Submitted:
08 February 2024
Posted:
09 February 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material and treatments
2.2. Characterisation
3. Results
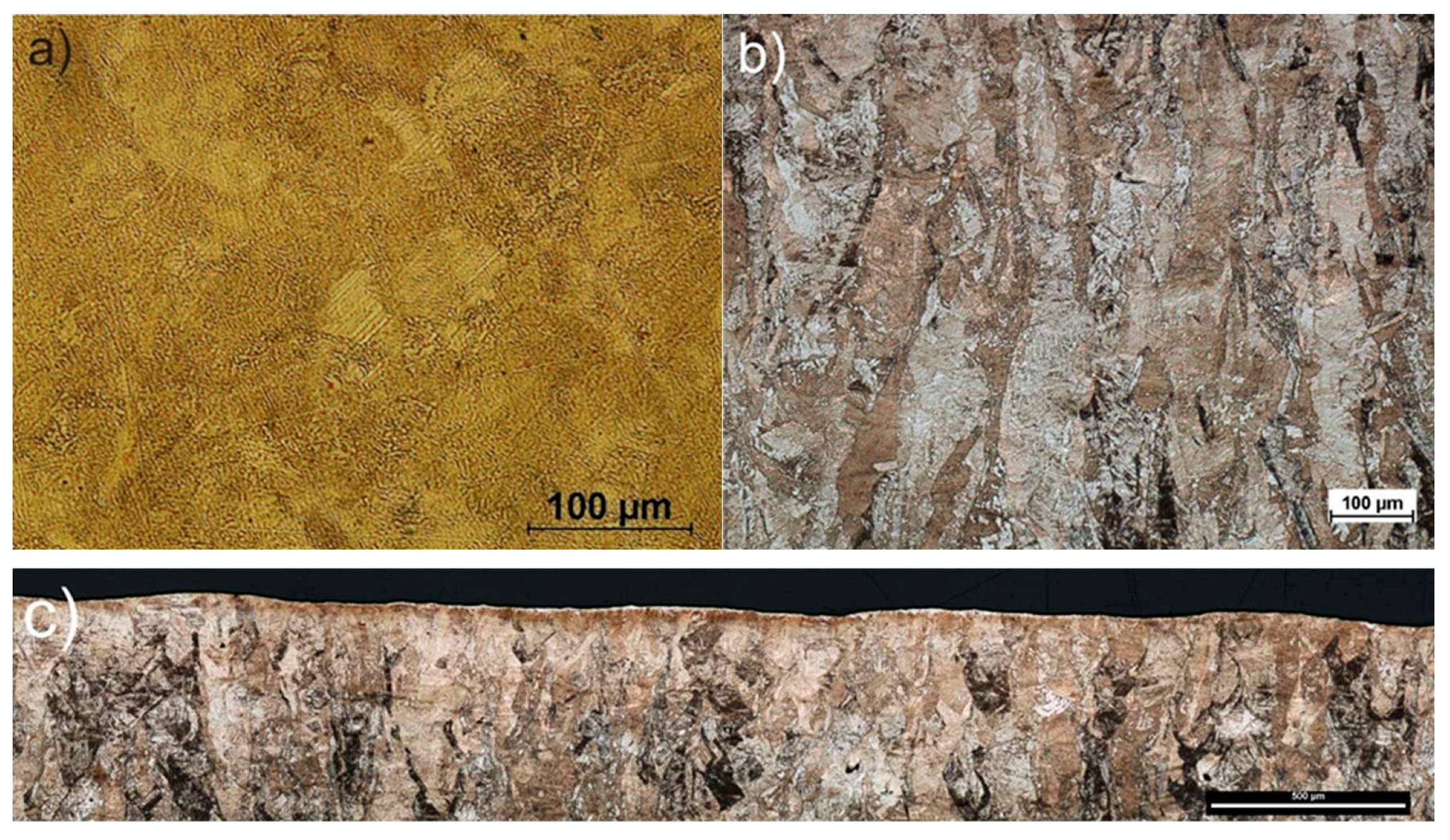
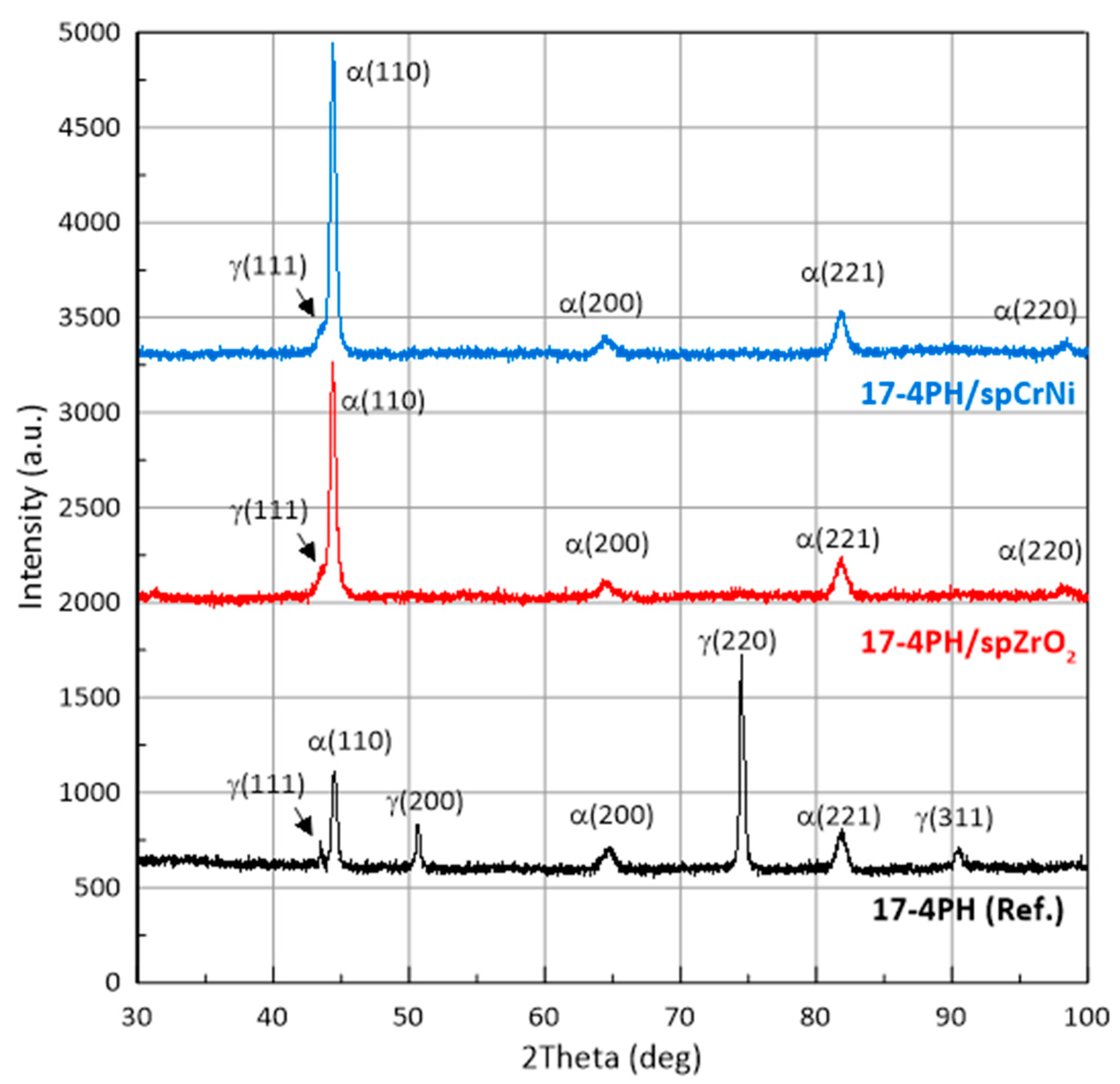
3.1. Structure analysis
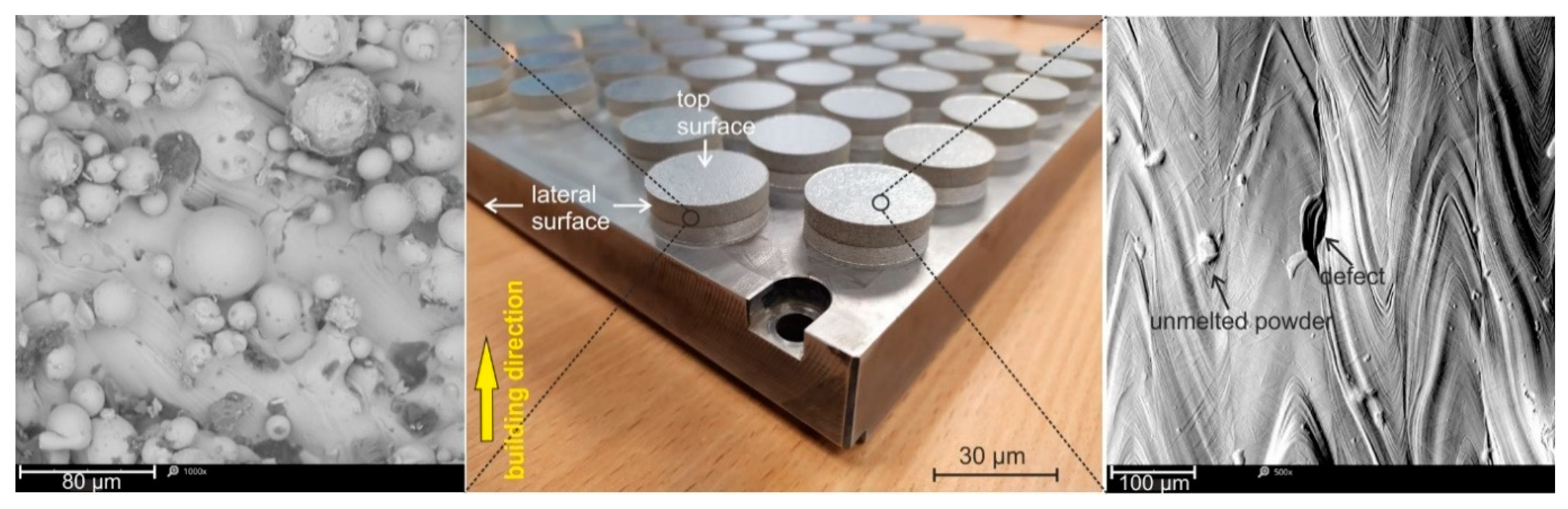
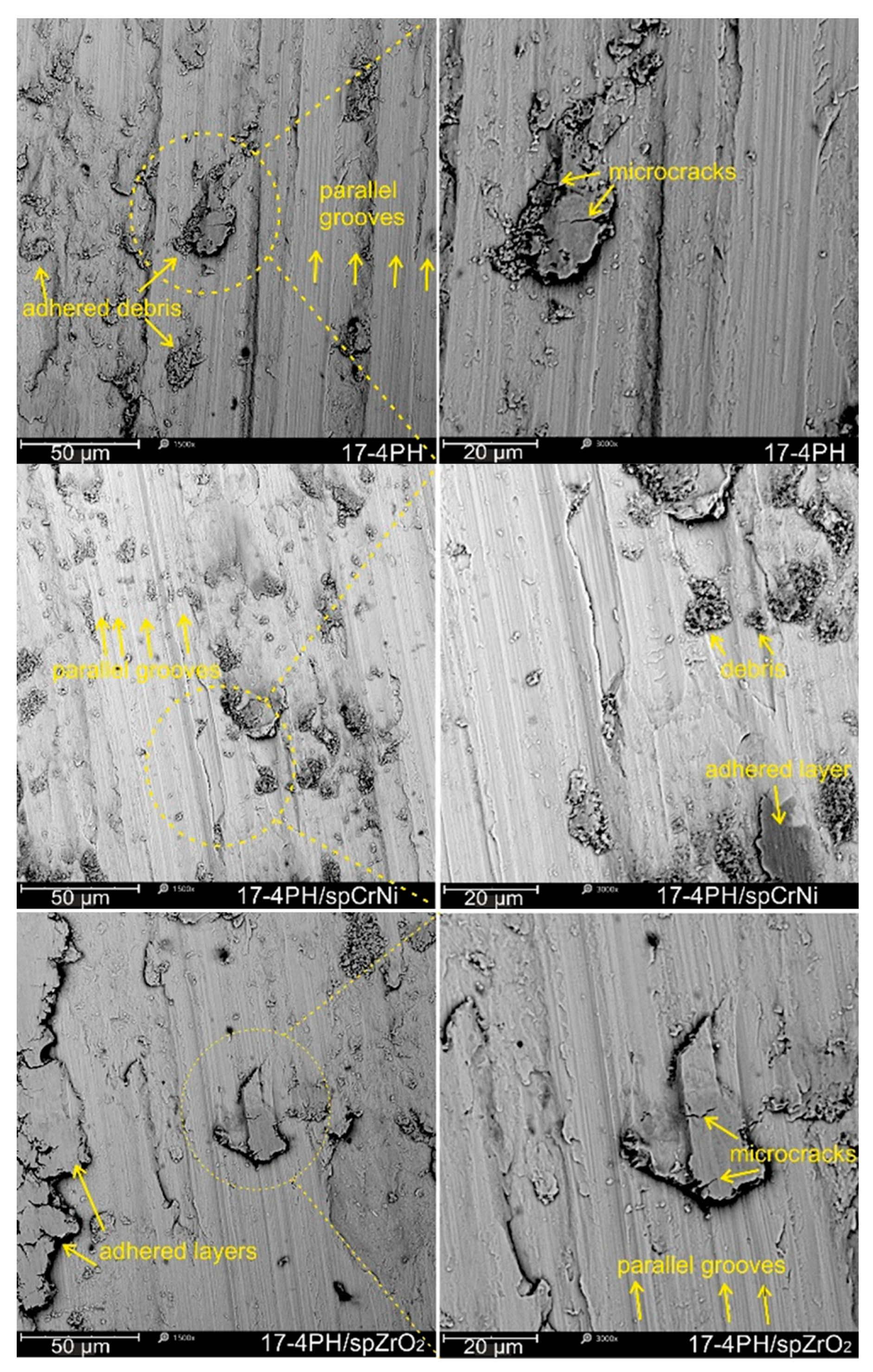
