driven cybersecurity solution after identifying vulnerabilities in its ConnectedDrive system. By analyzing data patterns and integrating machine learning algorithms, BMW strengthened its encryption protocols and improved system resilience against cyberattacks. This proactive approach ensured that potential breaches were addressed before they could impact users, showcasing the effectiveness of predictive analytics in safeguarding vehicle systems.
3. Collaboration Between Automakers and Cybersecurity Firms
Several automakers have partnered with cybersecurity companies to develop BDA-driven solutions for AVs. For example, Toyota’s collaboration with BlackBerry’s QNX platform focuses on integrating analytics to detect and mitigate threats in connected and autonomous vehicles.
C. Key Takeaways
- ♦
Proactive Monitoring is Essential: Real-time analytics can detect anomalies before they escalate, preventing potential breaches and minimizing risk.
- ♦
Predictive Models Drive Preemptive Actions: By leveraging historical data, BDA enables organizations to identify vulnerabilities and mitigate threats proactively.
- ♦
Collaboration Enhances Outcomes: Partnerships between automakers, technology providers, and cybersecurity firms accelerate the development and deployment of effective defense mechanisms.
- ♦
Continuous Learning and Adaptation: BDA allows systems to evolve in response to new threats, ensuring long-term resilience.
These examples demonstrate that BDA is not merely a theoretical tool but a proven method for enhancing cybersecurity in autonomous vehicles.
6. Challenges in Implementing Big Data Analytics for Cyber Defense
While Big Data Analytics (BDA) offers transformative capabilities for enhancing cybersecurity in autonomous vehicles (AVs), its implementation comes with notable challenges. Addressing these challenges is critical for maximizing BDA’s potential while ensuring compliance with ethical standards and technological feasibility.
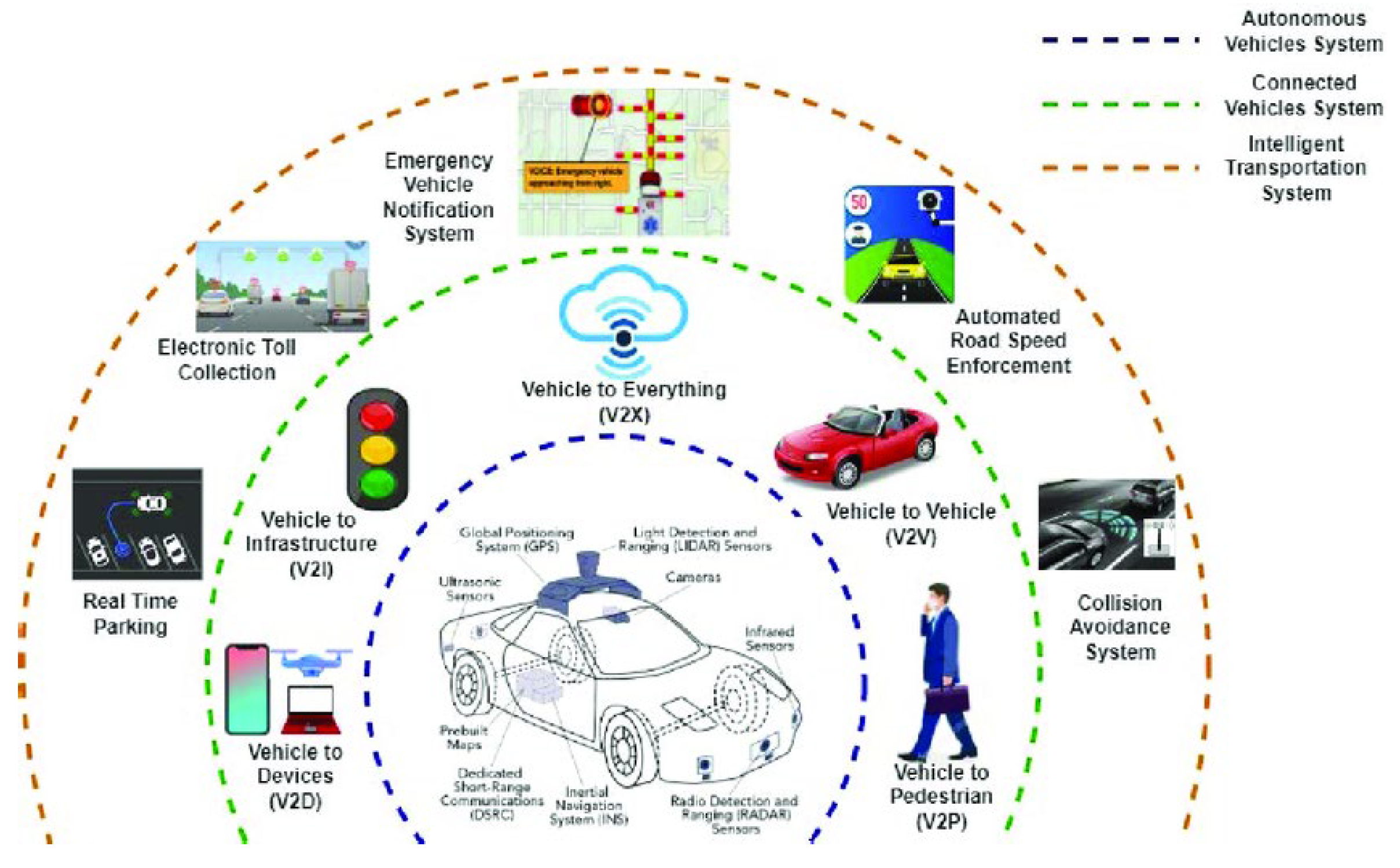
A. Data Privacy and Ethical Concerns
1. Collection and Use of Personal Data
Autonomous vehicles generate and process large amounts of sensitive data, including location history, driving behavior, and user preferences. Ensuring that this data is handled responsibly is essential to prevent misuse or unauthorized access. Privacy laws such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) mandate strict compliance, but achieving this while maintaining operational efficiency is a complex task.
2. Anonymization and Security of Data
Protecting user identity during data collection and analysis is a critical ethical consideration. Implementing anonymization techniques can mitigate risks, but these methods can sometimes reduce data quality or analytical accuracy, complicating the trade-off between privacy and system effectiveness.
3. User Consent and Transparency
AV users may be unaware of the extent to which their data is collected and used for cybersecurity purposes. Building trust requires transparent policies and clear communication about data handling practices, which can be challenging in a fast-evolving technological landscape.
