Submitted:
17 July 2024
Posted:
18 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. Related Work
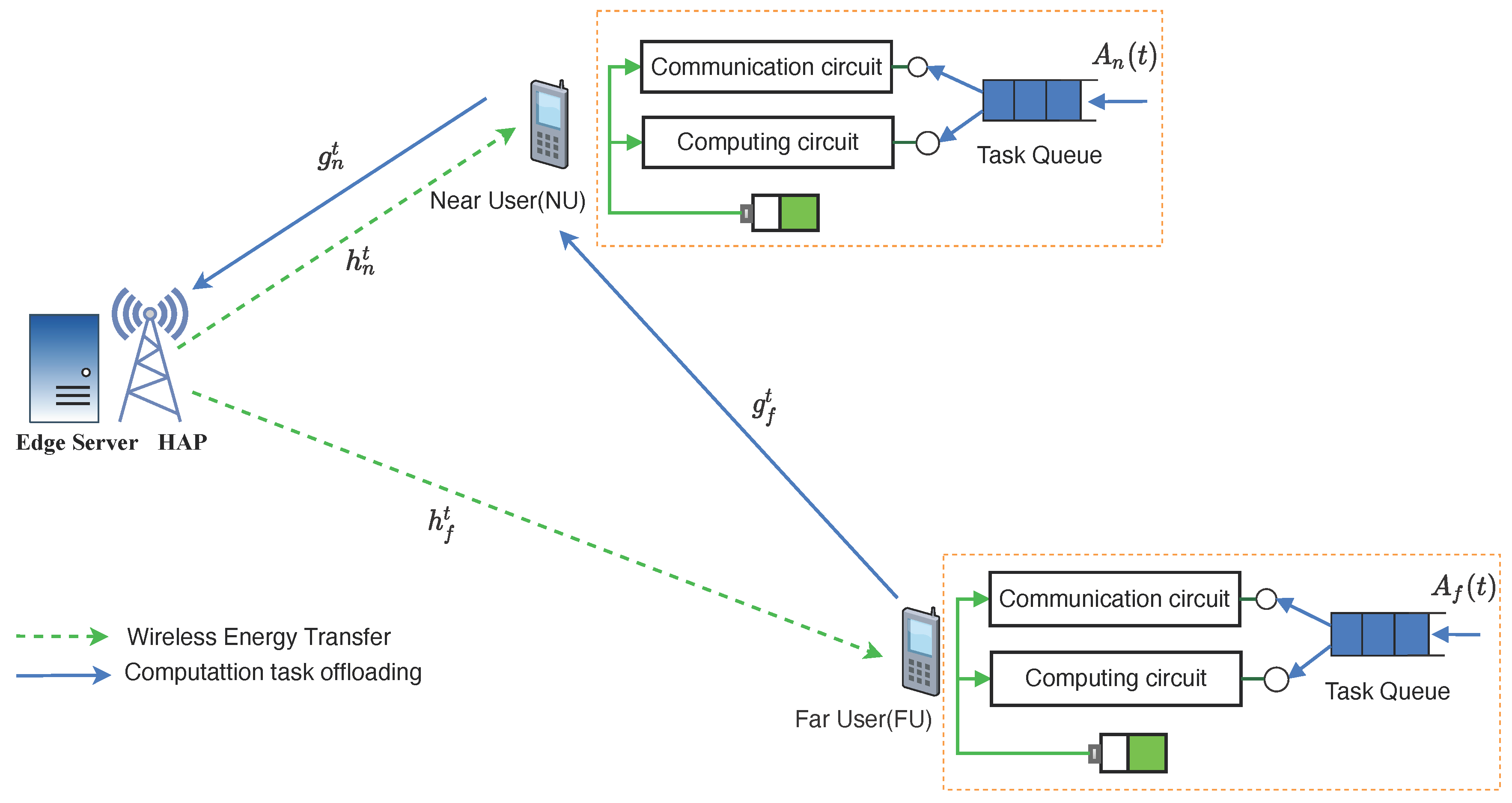
2. System Model
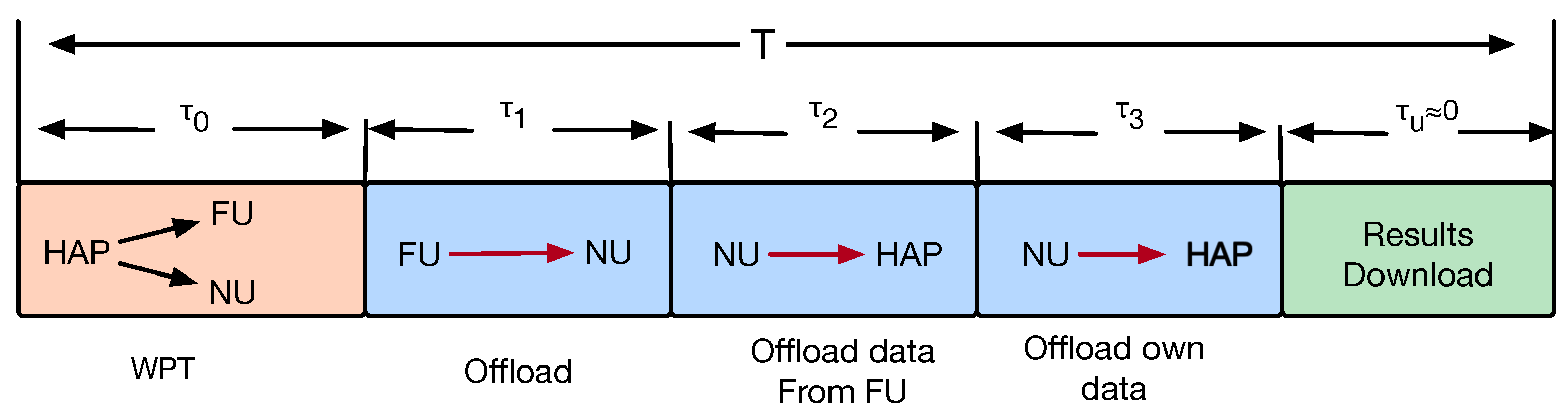
2.1. Communication Model
2.2. Task Queue Model
2.3. Computation Model
2.4. Energy Consumption Model
2.5. Problem Formulation
3. Algorithm Design
3.1. Lyapunov Optimization
| Algorithm 1: User-Assisted Dynamic Resource Allocation Algorithm |
 |
3.2. Algorithm Complexity Analysis
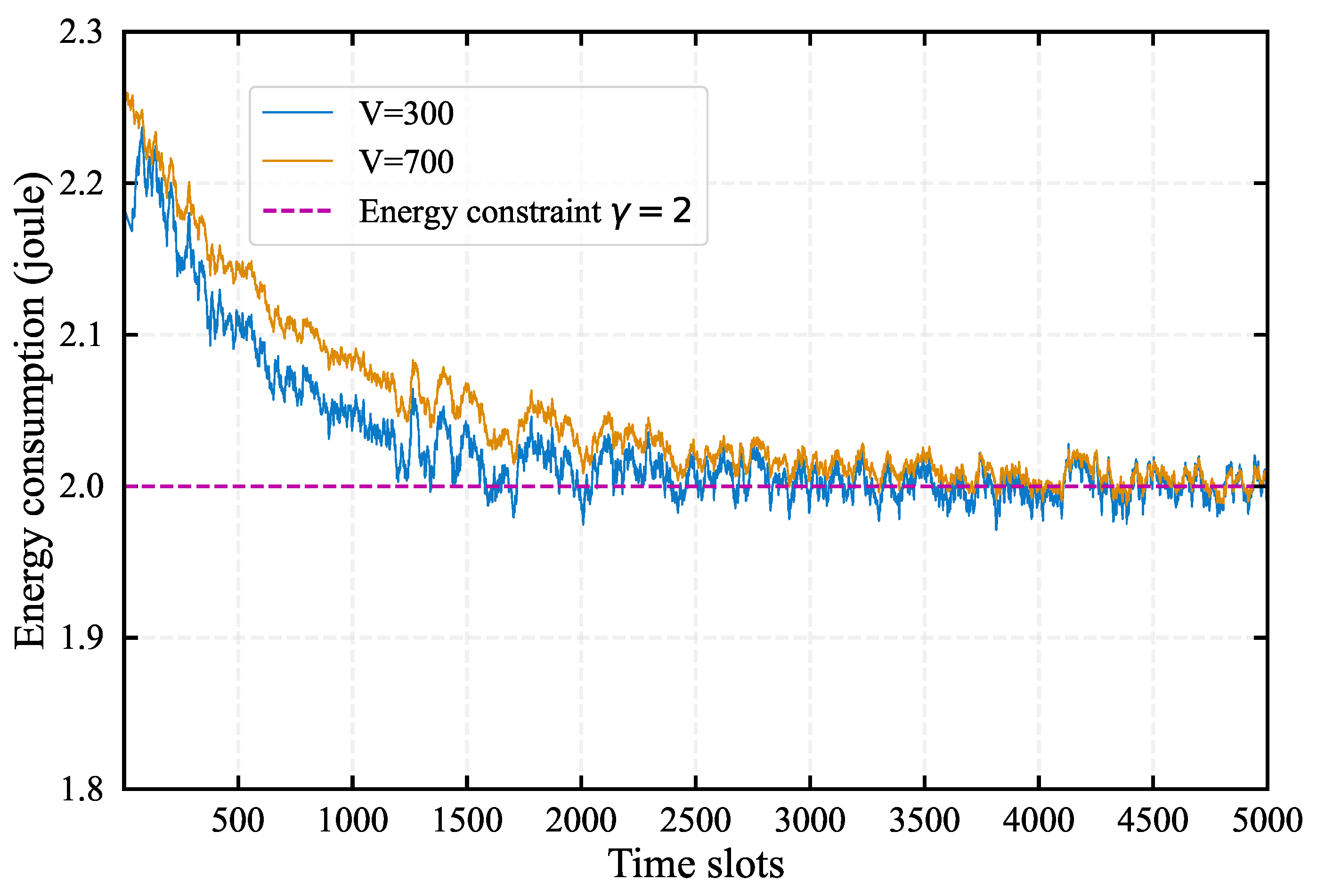
3.3. Algorithm Performance Analysis
- All queues , , are mean rate stable, thereby satisfying the constraints.
4. Simulation Results
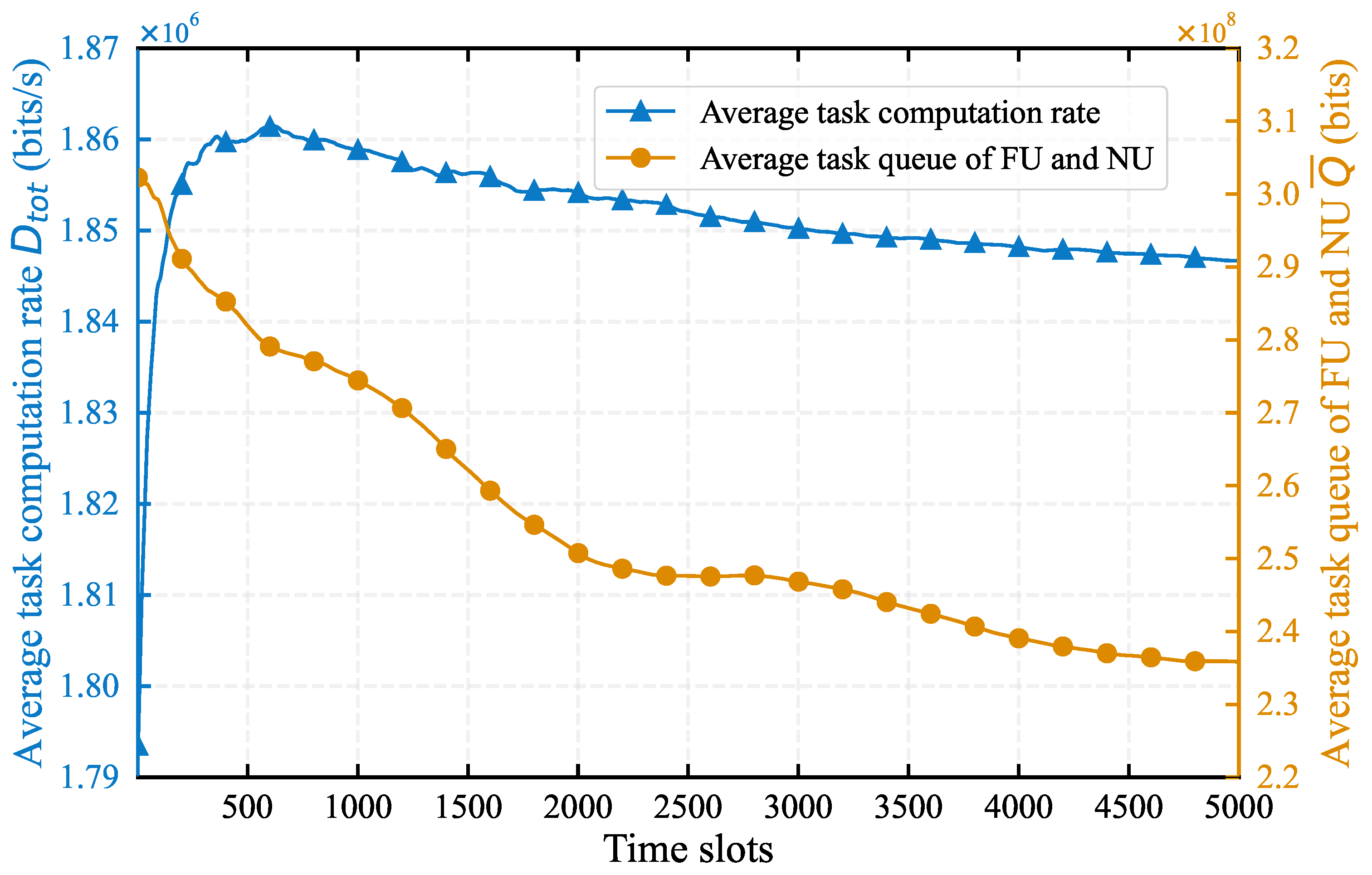
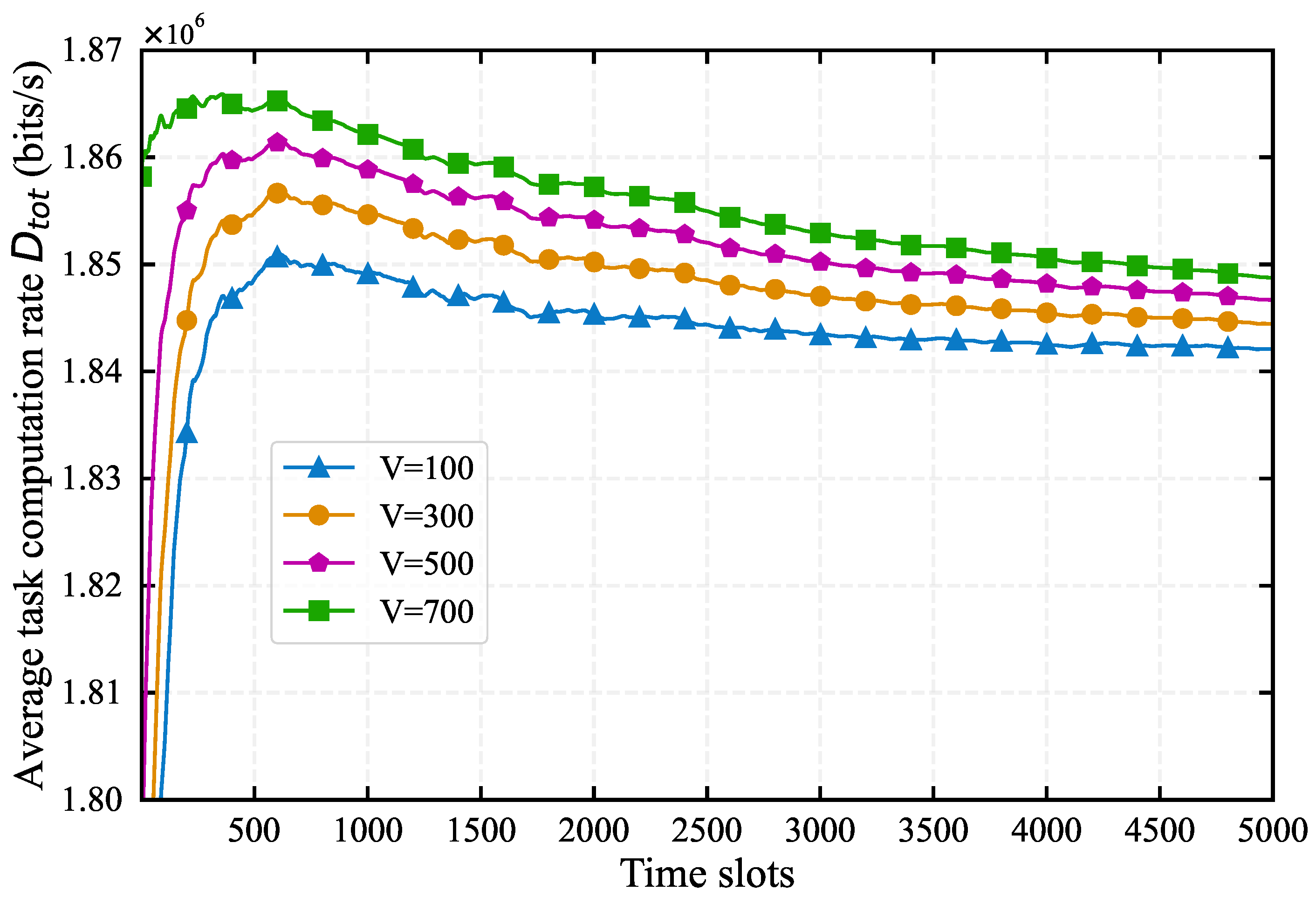
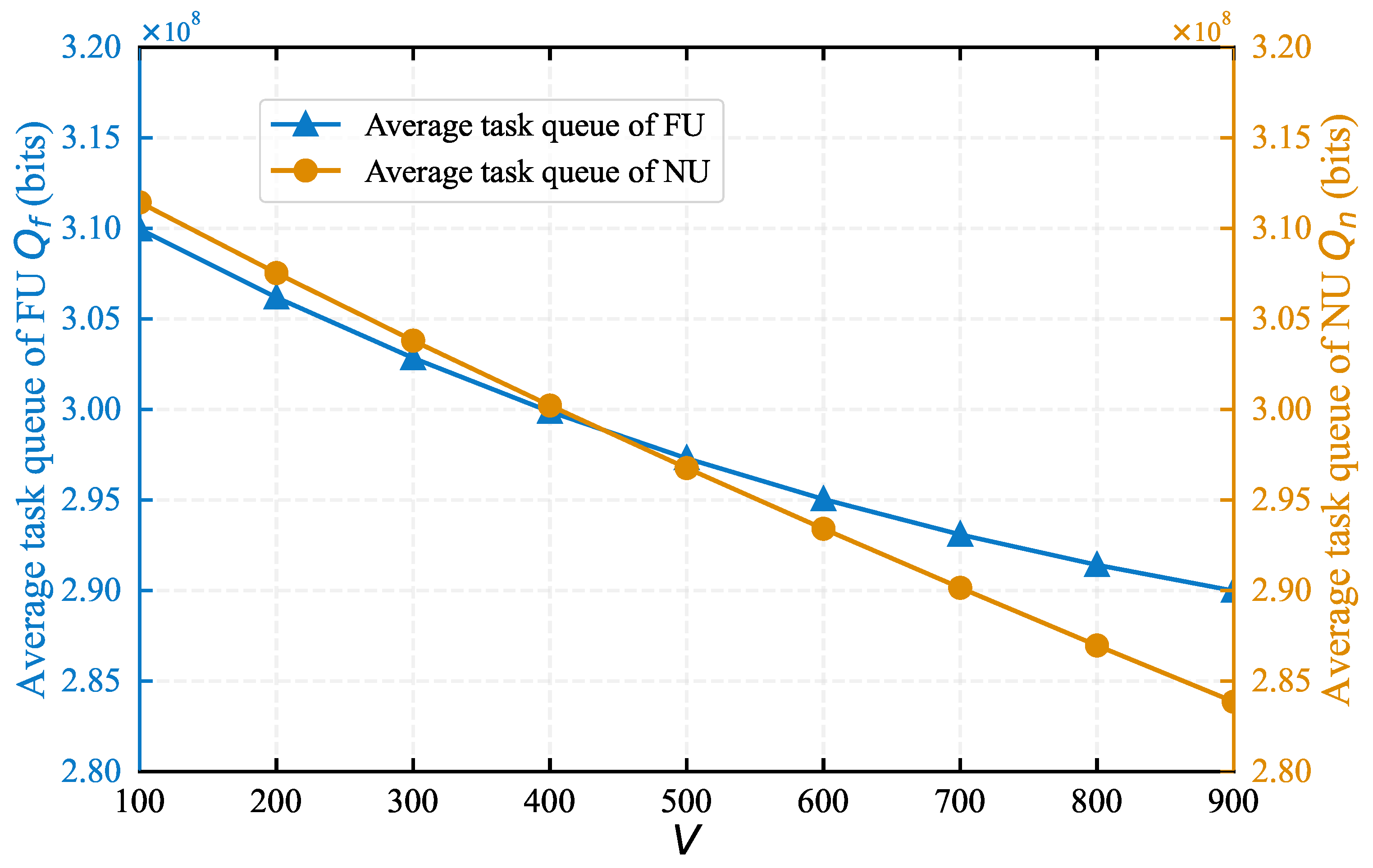
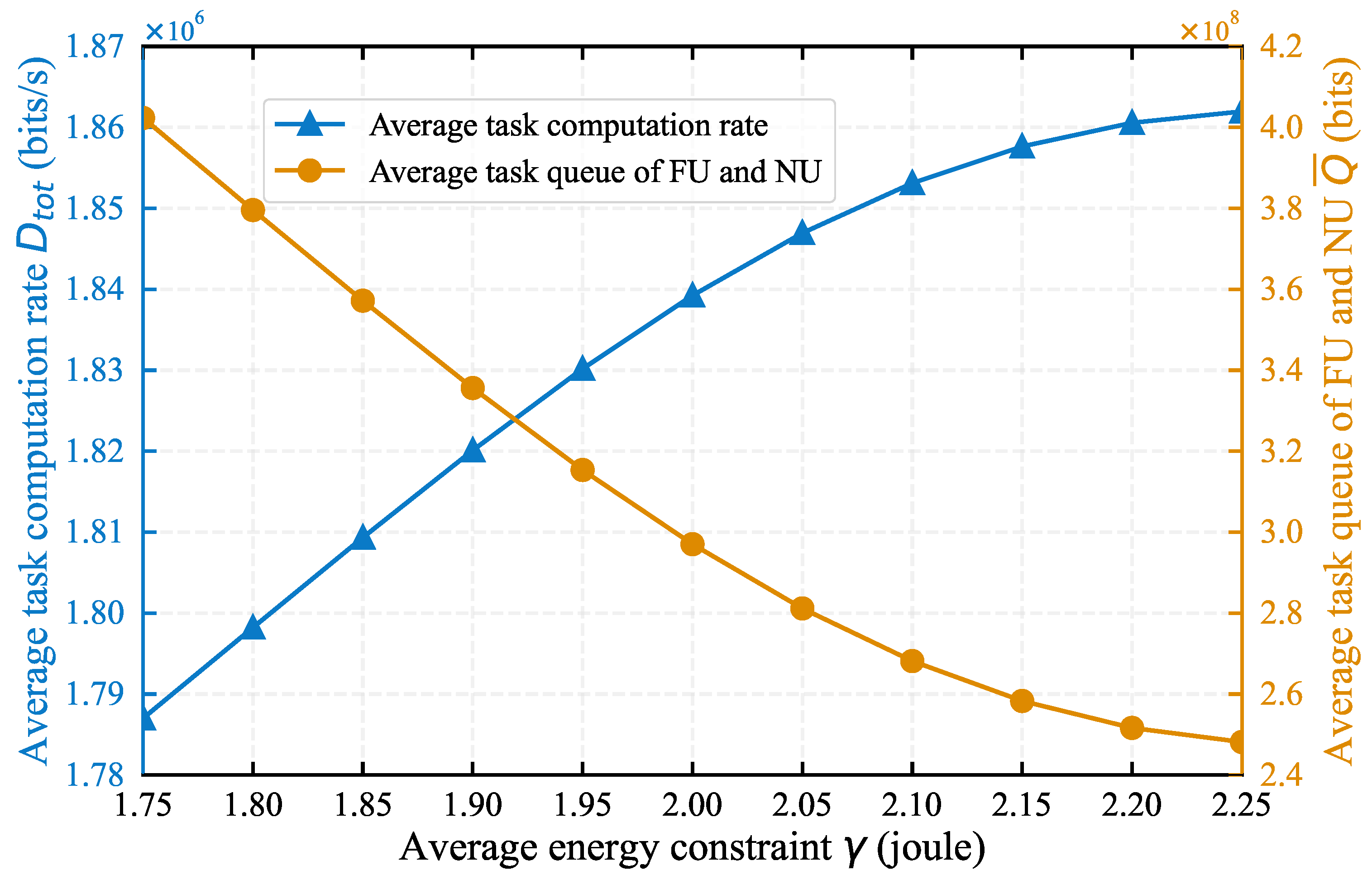
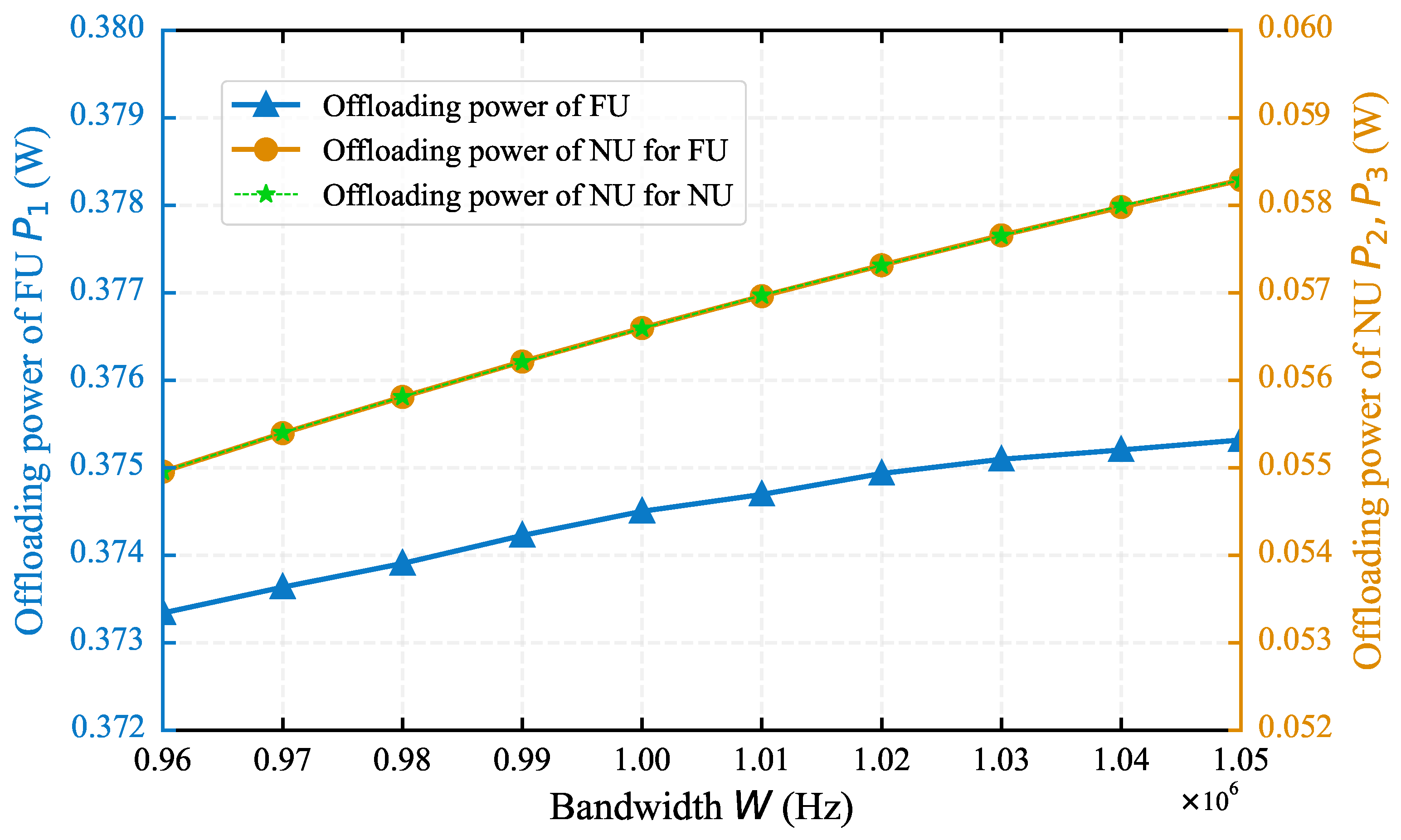
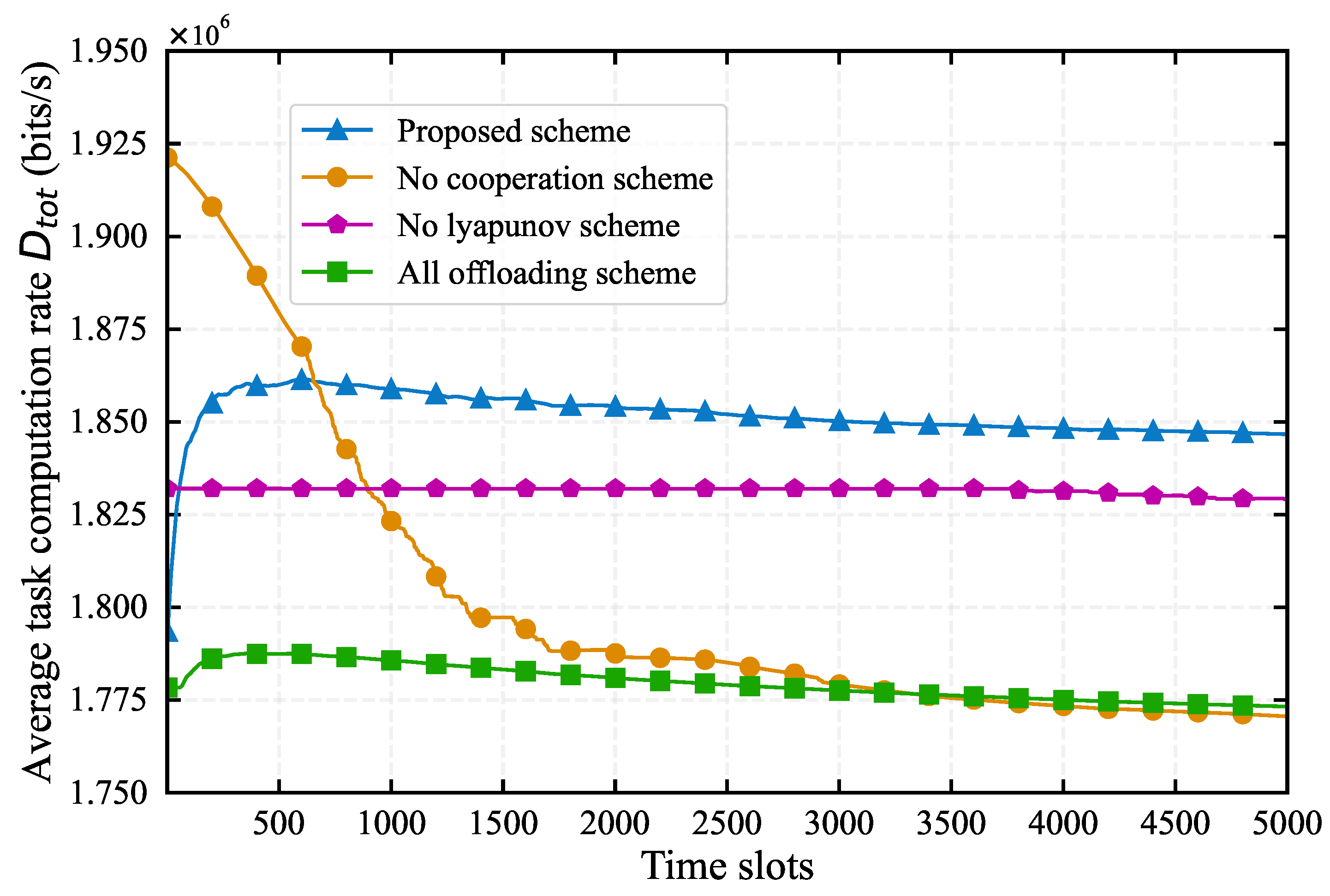
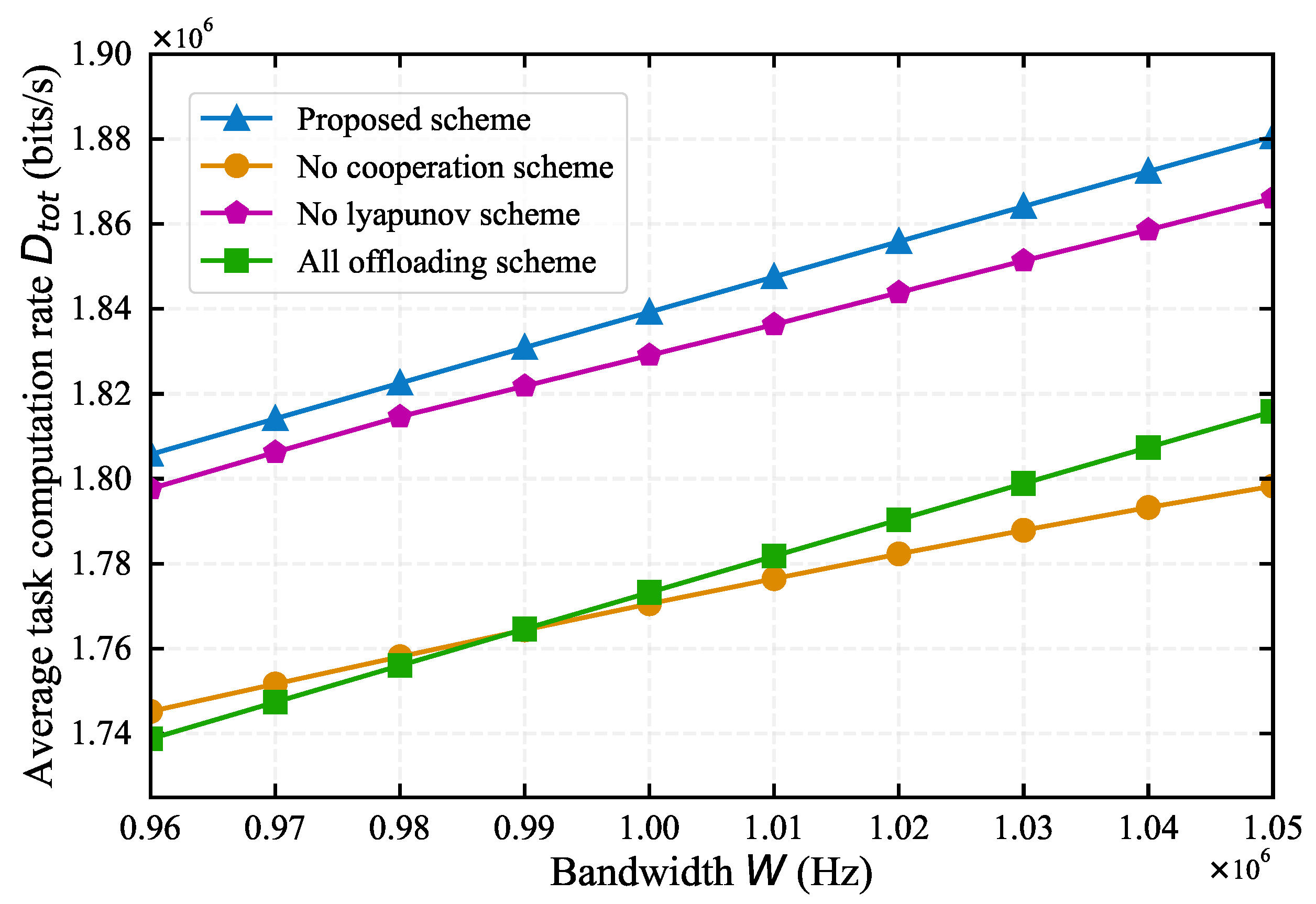
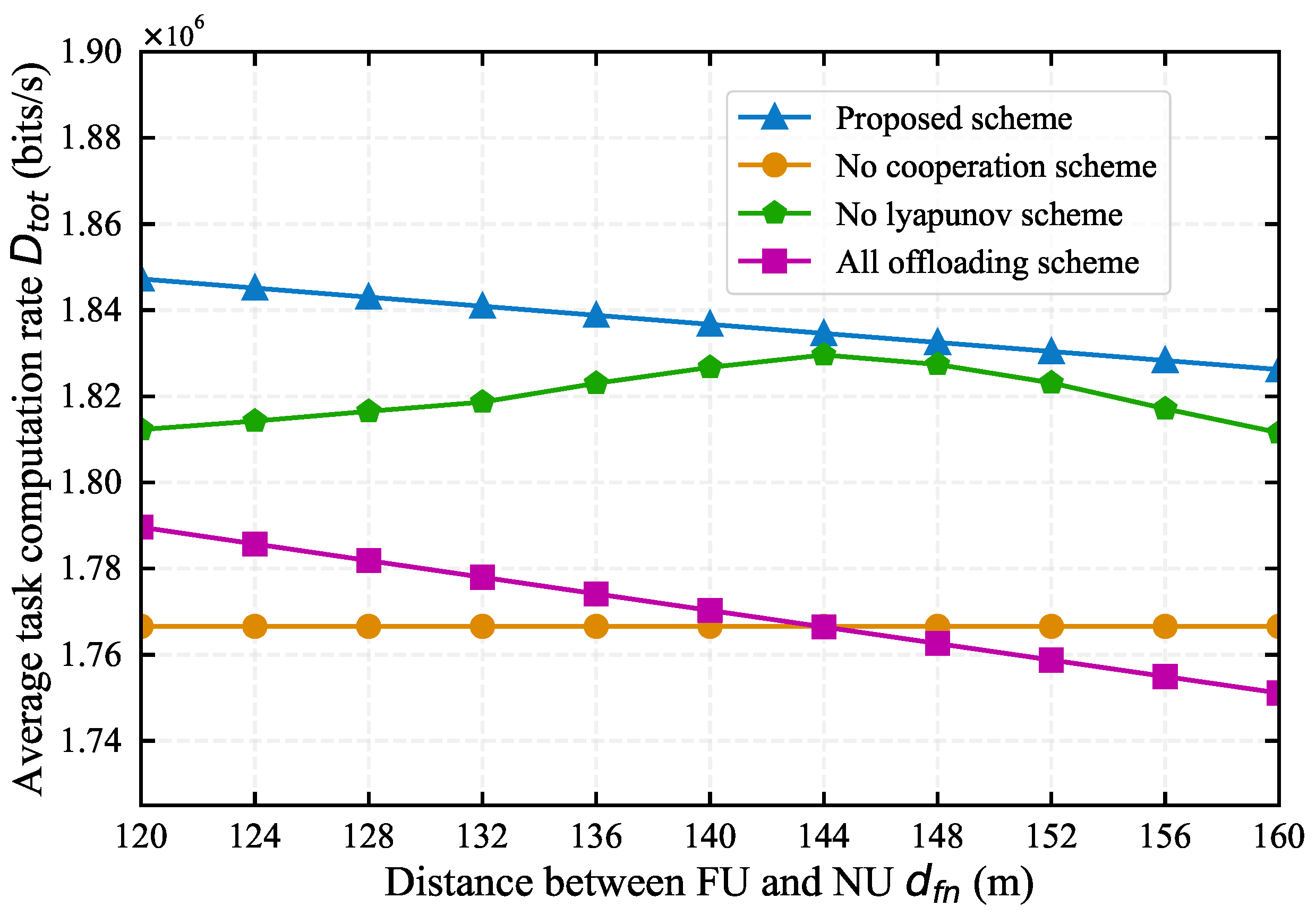
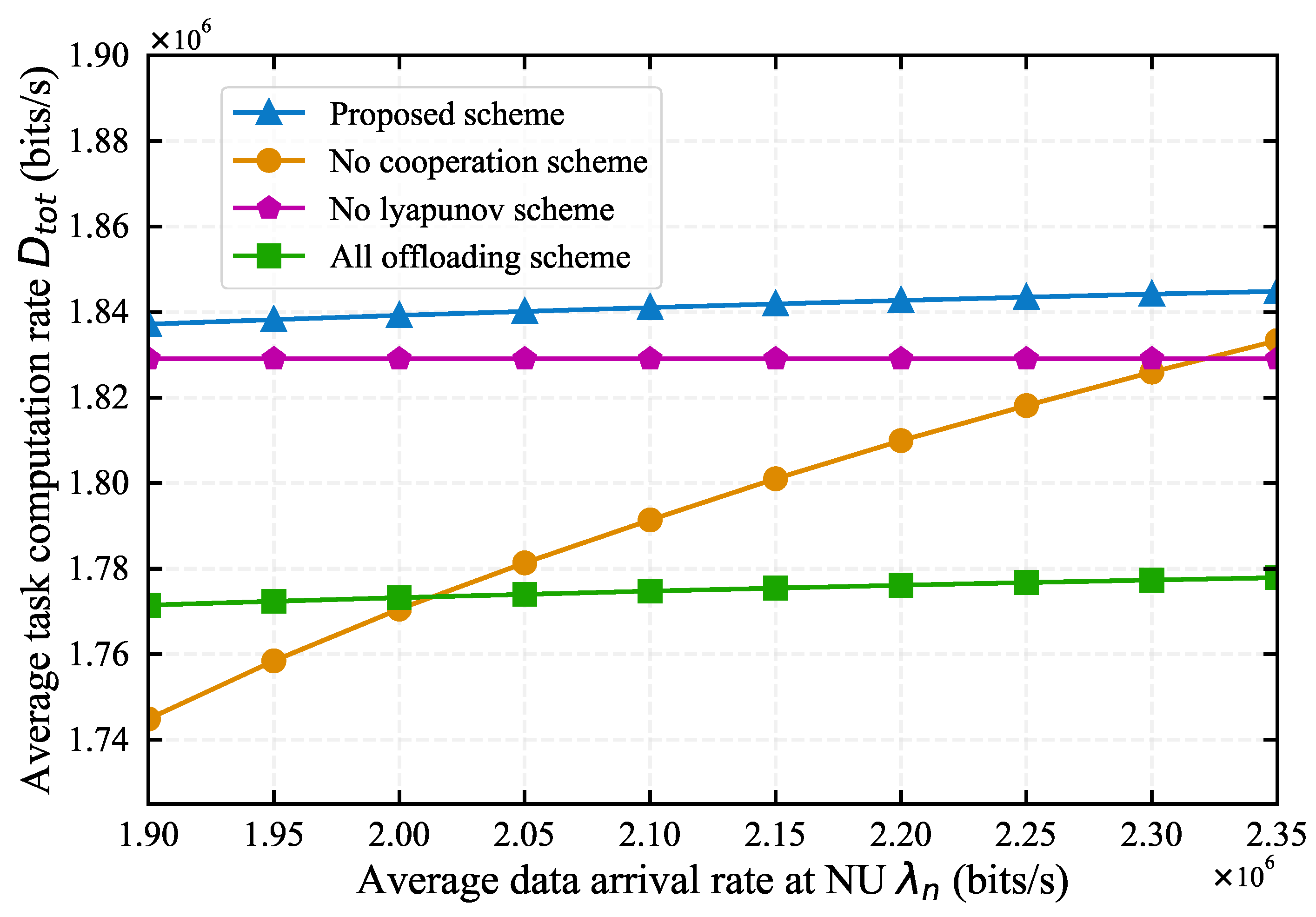
4.1. Impact of System Parameters on Algorithm Performance
4.2. Comparison with Baseline Algorithms
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, W.; Zhou, F.; Hu, R.Q.; Wang, B. Energy-efficient resource allocation for secure NOMA-enabled mobile edge computing networks. IEEE Transactions on Communications 2019, 68, 493–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, Z.; Liu, Y.; Shi, J.; Liu, C.; Gao, Z. UAV-supported clustered NOMA for 6G-enabled Internet of Things: Trajectory planning and resource allocation. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 2020, 8, 15041–15048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Zhu, F.; Tang, M.; He, L. Profit maximization in cache-aided intelligent computing networks. Physical Communication 2023, 58, 