3.2. Surface morphology
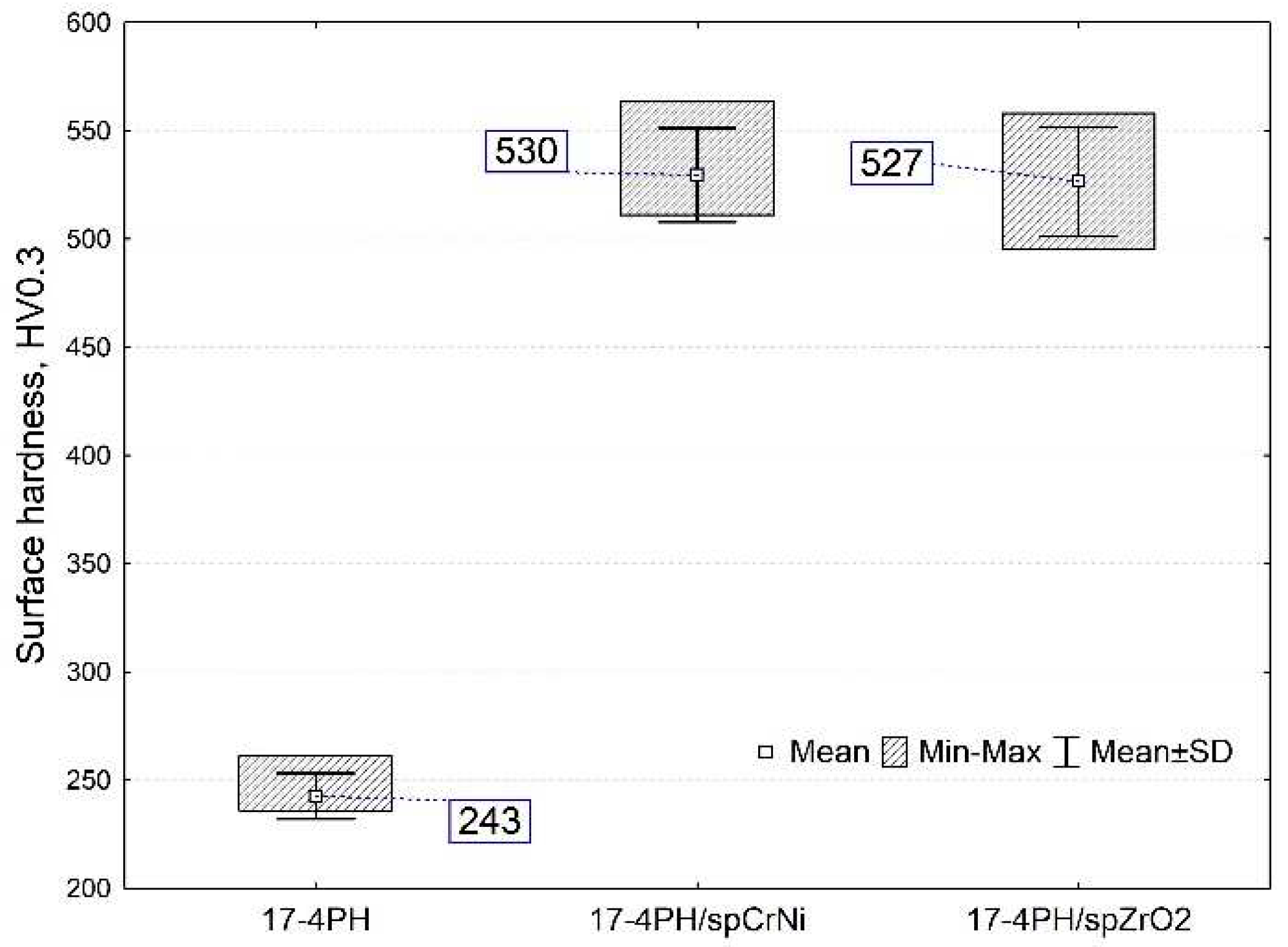
3.3. Hardness
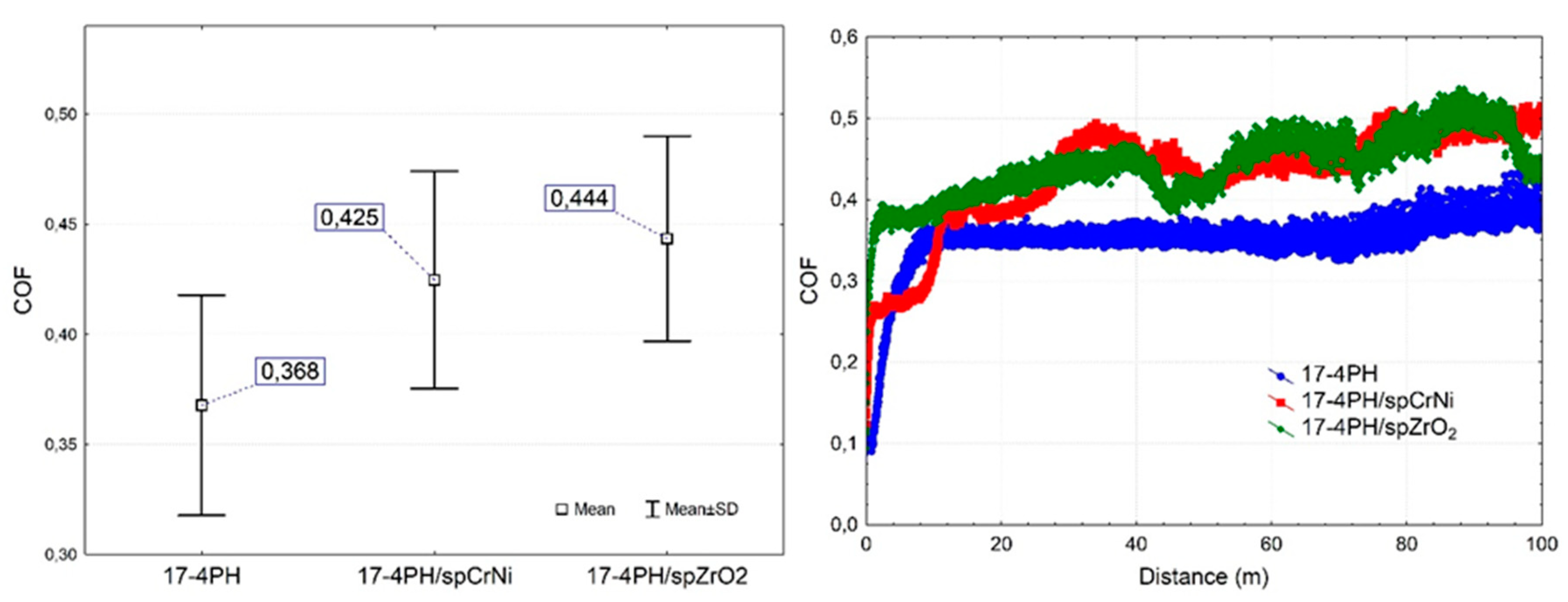
3.4. Tribological behaviour
4. Conclusions
- Austenite originating peaks including (200, 220, 311) are reduced in the samples after SP, the increase of peak intensity was noted for 110 indications. Strain inducted austenite phase transformation.