B. Scalability and Infrastructure Limitations
1. Data Volume and Velocity
The data generated by AVs is enormous, requiring robust storage and processing capabilities. Existing infrastructure may struggle to keep up with the velocity and volume of real-time data streams, especially during peak operational periods or when scaling for large fleets.
2. High Computational Costs
Advanced analytics, such as machine learning and predictive modeling, demand significant computational resources. Implementing and maintaining these capabilities can be cost-prohibitive, particularly for smaller manufacturers or operators with limited budgets.
3. Cloud Dependency and Latency
Many BDA systems rely on cloud computing for data storage and analysis. While this approach offers scalability, it can introduce latency issues, impacting the real-time responsiveness needed for AV cybersecurity. Developing hybrid solutions that balance cloud and edge computing is critical but technically challenging.
C. Integration with Existing AV Technologies
1. Compatibility Issues
Integrating BDA systems with existing AV architectures often involves reconciling diverse hardware and software platforms. Legacy systems may lack the interoperability needed to support advanced analytics, necessitating extensive upgrades or redesigns.
2. Real-Time Data Processing Constraints
AVs require split-second decisions, making the seamless integration of real-time analytics essential. Ensuring that BDA systems do not disrupt core AV functionalities requires meticulous engineering and testing, which can be time-intensive and costly.
3. Evolving Threat Landscape
Cybersecurity threats are constantly evolving, demanding that BDA systems adapt quickly to new attack vectors. Integrating adaptive algorithms into existing technologies can be technically complex and may require continuous updates, adding to the overall implementation burden.
7. Future Directions
The field of cybersecurity for autonomous vehicles (AVs) is rapidly evolving, and Big Data Analytics (BDA) is poised to play an even greater role in safeguarding these advanced systems. Emerging technologies and collaborative strategies will shape the future of cyber defense, enhancing the security and resilience of AVs in a dynamic threat landscape.
A. Advances in Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning for Better Cybersecurity
1. Enhanced Threat Detection with AI
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) algorithms are becoming increasingly sophisticated in identifying and mitigating cyber threats. These technologies enable AV systems to:
- ✧
Detect anomalies with greater accuracy by analyzing complex patterns in data.
- ✧
Adapt to new attack vectors through continuous learning models.
- ✧
Automate decision-making processes for real-time threat neutralization.
Future developments in AI and ML are expected to focus on improving the speed and accuracy of these systems. Techniques such as deep reinforcement learning and neural network optimization will allow AVs to anticipate threats with minimal false positives, ensuring robust and reliable cybersecurity.
