Submitted:
11 May 2024
Posted:
13 May 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Selection
2.2. Genetic and Bioinformatic Analysis
2.2.1. CMA and Classification of Results
2.2.2. Next-Generation Sequencing and Variant Interpretation
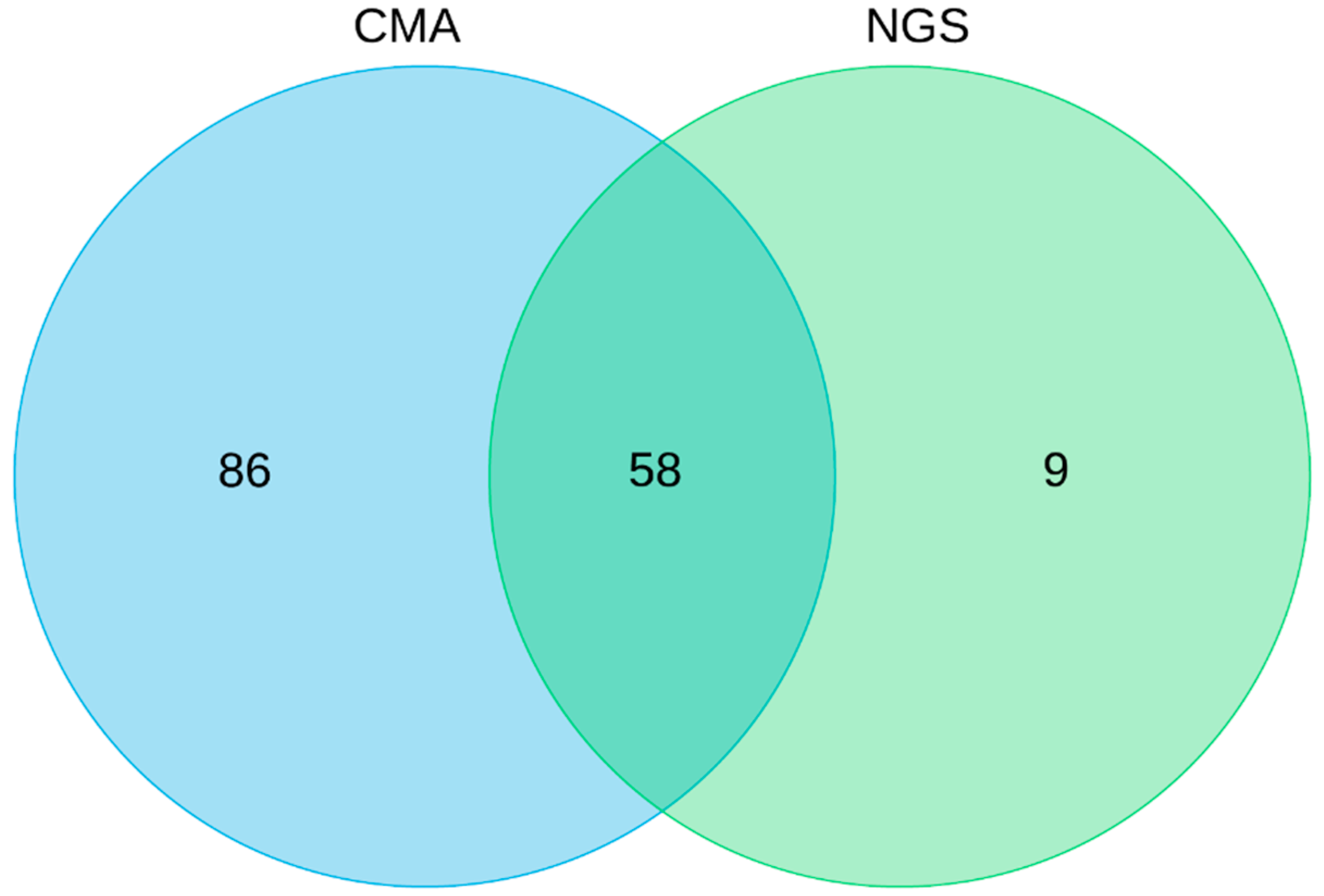
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lalani, S.R. Other Genomic Disorders and Congenital Heart Disease. American J of Med Genetics Pt C 2020, 184, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diab, N.S.; Barish, S.; Dong, W.; Zhao, S.; Allington, G.; Yu, X.; Kahle, K.T.; Brueckner, M.; Jin, S.C. Molecular Genetics and Complex Inheritance of Congenital Heart Disease. Genes 2021, 12, 1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suluba, E.; Shuwei, L.; Xia, Q.; Mwanga, A. Congenital Heart Diseases: Genetics, Non-Inherited Risk Factors, and Signaling Pathways. Egypt J Med Hum Genet 2020, 21, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotiou, E.; Williams, S.; Martin-Geary, A.; Robertson, D.L.; Tenin, G.; Hentges, K.E.; Keavney, B. Integration of Large-Scale Genomic Data Sources With Evolutionary History Reveals Novel Genetic Loci for Congenital Heart Disease. Circ: Genomic and Precision Medicine 2019, 12, e002694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, D.J.; Miossec, M.J.; Williams, S.G.; Monaghan, R.M.; Fotiou, E.; Cordell, H.J.; Sutcliffe, L.; Topf, A.; Bourgey, M.; Bourque, G.; et al. Whole Exome Sequencing Reveals the Major Genetic Contributors to Nonsyndromic Tetralogy of Fallot. Circ Res 2019, 124, 553–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shabana, N.; Shahid, S.U.; Irfan, U. Genetic Contribution to Congenital Heart Disease (CHD). Pediatr Cardiol 2020, 41, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geddes, G.C.; Basel, D.; Frommelt, P.; Kinney, A.; Earing, M. Genetic Testing Protocol Reduces Costs and Increases Rate of Genetic Diagnosis in Infants with Congenital Heart Disease. Pediatr Cardiol 2017, 38, 1465–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahrens-Nicklas, R.C.; Khan, S.; Garbarini, J.; Woyciechowski, S.; D’Alessandro, L.; Zackai, E.H.; Deardorff, M.A.; Goldmuntz, E. Utility of Genetic Evaluation in Infants with Congenital Heart Defects Admitted to the Cardiac Intensive Care Unit. American J of Med Genetics Pt A 2016, 170, 3090–3097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roos-Hesselink, J.W.; Kerstjens-Frederikse, W.S.; Meijboom, F.J.; Pieper, P.G. Inheritance of Congenital Heart Disease. Neth Heart J 2005, 13, 88–91. [Google Scholar]