- The SP process of 17-4PH steel leads to the austenite-martensite phase transition, accompanied by the texture of martensite grains in the direction <110> perpendicular to the surface of the sample.
- CrNi steel shot peened surfaces showed an overall increase of 12.79 % Ra mean value when compared to reference. In addition, SP with ZrO2 allowed a reduction in Ra parameter by 7.82 %.
- The peening process almost doubled the surface hardness of 243 to ~530 HV0.3 for CrNi steel and ZrO2 peened samples, respectively. The increase of 118.1% and 116.9% in hardness for CrNi steel and ZrO2 peened surfaces, respectively, was noted.
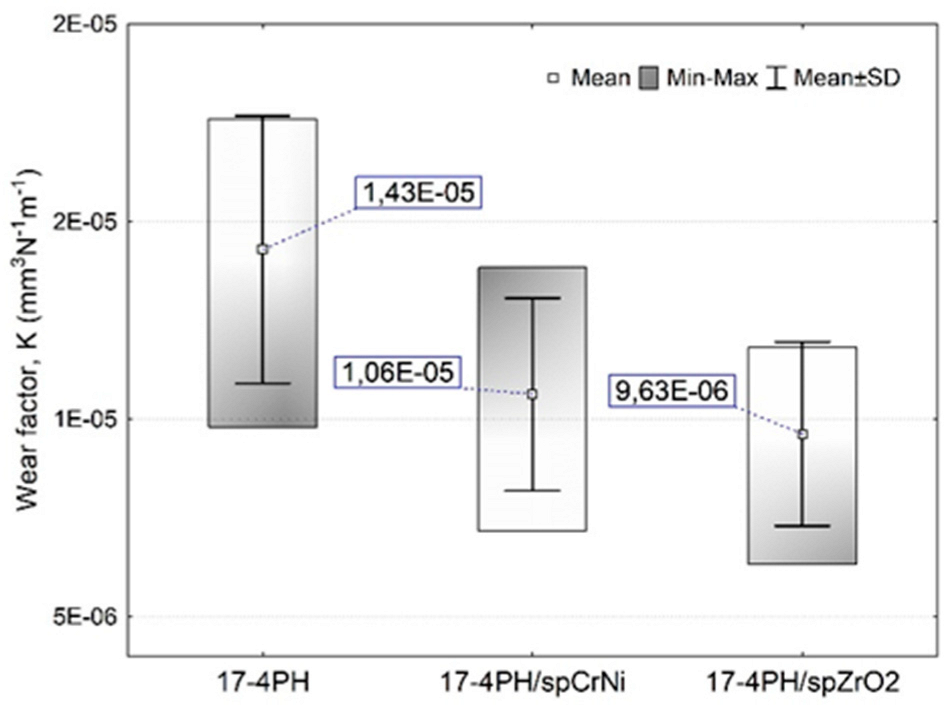
- The peening process with both steel balls and ceramic shots had a favorable effect on the wear resistance of DMLS steel in 0.9%NaCl solution.
- Similar hardness parameters, roughness and condition of the surface layer were a determinant factor affecting the tribological wear resistance in peened samples.
- ZrO2 shot peened surface proves to have a slightly better wear resistance compared to the CrNi steel shots. Then, the overall reduction of wear factor (K) relative to the reference surface was significant and reached 25.9 %, 32.7 % for 17-4PH/spCrNi and 17-4PH/spZrO2 samples, respectively.