102065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Sun, Q.; Lu, W.; Wu, C.; Ding, H. Big-data-based intelligent spectrum sensing for heterogeneous spectrum communications in 5G. IEEE Wireless Communications 2020, 27, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; You, C.; Zhang, J.; Huang, K.; Letaief, K.B. A Survey on Mobile Edge Computing: The Communication Perspective. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials 2017, 19, 2322–2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Hao, Y. Task Offloading for Mobile Edge Computing in Software Defined Ultra-Dense Network. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications 2018, 36, 587–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Zhou, J.; Liuliang, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, W. Computation Offloading with Virtual Resources Management in Mobile Edge Networks. 2018 IEEE 87th Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC Spring), 2018, pp. 1–5. [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Zhang, J.; Liu, J.; Zhang, H. Energy-Aware Computation Offloading and Transmit Power Allocation in Ultradense IoT Networks. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 2019, 6, 4317–4329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Zhou, F.; Hu, R.Q. Joint Offloading and Computation Energy Efficiency Maximization in a Mobile Edge Computing System. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology 2019, 68, 3052–3056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anajemba, J.H.; Yue, T.; Iwendi, C.; Alenezi, M.; Mittal, M. Optimal Cooperative Offloading Scheme for Energy Efficient Multi-Access Edge Computation. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 53931–53941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Luo, Y.; Liu, A.; Bhuiyan, M.Z.A.; Zhang, S. Multiagent Deep Reinforcement Learning for Vehicular Computation Offloading in IoT. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 2021, 8, 9763–9773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Chen, X.; Li, E.; Zeng, L.; Luo, K.; Zhang, J. Edge Intelligence: Paving the Last Mile of Artificial Intelligence With Edge Computing. Proceedings of the IEEE 2019, 107, 1738–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, S.; Leng, S.; Maharjan, S.; Zhang, Y. Energy Efficiency and Delay Tradeoff for Wireless Powered Mobile-Edge Computing Systems With Multi-Access Schemes. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications 2020, 19, 1855–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Letaief, K.B. Dynamic Computation Offloading for Mobile-Edge Computing With Energy Harvesting Devices. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications 2016, 34, 3590–3605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Lau, V.K.N. Enabling Wireless Power Transfer in Cellular Networks: Architecture, Modeling and Deployment. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications 2014, 13, 902–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, S.; Wu, J.; Liu, L.; Lan, D.; Taherkordi, A. Energy-Efficient Cooperative Communication and Computation for Wireless Powered Mobile-Edge Computing. IEEE Systems Journal 2022, 16, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margolies, R.; Gorlatova, M.; Sarik, J.; Stanje, G.; Zhu, J.; Miller, P.; Szczodrak, M.; Vigraham, B.; Carloni, L.; Kinget, P.; others. Energy-harvesting active networked tags (enhants) prototyping and experimentation. ACM Transactions on Sensor Networks (TOSN) 2015, 11, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tataria, H.; Shafi, M.; Molisch, A.F.; Dohler, M.; Sjöland, H.; Tufvesson, F. 6G Wireless Systems: Vision, Requirements, Challenges, Insights, and Opportunities. Proceedings of the IEEE 2021, 109, 1166–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, H.; Zhang, R. Throughput Maximization in Wireless Powered Communication Networks. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications 2014, 13, 418–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, L.; Guo, S. Energy-Efficient Cooperative Resource Allocation in Wireless Powered Mobile Edge Computing. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 2019, 6, 4744–4754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhou, X.; Qiu, T.; Zhao, Q.; Li, K. Multi-Relay Assisted Computation Offloading for Multi-Access Edge Computing Systems With Energy Harvesting. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology 2021, 70, 10941–10956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mach, P.; Becvar, Z. Device-to-Device Relaying: Optimization, Performance Perspectives, and Open Challenges Towards 6G Networks. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials 2022, 24, 1336–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, B.; Ni, Q.; Yu, W.; Pervaiz, H. Optimizing Computation Efficiency for NOMA-Assisted Mobile Edge Computing With User Cooperation. IEEE Transactions on Green Communications and Networking 2021, 5, 858–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Si, F.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, H. Wireless Powered Mobile Edge Computing With NOMA and User Cooperation. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology 2021, 70, 1957–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Xu, X.; Huang, Y.; Wu, Q.; Tao, X.; Zhang, P. Resource Management for Computation Offloading in D2D-Aided Wireless Powered Mobile-Edge Computing Networks. Ieee Internet of Things Journal 2021, 8, 8005–8020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chen, X.; Wu, W.; An, N.; Wang, L. Cooperative application execution in mobile cloud computing: A stackelberg game approach. IEEE Communications Letters 2015, 20, 946–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, C.; Huang, K. Exploiting Non-Causal CPU-State Information for Energy-Efficient Mobile Cooperative Computing. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications 2018, 17, 4104–4117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Wong, K.K.; Yang, K. Wireless Powered Cooperation-Assisted Mobile Edge Computing. Ieee Transactions on Wireless Communications 2018, 17, 2375–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Xu, J.; Ding, Z. Optimized Multiuser Computation Offloading with Multi-Antenna NOMA. 2017 IEEE Globecom Workshops (GC Wkshps), 2017, pp. 1–7. [CrossRef]
- Bi, S.; Huang, L.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.J.A. Lyapunov-guided deep reinforcement learning for stable online computation offloading in mobile-edge computing networks. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications 2021, 20, 7519–7537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Bao, S.; Chi, K.; Yu, K.; Mumtaz, S. DRL-based computation rate maximization for wireless powered multi-AP edge computing. IEEE Transactions on Communications 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Ye, Y.; Chu, X.; Lu, G. Computation Energy Efficiency Maximization for a NOMA-Based WPT-MEC Network. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 2021, 8, 10731–10744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Zhu, F.; Xia, J.; Gao, C.; Cui, T.; Lai, S. Intelligent computing for WPT–MEC-aided multi-source data stream. EURASIP Journal on Advances in Signal Processing 2023, 