- Pierpont, M.E.; Basson, C.T.; Benson, D.W.; Gelb, B.D.; Giglia, T.M.; Goldmuntz, E.; McGee, G.; Sable, C.A.; Srivastava, D.; Webb, C.L. Genetic Basis for Congenital Heart Defects: Current Knowledge: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association Congenital Cardiac Defects Committee, Council on Cardiovascular Disease in the Young: Endorsed by the American Academy of Pediatrics. Circulation 2007, 115, 3015–3038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearney, H.M.; Thorland, E.C.; Brown, K.K.; Quintero-Rivera, F.; South, S.T. American College of Medical Genetics Standards and Guidelines for Interpretation and Reporting of Postnatal Constitutional Copy Number Variants. Genetics in Medicine 2011, 13, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richards, S.; Aziz, N.; Bale, S.; Bick, D.; Das, S.; Gastier-Foster, J.; Grody, W.W.; Hegde, M.; Lyon, E.; Spector, E.; et al. Standards and Guidelines for the Interpretation of Sequence Variants: A Joint Consensus Recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genetics in Medicine 2015, 17, 405–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Li, R.; Fu, F.; Pan, M.; Han, J.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, F.; Liao, C. Chromosome Microarray Analysis in the Investigation of Children with Congenital Heart Disease. BMC Pediatr 2017, 17, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jerves, T.; Beaton, A.; Kruszka, P. The Genetic Workup for Structural Congenital Heart Disease. American J of Med Genetics Pt C 2020, 184, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.; Picker, J.; Zheng, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Hisama, F.; Brown, D.W.; Mullen, M.P.; Harris, D.; Stoler, J.; et al. Chromosome Microarray Testing for Patients with Congenital Heart Defects Reveals Novel Disease Causing Loci and High Diagnostic Yield. BMC Genomics 2014, 15, 1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Li, R.; Fu, F.; Huang, R.; Li, D.; Liao, C. Prenatal Genetic Diagnosis Associated with Fetal Ventricular Septal Defect: An Assessment Based on Chromosomal Microarray Analysis and Exome Sequencing. Front. Genet. 2023, 14, 1260995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slavotinek, A.M.; Thompson, M.L.; Martin, L.J.; Gelb, B.D. Diagnostic Yield after Next-Generation Sequencing in Pediatric Cardiovascular Disease. Human Genetics and Genomics Advances 2024, 5, 100286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Fu, F.; Yu, Q.; Wang, D.; Jing, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, F.; Li, F.; Han, J.; Pan, M.; et al. Prenatal Exome Sequencing in Fetuses with Congenital Heart Defects. Clinical Genetics 2020, 98, 215–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Souza, E.E.; Findley, T.O.; Hu, R.; Khazal, Z.S.H.; Signorello, R.; Dash, C.; D’Gama, A.M.; Feldman, H.A.; Agrawal, P.B.; Wojcik, M.H.; et