- SEM observations of the wear marks revealed two dominant, parallel mechanisms of abrasive wear determined by paraller grooves and adhesive wear related to the transfer of secondary wear products.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yeli, G.; Auger, M.A.; Wilford, K.; Smith, G.D.W.; Bagot, P.A.J.; Moody, M.P. Sequential Nucleation of Phases in a 17-4PH Steel: Microstructural Characterisation and Mechanical Properties. Acta Materialia 2017, 125, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Hebert, R.J.; Aindow, M. Effect of Heat Treatments on Microstructural Evolution of Additively Manufactured and Wrought 17-4PH Stainless Steel. Materials & Design 2018, 156, 429–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreacola, F.R.; Capasso, I.; Pilotti, L.; Brando, G. Influence of 3d-Printing Parameters on the Mechanical Properties of 17-4PH Stainless Steel Produced through Selective Laser Melting. Frattura ed Integrità Strutturale 2021, 15, 282–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, T.-H.; Chang, Y.-J.; Huang, C.-Y.; Yen, H.-W.; Chen, C.-P.; Jen, K.-K.; Yeh, A.-C. Microstructure and Property of a Selective Laser Melting Process Induced Oxide Dispersion Strengthened 17-4 PH Stainless Steel. Journal of Alloys and Compounds 2019, 803, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjan Pradhan, S.; Singh, R.; Singh Banwait, S. Comparison of DMLS and DMLS-Waste Assisted Investment Casting. Materials Letters 2022, 324, 132782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laleh, M.; Sadeghi, E.; Revilla, R.I.; Chao, Q.; Haghdadi, N.; Hughes, A.E.; Xu, W.; De Graeve, I.; Qian, M.; Gibson, I.; et al. Heat Treatment for Metal Additive Manufacturing. Progress in Materials Science 2023, 133, 101051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleksander Świetlicki; Mariusz Walczak; Mirosław Szala; Marcin Turek; Dariusz Chocyk Effects of ageing heat treatment temperature on the properties of DMLS additive manufactured 17-4PH steel. Bulletin of the Polish Academy of Sciences Technical Sciences 2023. [CrossRef]
- Żebrowski, R.; Walczak, M. Effect of the shot peening on surface properties and tribological performance of Ti-6Al-4V alloy produced by means of DMLS technology. Archives of Metallurgy and Materials 2019, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferri, O.M.; Ebel, T.; Bormann, R. High Cycle Fatigue Behaviour of Ti–6Al–4V Fabricated by Metal Injection Moulding Technology. Materials Science and Engineering: A 2009, 504, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lashgari, H.R.; Adabifiroozjaei, E.; Kong, C.; Molina-Luna, L.; Li, S. Heat Treatment Response of Additively Manufactured 17-4PH Stainless Steel. Materials Characterization 2023, 197, 112661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, E.; Chen, G.; Tan, Z.; Wu, S. Shot Peening and Thermal Stress Relaxation in 17-4 PH Stainless Steel. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 2015, 24, 4578–4583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, M.; Kalvala, P.R.; Misra, M.; Menezes, P.L. Peening Techniques for Surface Modification: Processes, Properties, and Applications. Materials 2021, 14, 3841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soyama, H.; Korsunsky, A.M. A Critical Comparative Review of Cavitation Peening and Other Surface Peening Methods. Journal of Materials Processing Technology 2022, 305, 117586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Świetlicki, A.; Szala, M.; Walczak, M. Effects of Shot Peening and Cavitation Peening on Properties of Surface Layer of Metallic Materials—A Short Review. Materials 2022, 15, 2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matuszak, J. Analysis of Geometric Surface Structure and Surface Layer Microhardness of Ti6Al4V Titanium Alloy