2. Behavioral Analysis for Proactive Defense
Emerging AI tools will focus on behavioral analysis to predict potential cyberattacks. By studying the behavioral patterns of users, systems, and attackers, these tools can anticipate threats before they materialize. For instance, ML-driven profiling can flag unusual communication patterns in AV-to-infrastructure systems, preventing breaches preemptively.
B. Collaboration Between Manufacturers, Cybersecurity Firms, and Policymakers
1. Standardization of Cybersecurity Protocols
The AV industry’s diverse ecosystem necessitates standardized cybersecurity protocols. Collaboration between manufacturers, cybersecurity firms, and policymakers can lead to the development of universal standards that ensure interoperability and compliance. Initiatives like the ISO/SAE 21434 framework for automotive cybersecurity are early examples of such efforts.
2. Public-Private Partnerships for Threat Intelligence Sharing
Partnerships between private companies and government agencies can facilitate real-time sharing of threat intelligence. These collaborations can create centralized databases of known vulnerabilities and attack patterns, helping manufacturers and cybersecurity firms implement preemptive measures.
3. Policy and Regulation Support
Policymakers play a crucial role in creating a regulatory environment that fosters innovation while ensuring robust security. Future efforts may include:
- ❖
Mandating regular cybersecurity audits for AV systems.
- ❖
Incentivizing investment in advanced security technologies.
- ❖
Promoting transparency in data handling and privacy practices.
C. Potential of Quantum Computing in Future AV Cybersecurity
1. Quantum-Resistant Cryptography
Quantum computing, while a potential threat to current encryption methods, also offers opportunities to enhance cybersecurity. Quantum-resistant cryptographic algorithms, which can withstand the computational power of quantum computers, are already under development. These algorithms will be essential for protecting AV communication channels and data integrity in the future.
2. Accelerated Threat Analysis
The immense processing power of quantum computers can enable faster and more comprehensive analysis of cyber threats. Tasks that currently require significant time and resources, such as decrypting complex data streams or simulating attack scenarios, can be performed in seconds, providing AV systems with a decisive edge in cybersecurity.
8. Conclusions
The integration of autonomous vehicles (AVs) into modern transportation systems offers transformative benefits but also introduces significant cybersecurity challenges. Big Data Analytics (BDA) has emerged as a powerful ally in mitigating these risks by enabling real-time threat detection, efficient incident response, and enhanced system resilience. Through case studies and examples, it is evident that BDA-driven solutions have already demonstrated their effectiveness in addressing the complex cyber threats facing AVs.
However, the journey toward fully secure AV systems is not without obstacles. Data privacy concerns, scalability limitations, and integration challenges must be addressed to unlock the full potential of BDA. Furthermore, the rapidly evolving threat landscape demands continuous innovation and adaptability in cybersecurity strategies.
Looking ahead, advances in artificial intelligence and machine learning will drive more precise and proactive threat mitigation. Collaboration among manufacturers, cybersecurity firms, and policymakers will ensure a unified approach to security, fostering trust and safety. Quantum computing, with its potential to revolutionize encryption and threat analysis, represents a promising frontier in cyber defense.
By embracing these advancements and overcoming existing challenges, the AV industry can build a robust cybersecurity framework that not only protects users but also accelerates the adoption of autonomous technologies.
References
- Noman, Inshad Rahman, et al. "Data-driven security: Improving autonomous systems through data analytics and cybersecurity." Journal of Computer Science and Technology Studies 4.2 (2022): 182-190.
- Noman, I. R. , Bortty, J. C., Bishnu, K. K., Aziz, M. M., & Islam, M. R. (2022). Data-driven security: Improving autonomous systems through data analytics and cybersecurity. Journal of Computer Science and Technology Studies, 4(2), 182-190.
- Noman, Inshad Rahman, Joy Chakra Bortty, Kanchon Kumar Bishnu, Md Munna Aziz, and Md Rashedul Islam. "Data-driven security: Improving autonomous systems through data analytics and cybersecurity." Journal of Computer Science and Technology Studies 4, no. 2 (2022): 182-190.
- Noman, I.R. , Bortty, J.C., Bishnu, K.K., Aziz, M.M. and Islam, M.R., 2022. Data-driven security: Improving autonomous systems through data analytics and cybersecurity. Journal of Computer Science and Technology Studies, 4(2), pp.182-190.
- Noman IR, Bortty JC, Bishnu KK, Aziz MM, Islam MR. Data-driven security: Improving autonomous systems through data analytics and cybersecurity. Journal of Computer Science and Technology Studies. 2022;4(2):182-90.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).