al. Genomic Testing and Molecular Diagnosis among Infants with Congenital Heart Disease in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit. J Perinatol 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hays, T.; Hernan, R.; Disco, M.; Griffin, E.L.; Goldshtrom, N.; Vargas, D.; Krishnamurthy, G.; Bomback, M.; Rehman, A.U.; Wilson, A.T.; et al. Implementation of Rapid Genome Sequencing for Critically Ill Infants With Complex Congenital Heart Disease. Circ: Genomic and Precision Medicine 2023, 16, 415–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shreeve, N.; Sproule, C.; Choy, K.W.; Dong, Z.; Gajewska-Knapik, K.; Kilby, M.D.; Mone, F. Incremental Yield of Whole-genome Sequencing over Chromosomal Microarray Analysis and Exome Sequencing for Congenital Anomalies in Prenatal Period and Infancy: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Ultrasound in Obstet & Gyne 2024, 63, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helm, B.M.; Ware, S.M. Clinical Decision Analysis of Genetic Evaluation and Testing in 1013 Intensive Care Unit Infants with Congenital Heart Defects Supports Universal Genetic Testing. Genes 2024, 15, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Category | N of neonates (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| Isolated CHD | Simple | 29 (15) |
| Association | 18 (10) | |
| Complex | 20 (11) | |
| CHD with extracardiac defect | 121 (64) | |
| N | Congenital heart disease | Extracardiac defects | Results of genetic diagnostics | Geneticlassification | Syndrome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | sASD | kidney anomaly | arr[hg19] 7q11.23(72,766,313-74,133,332)x1 | P | Williams syndrome |
| 2 | SVAS + stenosis of both pulmonary arteries | / | arr[hg19] 7q11.23(73,474,931-73,493,893)×1 | P | Williams syndrome |
| 3 | mVSD, BAV | hypotonia, hypoplasia of the corpus callosum, feeding difficulties, cryptorchidism, dysmorphic facies | 46,XY, del(8)(p23.3p23.3),dup(8)(p12p23)dn | P | 8p inverted duplication/deletion syndrome |
| 4 | VSD | congenital hydronephrosis, dysmorphic facies | arr[GRCh37] 10q26.13q26.3(126528827-135061104)×1 | P | 10q26 deletion syndrome |
| 5 | VSD, ASD | dysmorphic facies | arr[GRCh37] 22q11.21(21081260-21431174)×1 | P | 22q11.2 microdeletion syndrome |
| 6 | pmVSD | coloboma of irises, hypotonia, anorectal anomaly, feeding difficulty | arr[GRCh37]11q23.3q25(119369472-134904063)x1 | P | Jacobsen syndrome |
| 7 | TGA, ASD, PDA | LGA | arr[GRCh37] 17q12(35149908-36214026)×3, mat | P | 17q12 microduplication syndrome |
| EZH2(NM_004456.5): c.2051G>A | P | Weaver syndrome | |||