after Vibratory Shot Peening. Materials 2023, 16, 6983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bazri, S.; Mapelli, C.; Barella, S.; Gruttadauria, A.; Mombelli, D.; Liu, C. Mechanical and Tribo-Metallurgical Behavior of 17-4 Precipitation Hardening Stainless Steel Affected by Severe Cold Plastic Deformation: A Comprehensive Review Article. J Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 2022, 44, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, E.; Pant, P.; Jafari, R.; Peng, R.L.; Karimi, P. Subsurface Grain Refinement in Electron Beam-Powder Bed Fusion of Alloy 718: Surface Texture and Oxidation Performance. Materials Characterization 2020, 168, 110567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Jiang, C.; Gan, X.; Chen, Y.; Ji, V. Influence of Shot Peening on the Fatigue Life of Laser Hardened 17-4PH Steel. International Journal of Fatigue 2011, 33, 549–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghan-Manshadi, A.; Yu, P.; Dargusch, M.; StJohn, D.; Qian, M. Metal Injection Moulding of Surgical Tools, Biomaterials and Medical Devices: A Review. Powder Technology 2020, 364, 189–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Świetlicki, A.; Walczak, M.; Szala, M. Effect of Shot Peening on Corrosion Resistance of Additive Manufactured 17-4PH Steel. Materials Science-Poland 2022, 40, 135–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walczak, M.; Szala, M. Effect of Shot Peening on the Surface Properties, Corrosion and Wear Performance of 17-4PH Steel Produced by DMLS Additive Manufacturing. Archiv.Civ.Mech.Eng 2021, 21, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.L.; Yan, M.F. Improvement of Wear and Corrosion Resistances of 17-4PH Stainless Steel by Plasma Nitrocarburizing. Materials & Design (1980-2015) 2010, 31, 2355–2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esfandiari, M.; Dong, H. The Corrosion and Corrosion–Wear Behaviour of Plasma Nitrided 17-4PH Precipitation Hardening Stainless Steel. Surface and Coatings Technology 2007, 202, 466–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bressan, J.D.; Daros, D.P.; Sokolowski, A.; Mesquita, R.A.; Barbosa, C.A. Influence of Hardness on the Wear Resistance of 17-4 PH Stainless Steel Evaluated by the Pin-on-Disc Testing. Journal of Materials Processing Technology 2008, 205, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kc, S.; Nezhadfar, P.D.; Phillips, C.; Kennedy, M.S.; Shamsaei, N.; Jackson, R.L. Tribological Behavior of 17–4 PH Stainless Steel Fabricated by Traditional Manufacturing and Laser-Based Additive Manufacturing Methods. Wear 2019, 440–441, 203100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davanageri, M.; Devananda, R.; Rangaswamy, Hanumantharaya.R. Tribological Wear Behavior of AISI 630 (17-4 PH) Stainless Steel Hardened by Precipitation Hardening. American Journal of Materials Science 2016, 2016, 6–14. [CrossRef]
- Alamos, F.J.; Schiltz, J.; Attardo, R.; Aboud Gatrell, B.; Tomonto, C.; Budzinski, J.; McGuffin-Cawley, J.; Pelletiers, T.; Schmid, S.R. Effect of Powder Reuse on Orthopedic Metals Produced through Selective Laser Sintering. Manufacturing Letters 2021, S2213846321000407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clare, A.T.; Mishra, R.S.; Merklein, M.; Tan, H.; Todd, I.; Chechik, L.; Li, J.; Bambach, M. Alloy Design and Adaptation for Additive Manufacture. Journal of Materials Processing Technology 2022, 299, 117358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michla, J.R.J.; Ravikumar, B.; Prabhu, T.R.; Siengchin, S.; Kumar, M.A.; Rajini, N. Effect of Nitriding on Mechanical and Microstructural Properties of Direct Metal Laser Sintered 17-4PH Stainless Steel. Journal of Materials Research and Technology 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Luan, W.; Huang, J.; Jiang, C. XRD