2023, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Chi, K.; Liu, J.; Yu, K.; Mumtaz, S. Efficient Offloading for Minimizing Task Computation Delay of NOMA-Based Multiaccess Edge Computing. IEEE Transactions on Communications 2022, 70, 3186–3203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Zhou, X.; Fang, F.; Zhang, H.; Yuan, D. Joint time and power allocation for cooperative NOMA based MEC system. 2020 IEEE 92nd Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC2020-Fall). IEEE, 2020, pp. 1–5.
- He, B.; Bi, S.; Xing, H.; Lin, X. Collaborative Computation Offloading in Wireless Powered Mobile-Edge Computing Systems. 2019 IEEE Globecom Workshops (GC Wkshps), 2019, pp. 1–7. [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Qiu, H.; Cai, J.; Xu, W.; Wang, J. D2D-assisted multi-user cooperative partial offloading, transmission scheduling and computation allocating for MEC. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications 2021, 20, 4858–4873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, S.; Wu, J.; Liu, L.; Lan, D.; Taherkordi, A. Energy-efficient cooperative communication and computation for wireless powered mobile-edge computing. IEEE Systems Journal 2020, 16, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.H.; Bi, S.; Su, G.; Zhang, Y.J.A. A Lyapunov-Based Approach to Joint Optimization of Resource Allocation and 3D Trajectory for Solar-Powered UAV MEC Systems. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Wang, Z.; Su, H.; Yu, H.; Lei, B.; Guizani, M. Profit Maximization of Independent Task Offloading in MEC-Enabled 5G Internet of Vehicles. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.; Xie, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, G.; Zhang, H.; Yu, S. Joint differential game and double deep q–networks for suppressing malware spread in industrial internet of things. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, J.; Dai, L.; Tong, Z.; Zhang, L.; Li, K. Lyapunov optimized energy-efficient dynamic offloading with queue length constraints. Journal of Systems Architecture 2023, 143, 102979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sheng, M.; Wang, X.; Wang, L.; Li, J. Mobile-edge computing: Partial computation offloading using dynamic voltage scaling. IEEE Transactions on Communications 2016, 64, 4268–4282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neely, M. Stochastic network optimization with application to communication and queueing systems; Springer Nature, 2022.
- Boyd, S.; Vandenberghe, L. Convex optimization; Cambridge university press, 2004.
- Grant, M.; Boyd, S. CVX: Matlab software for disciplined convex programming, version 2.1, 2014.
- Mao, S.; Leng, S.; Maharjan, S.; Zhang, Y. Energy efficiency and delay tradeoff for wireless powered mobile-edge computing systems with multi-access schemes. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications 2019, 19, 1855–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; He, H.; Shen, H.; Tian, H. Energy Efficiency Maximization for Relay-aided Wireless Powered Mobile Edge Computing. IEEE Internet of Things Journal 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chen, F. NOMA-aided mobile edge computing via user cooperation. IEEE Transactions on Communications 2020, 68, 2221–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Notation | Definition |
|---|---|
| T | The time block |
| The time for WPT | |
| The time for offloading of FU | |
| The time for NU to offload FU’s data | |
| The time for NU to offload its own data. | |
| , | The energy harvested by MD and helper in slot t |
| , | The WPT channel gain between FU and HAP, NU and HAP |
| , | The offloading channel gain between FU and NU, NU and HAP |