| 8 | aortic valve stenosis, BAV, sASD | / | 47,XY,+mar.ish der(22)(pter->q11.21::p12->pter)(acro-p++,SE14/22+,CEP22+,N25+) | P | Cat eye syndrome |
| 9 | ToF, ASD | dysmorphic facies | arr[GRCh37] 1q21.1q21.2(146618988-149224043)×3 dn | P | 1q21.1 microduplication syndrome |
| 10 | VSD | hypocalcemia, dysmorphic facies | arr[GRCh37] 22q11.21(18912870-21431174)×1 dn | P | 22q11.2 microdeletion syndrome |
| 11 | ToF | EA/TEF | CHD7(NM_017780):c.5405-8C>G | P | CHARGE syndrome |
| 12 | pmVSD, multiple ASDs, PFO | SGA, palatoschisis, dysmorphic facies, proximal placement of thumb, pes calcaneovalgus | arr[GRCh37] 18q21.31q23(55111850-78002264)×1 | P | 18q deletion syndrome |
| 13 | VSD, ASD | renal cysts | arr[GRCh37] 17p11.2(16842163-20217777)×1 | P | Smith-Magenis syndrome |
| 14 | pmVSD, truncus arteriosus, | hypothyroidism | arr[GRCh37] 22q11.21(18917796_21431174)×1, | P | 22q11.2 microdeletion syndrome |
| 15 | VSD, ASD | dysmorphic facies | arr[GRCh37] 22q11.21(18917796_21431174)×1, | P | 22q11.2 microdeletion syndrome |
| 16 | VSD, ASD | dysmorphic facies | arr[GRCh37] 1q21.1q21.2(146618988_147826074)×1 dn | P | 1q21.1 microdeletion syndrome |
| 17 | mVSD, sASD, hypoplastic aortic arch | dysmorphic facies | arr[GRCh37] 22q11.21(18917796_21431174)×1, | P | 22q11.2 microdeletion syndrome |
| 18 | ASD, PDA | dysmorphic facies | arr[GRCh37] 16p13.11(15126709_16292235)×3 | P | 16p13. 11 microdeletion syndrome |
| arr[GRCh37] 9q34.13(134077089_134401452)×3 | VUS | ||||
| 19 | ASD | hypotonia, hydronephrosis | arr[GRCh37] 16p13.11(15126709_16292235)×3 | P | 16p13.11 microduplication syndrome |
| 20 | stenosis of aortic valve, BAV | dysmorphic features | arr(X)x1[0.8] | P | mosaic Turner syndrome |
| 21 | valvular pumonary stenosis, SVPS | dysmorphic facies, macrosomia, unilateral cryptorchidism, aplasia cutis | PTPN11(NM_002834.5):c.923A>G | P | Noonan syndrome |
| 22 | sASD | hypotonia, hypoplasia of the corpus callosum, dysmorphic features, palatoschisis, glossoschissis, hypermobility of joints, clinodactyly of 5th fingers | OFD1(NM_003611.3):c.1193_1196del | LP | Orofaciodigital syndrome I |
| 23 | AVSD | coloboma of iris, facial nerve palsy, mixed hearing loss, hypotonia dysmorphic features, feeding difficulties | CHD7(NM_017780.4):c.4353+1G>A | P | CHARGE syndrome |
| 24 | sASD, BAV, PDA | dysmorphic facies, palatoschisis, widely spaced nipples, barrel chest, hypermobility of joints, clinodactyly of 5th fingers | KMT2D(NM_003482.4):c.4364dup | P | Kabuki syndrome |
| 25 | sASD, cleft mitral valve with mild MVR, PDA | dysmorphic facies, chorioretinal coloboma, vocal cord paresis, feeding difficulties, hearing loss | CHD7(NM_017780.4):c.3655C>T | P | CHARGE syndrome |