Investigation of Microstructure Strengthening Mechanism of Shot Peening on Laser Hardened 17-4PH. Materials Science and Engineering: A 2011, 528, 6417–6425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskandari, H.; Lashgari, H.R.; Ye, L.; Eizadjou, M.; Wang, H. Microstructural Characterization and Mechanical Properties of Additively Manufactured 17–4PH Stainless Steel. Materials Today Communications 2022, 30, 103075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kameyama, Y.; Komotori, J. Effect of Micro Ploughing during Fine Particle Peening Process on the Microstructure of Metallic Materials. Journal of Materials Processing Technology 2009, 209, 6146–6155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mower, T.M.; Long, M.J. Mechanical Behavior of Additive Manufactured, Powder-Bed Laser-Fused Materials. Materials Science and Engineering: A 2016, 651, 198–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dörr T; Hilpert M; Beckmerhagen P; Kiefer A; Wagner L Infuence of Shot Peening on Fatigue Performance of High-Strength Aluminum-and Magnesium Alloys.; Warsaw, 1999.
- Ahmed, A.A.; Mhaede, M.; Wollmann, M.; Wagner, L. Effect of Micro Shot Peening on the Mechanical Properties and Corrosion Behavior of Two Microstructure Ti–6Al–4V Alloy. Applied Surface Science 2016, 363, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, W.J.; Son, Y.; Cho, S.Y.; Yang, S.W.; Shin, G.Y.; Shim, D.S. Solution Annealing and Precipitation Hardening Effect on the Mechanical Properties of 630 Stainless Steel Fabricated via Laser Melting Deposition. Materials Science and Engineering: A 2020, 794, 139999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Daoud, H.; Scherm, F.; Klötzer, B.; Hauck, C.; Glatzel, U. Stainless Steel Powder Produced by a Novel Arc Spray Process. Journal of Materials Research and Technology 2020, 9, 8314–8322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheruvathur, S.; Lass, E.A.; Campbell, C.E. Additive Manufacturing of 17-4 PH Stainless Steel: Post-Processing Heat Treatment to Achieve Uniform Reproducible Microstructure. JOM 2016, 68, 930–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Jiang, C.; Gan, X.; Chen, Y. Effect of Shot Peening on the Microstructure of Laser Hardened 17-4PH. Applied Surface Science 2010, 257, 1154–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlMangour, B.; Yang, J.-M. Improving the Surface Quality and Mechanical Properties by Shot-Peening of 17-4 Stainless Steel Fabricated by Additive Manufacturing. Materials & Design 2016, 110, 914–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.B.; Tao, N.R.; Li, S.; Wang, W.; Liu, G.; Lu, J.; Lu, K. Effect of Surface Nanocrystallization on Friction and Wear Properties in Low Carbon Steel. Materials Science and Engineering: A 2003, 352, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Khonsari, M.M.; Yang, H. Wear Anisotropy of Selective Laser Melted 316L Stainless Steel. Wear 2019, 428–429, 376–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
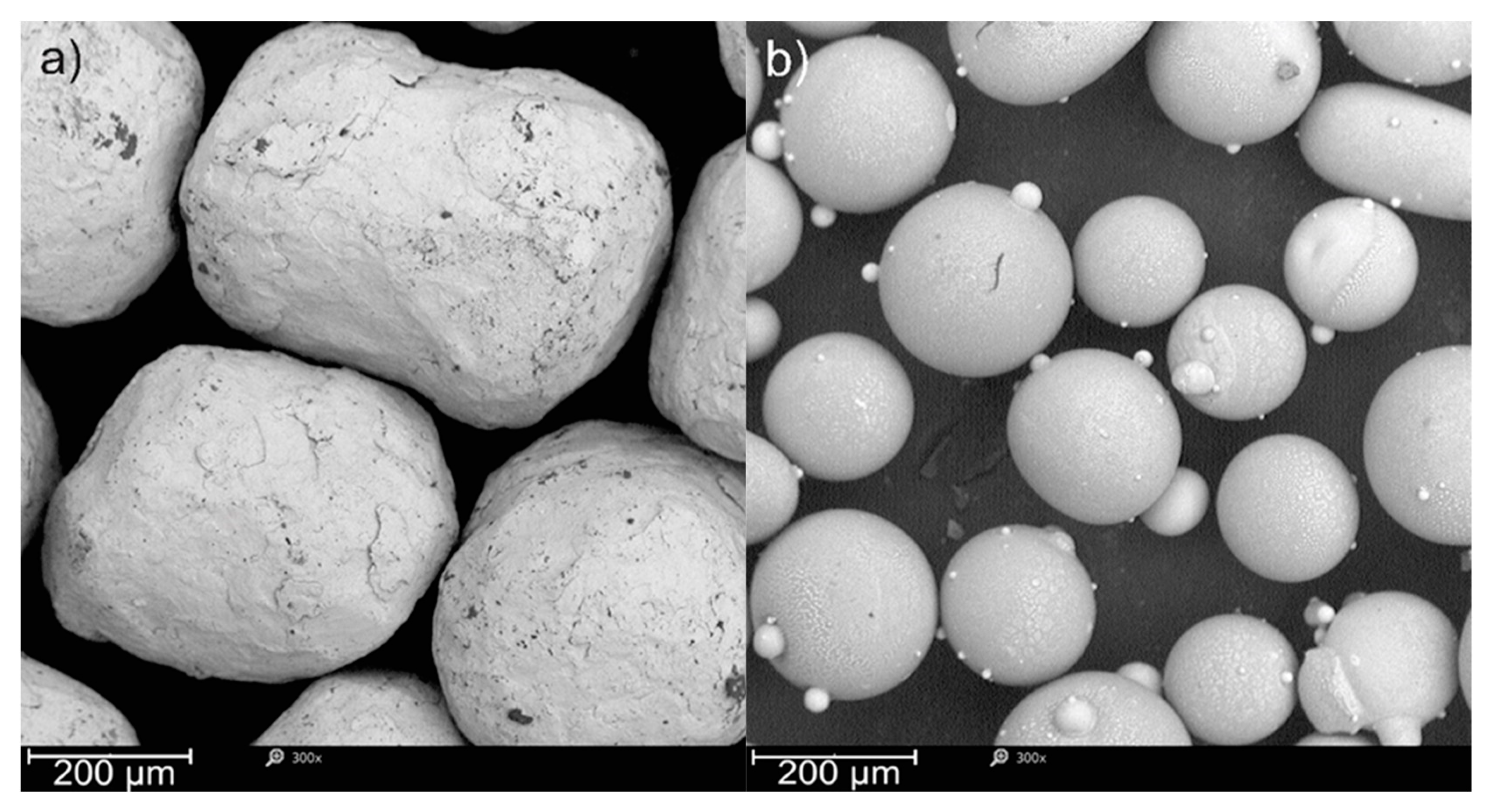



| Ceramic beads | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZrO2 | SiO2 | Al2O3 | CaO | TiO2 | Fe2O3 |
| 61.98 | 27.77 | 4.57 | 3.47 | 0.34 | 0.14 |
| CrNi steel shots | |||||
| Cr | Ni | Si | Mn | C | Fe |
| 16-20 | 7-9 | 1.8-2.2 | 0.7-1.2 | 0.05-0.2 | Bal. |
| C | Si | Mn | S | Cr | Mo | Ni | Cu | Co | Nb | V | N | Fe | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| As-build | 0.043 | 0.694 | 0.665 | 0.051 | 15.18 | 0.121 | 4.503 | 4.734 | 0.096 | 0.028 | 0.054 | 0.088 | Bal. |
| ASTM A564 | <0.07 | <0.7 | <1.5 | - | 5–17 | <0.6 | 3–5 | 3-5 | - | 5*C–0.45 | - | - | Bal. |
| EN 10088-1 | <0.07 | 1 | <1 | - | 15-17.5 | <0.5 | 3–5 | 3-5 | - | 0.15–0.45 | - | - | Bal. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