| ,,, | The transmit power for HAP, FU , NU to offload FU’s data |
| and NU to offload its own data in slot t | |
| The amount of tasks processed locally at FU in slot t | |
| The amount of tasks offloaded to NU at FU in slot t | |
| The amount of tasks processed locally at NU in slot t | |
| The amount of tasks that NU offloads to HAP from FU in slot t | |
| the amount of tasks that NU offloads to HAP from itself in slot t | |
| The energy consumed by processing tasks at FU in slot t | |
| The energy consumed by offloading tasks at FU in slot t | |
| The energy consumed by processing tasks at helper in slot t | |
| The energy consumed by NU to offload FU’s tasks in slot t | |
| the energy consumed by NU to offload its own tasks in slot t | |
| The amount of tasks processed in slot t | |
| , | The local CPU frequency at FU and NU |
| , | The CPU cycles required to compute one bit task at FU and NU |
| The energy conversion efficiency | |
| The computing energy efficiency | |
| W | The channel bandwidth |
| The additive white Gaussian noise |
| Symbol | Value |
|---|---|
| Time slot length | 1 s |
| Noise power | W |
| Distance between the HAP and the FU | 230 m |
| Distance between the FU and the NU | 140 m |
| Distance between the HAP and the NU | 200 m |
| CPU frequency of FU | 160 MHz |
| CPU frequency of NU | 220 MHz |
| CPU cycles to compute 1 bit task of FU | 180 cycles/bit |
| CPU cycles to compute 1 bit task of NU | 200 cycles/bit |
| Equal computing efficiency parameter | |
| Weight of the computation rate of FU | 0.55 |
| Weight of the computation rate of NU | 0.45 |
| the antenna gain in channel model | 3 |
| the carrier frequency in channel model | 915 MHz |
| the path loss exponent in channel model | 3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