| 26 | ToF | brachycephaly, ptosis of right eyelid, coloboma of optic nerve papilla, gnatoschisis, choanal atresia, feeding difficulties, unilateral renal agenesis, dysmorphic features, hockey-stick palmar crease, partial 2-3 toe syndactyly, hypotonia, hearing loss | CHD7(NM_017780.3):c.4203_4204delTA | P | CHARGE syndrome |
| 27 | sASD, aortic valve stenosis, BAV | AMC, dynamic upper airway obstruction, ptosis of right eyelid, cryptorchidism, bilateral congenital hip dislocation, clubfoot, fibromatosis colli | CHRNG(NM_005199.5):c.753_754del | P | Multiple pterygium syndrome – Escobar type |
| CHRNG(NM_005199.5):c.250G>A | LP | ||||
| 28 | sASD, PPS, PDA | dysmorphic facies, direct hyperbilirubinemia | JAG1(NM_000214.3):c.2122_2125del | P | Alagille syndrome |
| 29 | pulmonary valve stenosis, PDA, PFO | dysmorphic facies, LGA, renal cyst | PTPN11(NM_002834.5):c.922A>G | P | Noonan syndrome |
| 30 | pulmonary valve stenosis, BAV, bicuspid pulmonary valve, PFO | dysmorphic facies, bilateral coloboma of iris, macula and papilla, horseshoe kidney, ankyloglossia | CHD7(NM_017780.4):c.6292C>T | P | CHARGE syndrome |
| 31 | pmVSD | hypotonia, abnormal cortical gyration, feeding difficulties, dysmorphic facies, single palmar crease | SMARCA4(NM_003072.5):c.4114C>T | LP | Coffin-Siris syndrome 4 |
| 32 | left atrial isomerism | heterotaxy, polysplenia | DNAAF3(NM_001256715.2):c.73_82del | LP | Ciliary dyskinesia, primary, 2 |
| N | Congenital heart disease | Extracardiac defects | Results of genetic diagnostics | Genetic classification |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ASD, PDA | Partial ACC, feeding difficulties, dysmorphic features, occipital subcutaneous vascular malformation | arr[GRCh37] 15q25.2q25.3(85,149,690-85,666,309)x1 | VUS |
| 2 | CoA, hypoplastic distal aortic arch, BAV, pmVSD, ASD, PDA | hypotonia, hypocalcemia, dysmorphic facies | 9p21.2(25713810-26334159)×1 | VUS |
| 3 | ASD, pmVSD | arr[GRCh37] 2q32.3(196614799_196837193)×1dn | VUS | |
| arr[GRCh37] 8p23.2(2470592_4801373)×3 mat | VUS | |||
| 4* | ASD, VSD | hypotonia, HCC, moderate ventriculomegaly, dysmorphic facies, hypoplasia of distal phalanx of fifth finger | arr[GRCh37] Xp22.2(14325345_14757768)×2 mat | VUS |
| 5 | CoA, HLHS | arr[GRCh37] 2q24.2q24.3(163517375_164167131)×3 pat | VUS | |
| 6 | CoA, HLHS | hypotonia | arr[GRCh37] 16q24.1(85002353_85508509)×1 dn | VUS |
| 7 | ToF | coloboma of iris, dysmorphic features | NOTCH1(NM_017617.5):c.3190G>A | VUS |
| 8 | ASD | EA/TEF, annular pancreas, horseshoe kidney, extrarenal pelvis, spina bifida occulta, billiary ducts anomaly | ZNF462(NM_021224.6):c.6334C>T | VUS |
| 9 | CoA | polydactyly, hypospadias, SGA | TLL1(NM_012464.5):c.283G>A (pat) | VUS |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




